Abstract
Purpose
Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis is an increasingly recognized cause of stroke in children and neonates. Its true incidence appears to be underestimated. Despite being a rare event, certain studies have found a correlation between subdural hemorrhage and cerebral sinus thrombosis. The literature suggests that spontaneous cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in the pediatric population may lead to the occurrence of a subdural hemorrhage. In this report, we present a case of cerebral venous thrombosis associated with chronic subdural hematoma and review the literature to highlight the importance of these conditions.
Case report
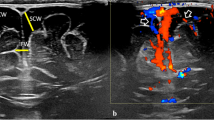
An 11-year-old boy was admitted in the neurosurgery department with headache and a neurological examination without changes. The imaging studies identified a heterogeneous subdural collection in the fronto-temporo-parietal region. The patient underwent surgical drainage of the subdural hematoma, and the procedure was performed without complications. The magnetic resonance and angiography showed an extensive thrombosis of the superior sagittal sinus, extending downward to the occipital sinus and partially to the right transverse sinus.
Conclusions
Appropriate management in the diagnosis and an early treatment of dural sinus thrombosis associated with subdural hemorrhage can reduce the risk of recurrence and improve the clinical outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The research data will be sent upon request.
References
Ferro JM et al (2016) Cerebral venous thrombosis. Presse Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lpm.2016.10.007
Lolli V, Molinari F, Pruvo JP, Soto AG (2016) Radiological and clinical features of cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in newborns and older children. J Neuroradiol 43(4):280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2015.12.001
Shlobin NA, LoPresti MA, Beestrum M, Lam S (2020) Treatment of pediatric cerebral venous sinus thromboses: the role of anticoagulation. Childs Nerv Syst 36(11):2621–2633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04829-7
McLean LA, Frasier LD, Hedlund GL (2012) Does intracranial venous thrombosis cause subdural hemorrhage in the pediatric population? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(7):1281–1284. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2967
Silvis SM, Middeldorp S, Zuurbier SM, Cannegieter SC, Coutinho JM (2016) Risk Factors for Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost 42(6):622–631. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1584132
Sellers A, Meoded A, Quintana J, Jallo G, Amankwah E, Nguyen ATH, Betensky M, Mills K, Goldenberg N, Shimony N (2020) Risk factors for pediatric cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: A case-control study with case validation. Thromb Res 194:8–15
Anderst J, Carpenter S, Frazier T et al (2021) Subdural hemorrhage in a cohort with cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: Application to abusive head trauma. Child Abuse Negl 117:105119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.105119
Burtard C, Panks J, Silverman LB et al (2023) Prevalence of cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol 53(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-022-05462-z
Funding
This research did not receive financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Suzana Maria Bezerra Serra Conducted the research, collected patient information, analyzed the data, reviewed the literature, drafted the article, edited the article, have approved the submitted version. Raiza Rafaela Borges de Oliveira Collected patient information, analyzed the data, reviewed the literature, drafted the article, edited the article, have approved the submitted version. Ismael Felipe Gonçalves Galvão Collected patient information, analyzed the data, reviewed the literature, drafted the article, edited the article, , performed the article submission, have approved the submitted version. Júlia Santos Maia Collected patient information, analyzed the data, reviewed the literature, drafted the article, edited the article, have approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Serra, S.M.B., de Oliveira, R.R.B., Galvão, I.F.G. et al. Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis as a cause of subdural hemorrhage in the pediatric population: Is there a correlation?. Childs Nerv Syst 40, 603–605 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-06199-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-06199-2