Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to determine whether extent of morphological brain injury in pediatric cerebellar tumor survivors correlates with neurocognitive function and health-related quality of life (HrQoL).
Methods
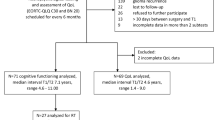
Seventeen cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma (cPA) and 17 medulloblastoma (MB) survivors were examined for HrQoL, intelligence using the German version of the WISC-III, attention, working memory, and visual motor coordination. MRI scans were analyzed for extent of posterior fossa brain tissue loss.
Results
We found significant correlations between amount and extent morphological brain lesions of pediatric cerebellar tumor survivors and several cognitive impairments including intelligence and attention in both patient groups. These were in total more pronounced in MB patients when compared to cPA patients. Still, function loss and brain lesions detected on conventional MRI did not influence HrQoL.
Conclusions
These findings support the notion that long-term neurocognitive deficits of pediatric posterior fossa tumor survivors significantly correlate with brain tissue damage. The cerebellum plays a role in regulating higher-order functions. On the contrary, the extent brain injury is not detected by HrQoL assessment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaatsch P, Rickert CH, Kuhl J, Schuz J, Michaelis J (2001) Population-based epidemiologic data on brain tumors in German children. Cancer 92:3155–3164
Pencalet P, Maixner W, Sainte-Rose C, Lellouch-Tubiana A, Cinalli G, Zerah M, Pierre-Kahn A, Hoppe-Hirsch E, Bourgeois M, Renier D (1999) Benign cerebellar astrocytomas in children. J Neurosurg 90:265–273
Gottardo NG, Gajjar A (2006). Current therapy for medulloblastoma. Current treatment options in neurology. 8/4(319-34)
Rueckriegel SM, Blankenburg F, Henze G, Baqué H, Driever PH (2009) Loss of fine motor function correlates with ataxia and decline of cognition in cerebellar tumor survivors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53(3):424–431
Palmer SL, Goloubeva O, Reddick WE, Glass JO, Gajjar A, Kun L, Merchant TE, Mulhern RK (2001) Patterns of intellectual development among survivors of pediatric medulloblastoma: a longitudinal analysis. J Clin Oncol 19:2302–2308
Aarsen FK, Van Dongen HR, Paquier PF, Van Mourik M, Catsman-Berrevoets CE (2004) Long-term sequelae in children after cerebellar astrocytoma surgery. Neurology 62:1311–1316
Mabbott DJ, Spiegler BJ, Greenberg ML, Rutka JT, Hyder DJ, Bouffet E (2005) Serial evaluation of academic and behavioral outcome after treatment with cranial radiation in childhood. J Clin Oncol 23:2256–2263
Maddrey AM, Bergeron JA, Lombardo ER, McDonald NK, Mulne AF, Barenberg PD, Bowers DC (2005) Neuropsychological performance and quality of life of 10 year survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 72:245–253
Beebe DW, Ris MD, Armstrong FD, Fontanesi J, Mulhern R, Holmes E, Wisoff JH (2005) Cognitive and adaptive outcome in low-grade pediatric cerebellar astrocytomas: evidence of diminished cognitive and adaptive functioning in National Collaborative Research Studies (CCG 9891/POG 9130). J Clin Oncol 23:5198–5204
Ribi K, Relly C, Landolt MA, Alber FD, Boltshauser E, Grotzer MA (2005) Outcome of medulloblastoma in children: long-term complications and quality of life. Neuropediatrics 36:357–365
Butler RW, Haser JK (2006) Neurocognitive effects of treatment for childhood cancer. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 12:184–191
Bull KS, Spoudeas HA, Yadegarfar G, Kennedy CR (2007) Reduction of health status 7 years after addition of chemotherapy to craniospinal irradiation for medulloblastoma: a follow-up study in PNET 3 trial survivors on behalf of the CCLG (formerly UKCCSG). J Clin Oncol 25:4239–4245
Aarsen FK, Paquier PF, Reddingius RE, Streng IC, Arts WF, Evera-Preesman M, Catsman-Berrevoets CE (2005) Functional outcome after low-grade astrocytoma treatment in childhood. Cancer 106:396–402
Zuzak TJ, Poretti A, Drexel B, Zehnder D, Boltshauser E, Grotzer MA (2008) Outcome of children with low-grade cerebellar astrocytoma: long-term complications and quality of life. Childs Nerv Syst 24:1447–1455
Schmahmann JD (2004) Disorders of the cerebellum: ataxia, dysmetria of thought, and the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. J Neuropsychiatr Clin Neurosci 16:367–378
Levisohn L, Cronin-Golomb A, Schmahmann JD (2000) Neuropsychological consequences of cerebellar tumour resection in children: cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome in a paediatric population. Brain 123(Pt 5):1041–1050
Tewes U, Rossmann P, Schallberger U (1999) HAWIK-III. Übersetzung und Adaptation der WISC-III von David Wechsler. Hans Huber, Bern
Tewes U (1994). Hamburg-Wechsler Intelligenztest für Erwachsene, Revision 1991. In: Kinderpsychologische Tests: ein Kompendium für Kinderärzte, 3rd edn. Thieme, Stuttgart, p63
Zimmermann P, Fimm B (2002) A test battery for attentional performance (Chapter 4). In: Leclercq M, Zimmermann P (eds) Applied Neuropsychology of Attention: Theory. Diagnosis and Rehabilitation. Psychology Press, London, pp 110–151
Rey A (1964) Léxamen clinique en psychologie [The clinical examination in psychology]. Universitaires de France, Paris
Helmstaedter C, Lendt M, Lux S (2001) Verbaler Lern- und Merkfähigkeitstest (VLMT). Beltz Test GmbH, Göttingen
Beery K (1997) The Beery-Buktenica developmental test of visual-motor integration (4th ed). Modern Curriculum Press, Parsippany, NJ
Ravens-Sieberer U, Bullinger M (1998). Assessing the health related quality of life in chronically ill children with the German KINDL: first psychometric and content-analytical results. Quality of Life Research, Vol. 4, No 7
Musial-Bright L, Panteli L, Hernáiz DP (2011) Pediatric low-grade glioma survivors experience high quality of life. Childs Nerv Syst 27(11):1895–1902
Bradley Eilertsen ME, Jozefiak T, Rannestad T, Indredavik MS, Vik T (2012) Quality of life in children and adolescents surviving cancer. Eur J Oncol Nurs 16(2):185–193
Luft AR, Skalej M, Welte D, Kolb R, Burk K, Schulz JB et al (1998) A new semiautomated, three-dimensional technique allowing precise quantification of total and regional cerebellar volume using MRI. Magn Reson Med 40:143–151
Kellie SJ, Chaku J, Lockwood LR, O'Regan P, Waters KD, Wong CK, Australian and New Zealand Children's Haematology Oncology Group (2005) Late magnetic resonance imaging features of leukoencephalopathy in children with central nervous system tumours following high-dose methotrexate and neuraxis radiation therapy. Eur J Cancer 41(11):1588–1596
Bermel RA, Bakshi R, Tjoa C, Puli SR, Jacobs L (2002) Bicaudate ratio as a magnetic resonance imaging marker of brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 59(2):275–280
Ronning C, Sundet K, Due-Tonnessen B, Lundar T, Helseth E (2005) Persistent Cognitive Dysfunction Secondary to Cerebellar Injury in Patients Treated for Posterior Fossa Tumors in Childhood. Pediatr Neurosurg 41:15–21
Hazin I, Dellatolas G, Garcia D, Pedrosa F, Pedrosa A (2011) Intellectual Impairment After Treatment for Medulloblastoma and Astrocytoma in Childhood: The Brazilian Experience. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 33:506–515
Reeves CB, Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Merchant TE, Buchanan GM, Gajjar A, Mulhern RK (2006) Attention and memory functioning among pediatric patients with medulloblastoma. J Pediatr Psychol 31(3):272–280
Steinlin M, Imfeld S, Zulauf P, Boltshauser E, Lovblad KO, Ridolfi Luthy A, Perrig W, Kaufmann F (2003) Neuropsychological long-term sequelae after posterior fossa tumour resection during childhood. Brain 126:1998–2008
Callu D, Viguier D, Laroussinie F, Puget S, Boddaert N, Kieffer V, Piana H, Escolano S, Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Grill J, Dellatolas G (2009) Cognitive and academic outcome after benign or malignant cerebellar tumor in children. Cogn Behav Neurol 22(4):270–278
Edelstein K, Spiegler BJ, Fung S, Panzarella T, Mabbott DJ, Jewitt N, Mammone D’Agostino N, Mason WP, Bouffet E, Tabori U, Laperriere N, Hodgson DC (2011) Early aging in adult survivors of childhood medulloblastoma: long-term neurocognitive, functional, and physical outcomes. Neuro-Oncology 13(5):536–545
Mulhern RK, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, Reddick WE, Kun LE (2004) Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. Lancet Oncol 5:399–408
Grill J, Viguier D, Kieffer V, Bulteau C, Sainte-Rose C, Hartmann O et al (2004) Critical risk factors for intellectual impairment in children with posterior fossa tumors: the role of cerebellar damage. J Neurosurg 101(2 Suppl):152–158
Riva D, Giorgi C (2000) The cerebellum contributes to higher functions during development: evidence from a series of children surgically treated for posterior fossa tumours. Brain 123(Pt 5):1051–1061
Reddick WE, Shan ZY, Glass JO, Helton S, Xiong X, Wu S, Bonner MJ, Howard SC, Christensen R, Khan RB, Pui C-H And Mulhern RK (2006) Smaller White-Matter Volumes Are Associated with Larger Deficits in Attention and Learning among Long-Term Survivors of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer 106:941–949
Reddick WE, White HA, Glass JO, Wheeler GC, Thompson SJ, Gajjar A, Leigh L, Mulhern RK (2003) Developmental Model Relating White Matter Volume to Neurocognitive Deficits in Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors. Cancer 97:2512–2519
Khong PL, Leung LH, Fung AS, Fong DY, Qiu D, Kwong DL, Ooi G-C, McAlanon G, Cao G, Chan GC (2006) White matter anisotropy in post-treatment childhood cancer survivors: Preliminary evidence of association with neurocognitive function. J Clin Oncol 24:884–890
Mabbot DJ, Noseworthy MD, Bouffet E, Rockel C, Laughlin S (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter after cranial radiation in children for medulloblastoma: correlation with IQ. Neuro-Oncology 8(3):244–252
Rueckriegel SM, Driever PH, Blankenburg F, Ludemann L, Henze G, Bruhn H (2010) Differences in supratentorial damage of white matter in pediatric survivors of posterior fossa tumors with and without adjuvant treatment as detected by magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3):859–866
Frange P, Alapetite EC, Gaboriaud EG, Bours ED, Zucker EJM, Zerah EM, Brisse EH, Chevignard EM, Mosseri EV, Bouffet EE, Doz EF (2009) From childhood to adulthood: long-term outcome of medulloblastoma patients. The Institut Curie experience (1980–2000). J Neurooncol 95:271–279
Roncadin C, Dennis M, Greenberg ML, Spiegler BJ (2008) Adverse medical events associated with childhood cerebellar astrocytomas and medulloblastomas: natural history and relation to very long-term neurobehavioral outcome. Childs Nerv Syst 24:995–1002
Turner CD, Chordas CA, Liptak CC, Rey-Casserly C, Delaney BL, Ullrich NJ, Goumnerova LC, Scott RM, Begley HC, Fletcher WJ, Yao X, Chi S, Kieran MW (2009) Medical, Psychological, Cognitive and Educational Late-Effects in Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma Survivors Treated With Surgery Only. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53:417–423
Acknowledgments
A doctoral thesis scholarship of the “Kind-Philipp-Stiftung” to SM Rueckriegel is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rajiv Kumar Khajuria, Friederike Blankenburg and Ines Wuithschick contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khajuria, R.K., Blankenburg, F., Wuithschick, I. et al. Morphological brain lesions of pediatric cerebellar tumor survivors correlate with inferior neurocognitive function but do not affect health-related quality of life. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 569–580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2635-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2635-4