Abstract
Purpose
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common malignant tumor of the central nervous system (CNS) in children. Despite its relative good survival rates, treatment can cause long time sequels and may impair patients’ lifespan and quality, making the search for new treatment options still necessary. Polo like kinases (PLKs) constitute a five-member serine/threonine kinases family (PLK 1–5) that regulates different stages during cell cycle. Abnormal PLKs expression has been observed in several cancer types, including MB. As gene regulators, miRNAs have also been described with variable expression in cancer.
Methods
We evaluated gene expression profiles of all PLK family members and related miRNAs (miR-100, miR-126, miR-219, and miR-593*) in MB cell lines and tumor samples.
Results
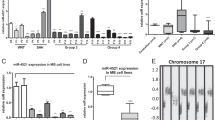
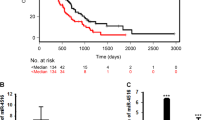
RT-qPCR analysis revealed increased levels of PLK1–4 in all cell lines and in most MB samples, while PLK5 was found underexpressed. In parallel, miR-100 was also found upregulated while miR-129, miR-216, and miR-593* were decreased in MB cell lines. Variable miRNAs expression patterns were observed in MB samples. However, a correlation between miR-100 and PLK4 expression was observed, and associations between miR-100, miR-126, and miR-219 expression and overall and event free survival were also evinced in our cohort. Moreover, despite the lack of association with clinico-pathological features, when comparing primary tumors to those relapsed, we found a consistent decrease on PLK2, miR-219, and miR-598* and an increase on miR-100 and miR-126.
Conclusion
Specific dysregulation on PLKs and associated miRNAs may be important in MB and can be used to predict prognosis. Although miRNAs sequences are fundamental to predict its target, the cell type may also be consider once that mRNA repertoire can define different roles for specific miRNA in a given cell.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bihannic L, Ayrault O (2016) Insights into cerebellar development and medulloblastoma. Bull Cancer 103:30–40. doi:10.1016/j.bulcan.2015.11.002
Sadighi Z, Vats T, Khatua S (2012) Childhood medulloblastoma: the paradigm shift in molecular stratification and treatment profile. J Child Neurol 27:1302–1307. doi:10.1177/0883073812449690
Kijima N, Kanemura Y (2016) Molecular classification of medulloblastoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). doi:10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0016
Crawford JR, MacDonald TJ, Packer RJ (2007) Medulloblastoma in childhood: new biological advances. Lancet Neurol 6:1073–1085. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70289-2
Remke M, Ramaswamy V, Taylor MD (2013) Medulloblastoma molecular dissection: the way toward targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 25:674–681. doi:10.1097/CCO.0000000000000008
Vaid R, Sharma N, Chauhan S et al (2016) Functions of polo-like kinases: a journey from yeast to humans. Protein Pept Lett 23:185–197
Johnson EF, Stewart KD, Woods KW et al (2007) Pharmacological and functional comparison of the polo-like kinase family: insight into inhibitor and substrate specificity. Biochemistry 46:9551–9563. doi:10.1021/bi7008745
De Falco M, De Luca A (2010) Cell cycle as a target of antineoplastic drugs. Curr Pharm Des 16:1417–1426
Palmisiano ND, Kasner MT (2015) Polo-like kinase and its inhibitors: ready for the match to start? Am J Hematol 90:1071–1076. doi:10.1002/ajh.24177
Pezuk JA, Brassesco MS, Morales AG et al (2013) Inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 induces cell cycle arrest and sensitizes glioblastoma cells to ionizing radiation. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 28:516–522. doi:10.1089/cbr.2012.1415
de Oliveira JC, Brassesco MS, Pezuk JA et al (2012) In vitro PLK1 inhibition by BI 2536 decreases proliferation and induces cell-cycle arrest in melanoma cells. J Drugs Dermatol 11:587–592
Liu Z, Sun Q, Wang X (2017) PLK1, a potential target for cancer therapy. Transl Oncol 10:22–32. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2016.10.003
Harris PS, Venkataraman S, Alimova I et al (2012) Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibition suppresses cell growth and enhances radiation sensitivity in medulloblastoma cells. BMC Cancer 12:80. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-80
Guerreiro AS, Fattet S, Kulesza DW et al (2011) A sensitized RNA interference screen identifies a novel role for the PI3K p110γ isoform in medulloblastoma cell proliferation and chemoresistance. Mol Cancer Res 9:925–935. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0200
Winkles JA, Alberts GF (2005) Differential regulation of polo-like kinase 1, 2, 3, and 4 gene expression in mammalian cells and tissues. Oncogene 24:260–266. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208219
Petrelli A, Perra A, Schernhuber K et al (2012) Sequential analysis of multistage hepatocarcinogenesis reveals that miR-100 and PLK1 dysregulation is an early event maintained along tumor progression. Oncogene 31:4517–4526. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.631
Ito T, Sato F, Kan T et al (2011) Polo-like kinase 1 regulates cell proliferation and is targeted by miR-593* in esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer 129:2134–2146. doi:10.1002/ijc.25874
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A et al (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol 123:465–472. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0922-z
Degenhardt Y, Lampkin T (2010) Targeting polo-like kinase in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 16:384–389. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1380
Guan R, Tapang P, Leverson JD et al (2005) Small interfering RNA-mediated polo-like kinase 1 depletion preferentially reduces the survival of p53-defective, oncogenic transformed cells and inhibits tumor growth in animals. Cancer Res 65:2698–2704. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2131
Pellegrino R, Calvisi DF, Ladu S et al (2010) Oncogenic and tumor suppressive roles of polo-like kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 51:857–868. doi:10.1002/hep.23467
Schmit TL, Ledesma MC, Ahmad N (2010) Modulating polo-like kinase 1 as a means for cancer chemoprevention. Pharm Res 27:989–998. doi:10.1007/s11095-010-0051-8
Triscott J, Lee C, Foster C et al (2013) Personalizing the treatment of pediatric medulloblastoma: polo-like kinase 1 as a molecular target in high-risk children. Cancer Res 73:6734–6744. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4331
Ou B, Zhao J, Guan S et al (2016) Plk2 promotes tumor growth and inhibits apoptosis by targeting Fbxw7/cyclin E in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 380:457–466. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.004
Cizmecioglu O, Warnke S, Arnold M et al (2008) Plk2 regulated centriole duplication is dependent on its localization to the centrioles and a functional polo-box domain. Cell Cycle 7:3548–3555
Archambault V, Glover DM (2009) Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:265–275. doi:10.1038/nrm2653
Yang Y, Bai J, Shen R et al (2008) Polo-like kinase 3 functions as a tumor suppressor and is a negative regulator of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha under hypoxic conditions. Cancer Res 68:4077–4085. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6182
Strebhardt K (2010) Multifaceted polo-like kinases: drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:643–660. doi:10.1038/nrd3184
de Cárcer G, Escobar B, Higuero AM et al (2011a) Plk5, a polo box domain-only protein with specific roles in neuron differentiation and glioblastoma suppression. Mol Cell Biol 31:1225–1239. doi:10.1128/MCB.00607-10
de Cárcer G, Manning G, Malumbres M (2011b) From Plk1 to Plk5: functional evolution of polo-like kinases. Cell Cycle 10:2255–2262. doi:10.4161/cc.10.14.16494
Voorhoeve PM, Agami R (2007) Classifying microRNAs in cancer: the good, the bad and the ugly. Biochim Biophys Acta - Rev Cancer 1775:274–282. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.11.003
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) MiRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:68–73. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1181
Chou C-H, Chang N-W, Shrestha S et al (2016) miRTarBase 2016: updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D239–D247. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1258
Sarachana T, Zhou R, Chen G, et al (2010) Investigation of post-transcriptional gene regulatory networks associated with autism spectrum disorders by microRNA expression profi ling of lymphoblastoid cell lines.
Shi W, Alajez NM, Bastianutto C et al (2010) Significance of Plk1 regulation by miR-100 in human nasopharyngeal cancer. Int J Cancer 126:2036–2048. doi:10.1002/ijc.24880
Zhao L-L, Jin F, Ye X et al (2015) Expression profiles of miRNAs and involvement of miR-100 and miR-34 in regulation of cell cycle arrest in Artemia. Biochem J 470:223–231. doi:10.1042/BJ20150116
Li BH, Zhou JS, Ye F et al (2011) Reduced miR-100 expression in cervical cancer and precursors and its carcinogenic effect through targeting PLK1 protein. Eur J Cancer 47:2166–2174. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.04.037
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M et al (2008) Distinct microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:15535–15540. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808266105
Ishizaki T, Tamiya T, Taniguchi K et al (2011) miR126 positively regulates mast cell proliferation and cytokine production through suppressing Spred1. Genes Cells 16:803–814. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2011.01529.x
Yang S, Li Y, Gao J et al (2013) MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene 32:4294–4303. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.432
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K et al (2008) MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:607–612. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.06.090
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Rosane de Paula Queiroz and Veridiana Kiill Suazo for assistance. We also thank to FAPESP for financial support Nos. 2011/01026-8 and 2011/11287-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial support
Fundacao de Amparo e Pesquisa do Estado de Sao Paulo (FAPESP Nos. 2011/01026-8 and 2011/11287-3).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pezuk, J.A., Brassesco, M.S., de Oliveira, R.S. et al. PLK1-associated microRNAs are correlated with pediatric medulloblastoma prognosis. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 609–615 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3366-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3366-5