Abstract
Introduction
Zonisamide (ZNS) is a new generation antiepileptic drug (AED) used in refractory epilepsy. This study assessed the effectiveness and reliability of ZNS in childhood refractory epilepsy.
Method
Sixty-eight epilepsy patients who were followed up in the paediatric neurology clinic, between 2013 and 2019, and in whom add-on therapy ZNS had been added as their seizures had continued despite multiple drugs being used, were included in this retrospective study. Their demographic findings, seizure aetiology, pre-treatment and post-treatment electroencephalography findings, treatment responses and any side effects of the drugs given were assessed in these patients.
Results
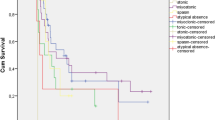
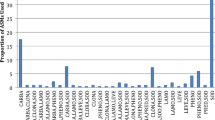
There were 46 (67.6%) patients in the refractory generalized epilepsy (RGE) group using multiple AEDs and 22 (32.35%) patients in the refractory focal epilepsy (RFE) group. Of these patients, 12 (17.65%) were being followed up for idiopathic epilepsy and 8 (11.76%) were being followed up for epilepsy of unknown aetiology. Twenty-two (32.36%) patients were followed up for structural abnormality, 8 patients (11.77%) were followed up for genetic disease, 4 patients (5.88%) were followed up for infectious sequel, 14 patients (20.59%) were followed up for metabolic reasons. In the RGE group, a more than 50% reduction was found in the seizures of 26 (56.5%) patients, while the seizures of 7 (15.2%) patients were found to have terminated completely. In the RFE group, a more than 50% reduction was found in the seizures of 19 (86.4%) patients, while the seizures of 2 (9.1%) patients were found to have terminated completely. The termination or a more than 50% reduction in seizures in 4 of the 6 patients followed up for a diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) was significant.
Conclusion
ZNS is an effective and reliable option as an add-on therapy in paediatric refractory epilepsy, especially in focal epilepsy. It can also be considered for treatment in TSC patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston MV (2010) Seizure in childhood. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE (eds) Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics, 18th edn. Philadelphia: Saunders, p 2457–70
Icardi J (2004) Epilepsy in children. 3th edn. Lippincott Williams &Wilkins edition, p 38
Olson B (2005) Treatment of refractory epilepsy Adv stumed 5:470–473
Berto P (2002) Quality of life in patients with epilepsy and impact of treatments. Pharmacoeconomics 20:1039–1059
Ohtahara S (2006) Zonisamide in the management of epilepsy-Japanese experience. Epilepsy Res 68(suppl 2):S25–S33
Guerrini R, Rosati A, Segieth J et al (2013) A randomized phase III trial of adjunctive zonisamide in pediatric patients with partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 54:1473–1480
Rock DM, Macdonald RL, Taylor CP (1989) Blockade of sustained repetitive action potentials in cultured spinal cord neurons by zonisamide, a novel anticonvulsant. Epilepsy Res 3:138–143
Ueda Y, Doi T, Tokumaru J, Willmore LJ (2003) Effect of zonisamide on molecular regulation of glutamate and GABA transporter proteins during epileptogenesis in rats with hippocampal seizures. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 116:1–6
Hoy SM (2013) Zonisamide: a review of its use in the management of adults with partial seizures. Drugs 73:1321–1338
Noda Y, Mori A, Packer L (1999) Zonisamide inhibits nitric oxide synthase activity induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate and buthionine sulfoximine in the rat hippocampus. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 105:23–33
Kwan S-Y, Chuang Y-C, Huang C-W, Chen T-C, Jou S-B, Dash A (2015) Zonisamide: review of recent clinical evidence for treatment of epilepsy. CNS Neurosci Ther 21:683–691
Ohtahara S, Yamatogi Y (2004) Safety of zonisamide therapy: prospective follow-up survey. Seizure 13(suppl 1):S50–S55
Shimizu A, Yamamoto J, Yamada Y et al (1988) The antiepileptic effect of zonisamide on patients with refractory seizures and its side effect. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol 42:583
You SJ, Kang HC, Kim HD et al (2008) Clinical efficacy of zonisamide in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: Korean multicentric experience. Brain Dev 30:287–290
Ohno M, Shimotsuji Y, Abe J et al (2000) Zonisamide treatment of early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol 23:341–344
Kishi T, Nejihashi Y, Kajiyama M, Ueda K (2000) Successful zonisamide treatment for infants with hypsarrhythmia. Pediatr Neurol 23:274–277
Arya R, Glauser TA (2013) Pharmacotherapy of focal epilepsy in children: a systematic review of approved agents. CNS Drugs 27:273–286
Thampratankul L, Khongkhatithum C, Visudtibhan A (2015) Efficacy and safety of zonisamide in Thai children and adolescents with intractable seizures. J Child Neurol 30(4):527–531
Karimzadeh P, Ashrafi MR, Bakhshandeh Bali MK, Nasehi MM, Taheri Otaghsara SM, Taghdiri MM, Ghofrani M (2013) Zonisamide efficacy as adjunctive therapy in children with refractory epilepsy. Iran J Child Neurol Spring 7(2):37–42
Glauser TA, Pellock JM (2002) Zonisamide in pediatric epilepsy: review of the Japanese experience. J Child Neurol 17:87–96
Coppola G, Grosso S, Verrotti A et al (2009) Zonisamide in children and young adults with refractory epilepsy: an open label, multicenter Italian study. Epilepsy Res 83(2–3):112–116
Lee YJ, Kang HC, Seo JH, Lee JS, Kim HD (2010) Efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive therapy with zonisamide in childhood intractable epilepsy. Brain Dev 32:208–212
Santos CC, Brotherton T (2005) Use of zonisamide in pediatric patients. Pediatr Neurol 33:12–14
Kim HL, Aldridge J, Rho JM (2005) Clinical experience with zonisamide monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in children with epilepsy at a tertiary care referral center. J Child Neurol 20:212–219
Tan HJ, Martland TR, Appleton RE, Kneen R (2010) Effectiveness and tolerability of zonisamide in children with epilepsy: a retrospective review. Seizure 19:31–35
Shinnar S, Pellock JM, Conry JA (2009) Open-label, long-term safety study of zonisamide administered to children and adolescents with epilepsy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 13:3–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Approval numbered 2019/10–6 was given by the ethical board for our study from the İnönü University Scientific Research and Publication Ethics Board.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained for the patient information.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslan, M., Gungor, S. Effectiveness of zonisamide in childhood refractory epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 38, 971–976 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05458-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05458-y