Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to report the incidence of technical complications and immediate complete angiographic occlusion, identify associated factors with failure of complete occlusion and identify predictors of technical complications in a single-center experience of pediatric arteriovenous malformations (AVM) treated with endovascular treatment with intent to cure.
Methods
Patients between 1 and 18 years of age undergoing endovascular embolization between 2011 and 2020 were included.
Results
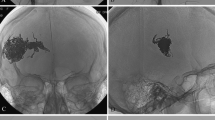
A total of 120 embolizations were performed in 69 patients. The most frequent clinical presentation was intracerebral hemorrhage (76.8%). Immediate obliteration of the malformations was achieved in 40 (58%) cases. The technical complication rate was 15%. AVM nidus size between 3 and 6 cm (OR: 3.91; 95% CI 1.1–13.85; p = 0.035) and the presence of multiple feeders (OR: 5.08; 95% CI 1.41–18.28; p = 0.074) were predictive of failure of immediate complete occlusion. The location of the temporal lobe (OR: 7.83; p = 0.048), deep venous drainage (OR: 4.67; p = 0.112), and the presence of an intranidal aneurysm (OR: 3.58; p = 0.134) were predictors of technical complications.
Conclusions
Embolization of pediatric AVMs with intent to cure shows a high rate of technical complications and acceptable immediate occlusion rates. Nidus size and the presence of multiple feeders were predictive of failure of complete occlusion, while temporal lobe location, deep venous drainage, and the presence of an intranidal aneurysm were predictors of technical complications. Further studies are needed to determine the best therapeutic approach in the pediatric population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Yang W, Anderson-Keightly H, Westbroek EM, Caplan JM, Rong X, Hung AL et al (2016) Long-term hemorrhagic risk in pediatric patients with arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18(3):329–338. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.3.PEDS15715
Di Rocco C, Tamburrini G, Rollo M (2000) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142(2):145–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050017
Hernesniemi JA, Dashti R, Juvela S, Väärt K, Niemelä M, Laakso A (2008) Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery Nov 63(5):823–829. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000330401.82582.5E
Itoyama Y, Uemura S, Ushio Y, Kuratsu JI, Nonaka N, Wada H et al (1989) Natural course of unoperated intracranial arteriovenous malformations: study of 50 cases. J Neurosurg 71(6):805–809. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1989.71.6.0805
Ondra SL, Troupp H, George ED, Schwab K (1990) The natural history of symptomatic arteriovenous malformations of the brain: a 24-year follow-up assessment. J Neurosurg 73(3):387–391. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1990.73.3.0387
Humphreys RP, Hoffman HJ, Drake JM, Rulka JT (1996) Choices in the 1990s for the management of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations?. Pediatr Neurosurg 25(5):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121140
Alexander MD, Hippe DS, Cooke DL, Hallam DK, Hetts SW, Kim H et al (2018) Targeted embolization of aneurysms associated with brain arteriovenous malformations at high risk for surgical resection: a case-control study. Neurosurgery 82(3):343–349
Blount JP, Oakes WJ, Tubbs RS, Humphreys RP (2006) History of surgery for cerebrovascular disease in children. Part III. Arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 20(6):E11
Copelan A, Drocton G, Caton MT, Smith ER, Cooke DL, Nelson J et al (2020) Brain arteriovenous malformation recurrence after apparent microsurgical cure: increased risk in children who present with arteriovenous malformation rupture. Stroke 51(10):2990–2996. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.030135
El-Ghanem M, Kass-Hout T, Kass-Hout O, Alderazi YJ, Amuluru K, Al-Mufti F et al (2016) Arteriovenous malformations in the pediatric population: review of the existing literature. Interv Neurol 5(3–4):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447605
Crowley RW, Ducruet AF, McDougall CG, Albuquerque FC (2014) Endovascular advances for brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 74 SUPPL 1:S74–82. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.000000000000017
Valavanis A, Pangalu A, Tanaka M (2005) Endovascular treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with emphasis on the curative role of embolisation. Interv Neuroradiol 11 (Suppl 1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/15910199050110S107
Van Rooij WJ, Jacobs S, Sluzewski M, Van Der Pol B, Beute GN, Sprengers ME (2012) Curative embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with onyx: patient selection, embolization technique, and results. Am J Neuroradiol 33(7):1299–1304. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2947
Mathews MS, Owen CM, Nguyen B V, Kostanian V, Nwagwu CI (2007) Angiographic exclusion of intracranial arteriovenous malformations using Onyx®. Neuroradiol J 20(6):711–717. https://doi.org/10.1177/197140090702000616
van Essen MJ, Han K Sen, Lo RTH, Woerdeman P, van der Zwan A, van Doormaal TPC (2018) Functional and educational outcomes after treatment for intracranial arteriovenous malformations in children. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 160(11):2199–2205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3665-y
Potts MB, Jahangiri A, Jen M, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Gupta N et al (2014) Deep arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia, thalamus, and insula: multimodality management, patient selection, and results. World Neurosurg 82(0):386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2014.03.033
Mosimann PJ, Chapot R (2018) Contemporary endovascular techniques for the curative treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations and review of neurointerventional outcomes. J Neurosurg Sci 62(4):505–513. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0390-5616.18.04421-1
Link TW, Winston G, Schwarz JT, Lin N, Patsalides A, Gobin P et al (2018) Treatment of unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations: a single-center experience of 86 patients and a critique of the a randomized trial of unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA) Trial. World Neurosurg 120:e1156-1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.09.025
Lv X, Li Y, Jiang C, Yang X, Wu Z (2010) Brain arteriovenous malformations and endovascular treatment: effect on seizures. Interv Neuroradiol 16(1):39–45
Baranoski JF, Grant RA, Hirsch LJ, Visintainer P, Gerrard JL, Günel M et al (2014) Seizure control for intracranial arteriovenous malformations is directly related to treatment modality: a meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg 6(9):684–690 https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010945
Wu EM, El Ahmadieh TY, McDougall CM, Aoun SG, Mehta N, Neeley OJ et al (2018) Embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with intent to cure: a systematic review. J Neurosurg 132(2): 388–99. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.10.JNS181791
Darsaut TE, Guzman R, Marcellus ML, Edwards MS, Tian L, Do HM et al (2011) Management of pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations: experience with multimodality therapy. Neurosurgery 69(3):540–556. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182181c00
Ashour R, Aziz-Sultan MA, Soltanolkotabi M, Schoeneman SE, Alden TD, Hurley MC et al (2012) Safety and efficacy of onyx embolization for pediatric cranial and spinal vascular lesions and tumors. Neurosurgery 71(4):773–784. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182648db6
Soltanolkotabi M, Schoeneman SE, Alden TD, Hurley MC, Ansari SA, DiPatri AJ et al (2013) Onyx embolization of intracranial arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients: clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr 11(4):431–437. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.1.PEDS12286
Zheng T, Wang QJ, Liu YQ, Cui XB, Gao YY, Lai LF et al (2014) Clinical features and endovascular treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Child’s Nerv Syst 30(4):647–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2277-3
de Castro-Afonso LH, Nakiri GS, Oliveira RS, Santos MV, Santos ACD, Machado HR et al (2016) Curative embolization of pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations using Onyx: the role of new embolization techniques on patient outcomes. Neuroradiology 58(6):585–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1666-1
Berenstein A, Ortiz R, Niimi Y, Elijovich L, Fifi J, Madrid M et al (2010) Endovascular management of arteriovenous malformations and other intracranial arteriovenous shunts in neonates, infants, and children. Childs Nerv Syst 26(10):1345–5138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1206-y
Rodriguez-Calienes A, Bustamante-Paytan D, Camacho K, Mayoria-Vargas A, Saal-Zapata G, Rodriguez-Varela R (2021) Early outcomes and complications of endovascular treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Pediatr Neurosurg 56 (2):116–124. https://doi.org/10.1159/000513577
Potts MB, Zumofen DW, Raz E, Nelson PK, Riina HA (2014) Curing arteriovenous malformations using embolization. Neurosurg Focus 37(3):E19. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.6.FOCUS14228
Bristol RE, Albuquerque FC, Spetzler RF, Rekate HL, McDougall CG, Zabramski JM (2006) Surgical management of arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 105(2):88–93. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2006.105.2.88
Rangel-Castilla L, Russin JJ, Martinez-del-Campo E, Soriano-Baron H, Spetzler RF, Nakaji P (2014) Molecular and cellular biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a review of current concepts and future trends in treatment. Neurosurg Focus 37(3): E1. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14214
Moftakhar P, Hauptman JS, Malkasian D, Martin NA (2009) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Part 2: physiology. Neurosurg Focus 26(5): E11
Frösen J, Joutel A (2018) Smooth muscle cells of intracranial vessels: from development to disease. Cardiovasc Res 114(4):501–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvy002
Kim L, Albuquerque F, Spetzler R, McDougall C (2006) Postembolization neurological deficits in cerebral arteriovenous malformationsstratification by arteriovenous malformation grade. Neurosurgery 59(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000219219.97287.91
Hartmann A, Pile-Spellman J, Stapf C, Sciacca RR, Faulstich A, Mohr JP et al (2002) Risk of endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 33(7):1816–1820. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000020123.80940.b2
Bell DL, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Yoo AJ, Rabinov JD, Butler WE, Bell JE et al (2015) Application of a novel brain arteriovenous malformation endovascular grading scale for transarterial embolization. Am J Neuroradiol 36(7):1303–1309. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4286
Gupta R, Adeeb N, Moore JM, Motiei-Langroudi R, Griessenauer CJ, Patel AS et al (2016) Validity assessment of grading scales predicting complications from embolization of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 151:102–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.10.019
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1996) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65(4):476–483. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1986.65.4.0476
Ledezma CJ, Hoh BL, Carter BS, Pryor JC, Putman CM, Ogilvy CS (2006) Complications of cerebral arteriovenous malformation embolization: multivariate analysis of predictive factors. Neurosurgery 58(4):602–610. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000204103.91793.77
Signorelli F, Gory B, Pelissou-Guyotat I, Guyotat J, Riva R, Dailler F et al (2014) Ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations associated with aneurysms: safety and efficacy of selective embolization in the acute phase of hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 56(9):763–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1395-2
Rammos SK, Gardenghi B, Bortolotti C, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G (2016) Aneurysms associated with brain arteriovenous malformations. Am J Neuroradiol 37(11):1966–1971. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The present study was approved by the institutional review board of our institution under code 102345.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Calienes, A., Bustamante-Paytan, D., Camacho-Caballero, K. et al. Single-center experience with endovascular treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with intent to cure in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 38, 343–351 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05376-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05376-5