Abstract
Purpose
We report on our experience in performing peri-insular functional hemispherectomy (PIH) in very young infants with catastrophic epilepsy.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of all infants with catastrophic epilepsy that underwent PIH under the age of 4 months at our institution.
Results
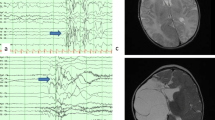
Four infants (three female, one male) were included (median age at time of surgery 2.9 months, range from 2.4 to 4.2 months; median patient’s weight at time of surgery 5650 g, range from 4300 to 7500 g). None of the patients experienced hemodynamic instability during surgery. All four patients were given red blood cell replacement (median 435 ml, range from 230 to 800 ml), three of the four patients experienced coagulopathy during surgery and were given platelet cells transfusion in one (50 ml) and fresh frozen plasma in two patients (191 and 320 ml). Two patients experienced severe complications that, however, did not cause a permanent morbidity due to prompt diagnosis and correct management. After a median follow-up time of 4.3 years (range from 1.3 to 7.9 years), three of four patients are completely seizure free. The remaining patient is experiencing brief daily staring episodes. All of them have a hemiparesis but are fully ambulatory and have a useful upper limb function.
Conclusion
In catastrophic epilepsy, PIH within the first months of life is feasible provided that an experienced multidisciplinary team is involved. Awareness of surgical challenges and potential complications is indispensible when the life-threatening nature of the epilepsy compels neurosurgeons to operate at this very young age.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basheer SN, Connolly MB, Lautzenhiser A, Sherman El MS, Hendson G, Steinbok P (2007) Hemispheric surgery in children with refractory epilepsy: seizure outcome, complications, and adaptive function. Epilepsia 48:133–140
Bharti N, Barta YK, Kaur H (2009) Paediatric perioperative cardiac arrest and its mortality: database of a 60-month period from a tertiary care paediatric centre. Eur J Anaesthesiol 26:490–495
Carson B, Javedan S, Freeman J, Vining EP, Zuckerberg A, Lauer JA, Guarnieri M (1996) Hemispherectomy: a hemidecortication approach and review of 52 cases. J Neurosurg 84:903–911
Dorfer C, Czech T, Dressler A, Gröppel G, Mühlebner-Fahrngruber A, Novak K, Feucht M (2013) Vertical perithalamic hemispherotomy: a single-center experience in 40 pediatric patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 54:1905–1912
Duchowny M, Jayakar P, Resnick T, Harvey AS, Alvarez L, Dean P, et al (1998) Epilepsy surgery in the first three years of life. Epilepsia 39:737–743
Dunkley C, Kung J, Scott RC, Nicolaides P, Neville B, Aylett SE, Harkness W, Cross JH (2011) Epilepsy surgery in children under 3 years. Epilepsy Res 93:96–106
Flick RP, Sprung J, Harrison T, Gleich SJ, Schroeder DR, Hanson AC, Buenvenida SL, Warner DO (2007) Perioperative cardiac arrest in children between 1988 and 2005 at a tertiary referral center. Anesthesiology 106:226–237
Gonzales-Martinez JA, Gupta A, Kotagal P, Lachhwani D, Wyllie E, Lüders HO, Bingaman WE (2005) Hemispherectomy for catastrophic epilepsy in infants. Epilepsia 46:1518–1525
Gowda S, Salazar F, Bingaman W, Kotagal P, Lachhwani DL, Gupta A, Davis S, Niezgoda J, Wyllie E (2010) Surgery for catastrophic epilepsy in infants 6 months of age and younger. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:603–607
Hoffman HJ, Hendrick EB, Humphreys RP, Buncic JR, Armstrong DL, Jenkin RD (1979) Hemispherectomy for Sturge-Weber syndrome. Childs Brain 5:233–248
Honda R, Kaido T, Sugai K, Takahashi A, Kaneko Y, Nakagwa E, Sasaki M, Otsuki T (2013) Long-term developmental outcome after early hemispherotomy for hemimegalencephaly in infants with epileptic encephalopathy. Epilepsy & Behaviour 29:30–35
Jonas R, Nguyen S, Asarnow RF, LoPresti C, Curtiss S, de Bode S, Yudovin S, Shields WD, Vinters HV, Mathern GW (2004) Cerebral hemispherectomy. Hospital course, seizure, developmental, language and motor outcomes. Neurology 62:1712–1721
Kwan A, Ng WH, Otsubo H, Ochi A, Snead 3rd OC, Tamber MS, Rutka JT (2010) Hemispherectomy for the control of intractable epilepsy in childhood: comparison of 2 surgical techniques in a single institution. Neurosurgery 67:ons429–ons436
Loddenkemper T, Holland DK, Stanford LD, Kotagal P, Bingaman W, Wyllie E (2007) Developmental outcome after epilepsy surgery in infancy. Pediatrics 119:930–935
Morita K, Kawashima Y, Irita K, Kobayayashi T, Goto Y, Iwao Y, Seo N, Tsuzaki K, Dohi S (2001) Perioperative mortality and morbidity in 1999 with a special reference to age in 466 certified training hospitals of Japanese Society of Anesthesiologists: report of Committee on Operating Room Safety of Japanese Society of Anesthesiologists. Masui 50:909–921
Morray JP, Geiduschek JM, Caplan RA, Posner KL, Gild WM, Cheney FW (1993) A comparison of pediatric and adult anesthesia closed malpractice claims. Anaesthesiology 78:461–467
Murat I, Constant I, Maud’huy H (2004) Perioperative anaesthetic morbidity in children: a database of 24,165 anaesthetics over a 30-month period. Paediatr Anaesth 14:158–166
Piastra M, Pietrini D, Caresta E, Chiaretti A, Viola L, Cota F, Pusateri A, Polidori G, Di Rocco C (2004) Hemispherectomy procedures in children: haematological issues. Childs Nerv Syst 20:453–458
Pulsifer MB, Brandt J, Salorio CF, Vining EPG, Carson BS, Freeman JM (2004) The cognitive outcome of hemispherectomy in 71 children. Epilepsia 3:243–254
Rowe MI, Rowe SA (2000) The last fifty years of neonatal surgical management. Am J Surg 180:345–352
Schramm J, Kuczaty S, Sassen R, Elger CE, von Lehe M (2012) Pediatric functional hemispherectomy: outcome in 92 patients. Acta Neurochir 154:2017–2028
Taha JM, Crone KR, Berger TS (1994) The role of hemispherectomy in the treatment of holohemispheric hemimegaloencephaly. J Neurosurg 81:37–42
Thomas SG, Daniel RT, Chacko AG, Thomas M, Russell PS (2010) Cognitive changes following surgery in intractable hemispheric and sub-hemispheric pediatric epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 26:1067–1073
Tiret L, Nivoche Y, Hatton F, Desmonts JM, Vourc’h G (1988) Complications related to anaesthesia in infants and children: a prospective survey of 40240 anaesthetics. Br J Anaesth 61:263–269
Van Schooneveld MM, Jennekens-Schinkel A, van Rijen PC, Braun KP, van Nieuwenhuizen O (2011) Hemispherectomy: a basis for mental development in children with epilepsy. Epileptic Disorders 13:47–55
Vining EP, Freeman J, Pillas D, Uematsu S, Carson BS, Brandt J, Boatman D, Pulsifer MB, Zuckerberg A (1997) Why would you remove half a brain? The outcome of 58 children after hemispherectomy—the Johns Hopkins experience: 1968–1996. Pediatrics 100:163–171
Wieser H, Blume W, Fish D, Goldensohn E, Hufnagel A, King D, Sperling MR, Lüders H (2001) Proposal for a new classification of outcome with respect to epileptic seizures following epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 42:282–286
Wyllie E, Comair YG, Kotagal P, Raja S, Ruggieri P (1996) Epilepsy surgery in infants. Epilepsia 37:625–637
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorfer, C., Ochi, A., Snead, O.C. et al. Functional hemispherectomy for catastrophic epilepsy in very young infants: technical considerations and complication avoidance. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 2103–2109 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2794-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2794-3