Abstract
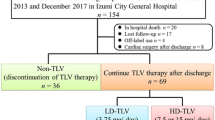
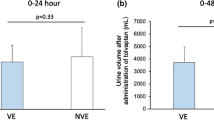
Tolvaptan has been gradually spread to use as a potent diuretic for congestive heart failure in the limited country. However, the response to this aquaretic drug still is unpredictable. A total of 92 patients urgently hospitalized due to congestive heart failure and treated with tolvaptan in addition to standard treatment was retrospectively analyzed. Responder of tolvaptan treatment was defined as a patient with peak negative fluid balance greater than 500 mL/day, and clinical profiles were compared between 76 responders and 16 non-responders. Responders started to increase daily urine volume (UV) from Day 1 through Day 3. In contrast, non-responders showed no significant increase in daily UV from the baseline up to Day 5. Time between admission and tolvaptan administration was shorter in responders, even without statistical significance (3.3 vs. 4.6 days, p = 0.053). Multivariate analysis revealed that blood urea nitrogen (BUN) [cutoff: 34 mg/dL, odds ratio (OR) 9.0, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.42–57.3, p < 0.01] and plasma renin activity (PRA) (cutoff: 4.7 ng/mL/h, OR 6.1, 95% CI 1.01–36.4, p < 0.01) at baseline were independent predictors for tolvaptan responsiveness. It suggests that renal perfusion may affect tolvaptan-induced UV. Finally, durations of stay in intensive care unit and total hospitalization were significantly shorter in responders (median: 6.0 vs. 13.0 days, p = 0.022; 15.0 vs. 25.0 days, p = 0.016, respectively). Responders of tolvaptan have lower BUN and renin activity at baseline, and shorten hospitalization period.
Trial Registration
The study was registered at University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN-CTR) with the identifier UMIN000023594. https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi-open-bin/ctr_e/ctr_view.cgi?recptno=R000024988




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 December 2017
In the original publication of the article, the values of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and plasma renin activity (PRA) have been published incorrectly and the corrected values are as follows.
References
Peacock WF, Costanzo MR, De Marco T, Lopatin M, Wynne J, Mills RM, Emerman CL (2009) Impact of intravenous loop diuretics on outcomes of patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: insights from the ADHERE registry. Cardiology 113:12–19
Hasselblad V, Gattis Stough W, Shah MR, Lokhnygina Y, O’Connor CM, Califf RM, Adams KF Jr (2007) Relation between dose of loop diuretics and outcomes in a heart failure population: results of the ESCAPE trial. Eur J Heart Fail 9:1064–1069
Lee CR, Watkins ML, Patterson JH, Gattis W, O’Connor CM, Gheorghiade M, Adams KF Jr (2003) Vasopressin: a new target for the treatment of heart failure. Am Heart J 146:9–18
Gheorghiade M, Konstam MA, Burnett JC Jr, Grinfeld L, Maggioni AP, Swedberg K, Udelson JE, Zannad F, Cook T, Ouyang J, Zimmer C, Orlandi C (2007) Short-term clinical effects of tolvaptan, an oral vasopressin antagonist, in patients hospitalized for heart failure: the EVEREST Clinical Status Trials. JAMA 297:1332–1343
Costello-Boerrigter LC, Smith WB, Boerrigter G, Ouyang J, Zimmer CA, Orlandi C, Burnett JC Jr (2006) Vasopressin-2-receptor antagonism augments water excretion without changes in renal hemodynamics or sodium and potassium excretion in human heart failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F273–F278
Uemura Y, Shibata R, Takemoto K, Uchikawa T, Koyasu M, Ishikawa S, Mitsuda T, Miura A, Imai R, Iwamiya S, Ozaki Y, Kato T, Miura T, Watarai M, Murohara T (2016) Clinical benefit of tolvaptan in patients with acute decompensated heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Heart Vessels 31:1643–1649
Hanatani A, Shibata A, Kitada R, Iwata S, Matsumura Y, Doi A, Sugioka K, Takagi M, Yoshiyama M (2017) Administration of tolvaptan with reduction of loop diuretics ameliorates congestion with improving renal dysfunction. Heart Vessels 32:287–294
Imamura T, Kinugawa K, Shiga T, Kato N, Muraoka H, Minatsuki S, Inaba T, Maki H, Hatano M, Yao A, Kyo S, Nagai R (2013) Novel criteria of urine osmolality effectively predict response to tolvaptan in decompensated heart failure patients–association between non-responders and chronic kidney disease. Circ J 77:397–404
Sato N, Kajimoto K, Keida T, Mizuno M, Minami Y, Yumino D, Asai K, Murai K, Muanakata R, Aokage T, Sakata Y, Mizuno K, Takano T (2013) Clinical features and outcome in hospitalized heart failure in Japan (from the ATTEND Registry). Circ J 77:944–951
Mentz RJ, Stevens SR, DeVore AD, Lala A, Vader JM, AbouEzzeddine OF, Khazanie P, Redfield MM, Stevenson LW, O’Connor CM, Goldsmith SR, Bart BA, Anstrom KJ, Hernandez AF, Braunwald E, Felker GM (2015) Decongestion strategies and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation in acute heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 3:97–107
Valente MA, Voors AA, Damman K, Van Veldhuisen DJ, Massie BM, O’Connor CM, Metra M, Ponikowski P, Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Davison B, Cleland JG, Givertz MM, Bloomfield DM, Fiuzat M, Dittrich HC, Hillege HL (2014) Diuretic response in acute heart failure: clinical characteristics and prognostic significance. Eur Heart J 35:1284–1293
Ter Maaten JM, Dunning AM, Valente MA, Damman K, Ezekowitz JA, Califf RM, Starling RC, van der Meer P, O’Connor CM, Schulte PJ, Testani JM, Hernandez AF, Tang WH, Voors AA (2015) Diuretic response in acute heart failure-an analysis from ASCEND-HF. Am Heart J 170:313–321
Tsuchihashi-Makaya M, Hamaguchi S, Kinugawa S, Yokota T, Goto D, Yokoshiki H, Kato N, Takeshita A, Tsutsui H (2009) Characteristics and outcomes of hospitalized patients with heart failure and reduced vs preserved ejection fraction. Report from the Japanese cardiac registry of heart failure in cardiology (JCARE-CARD). Circ J 73:1893–1900
Imamura T, Kinugawa K, Fujino T, Inaba T, Maki H, Hatano M, Yao A, Komuro I (2014) Increased urine aquaporin-2 relative to plasma arginine vasopressin is a novel marker of response to tolvaptan in patients with decompensated heart failure. Circ J 78:2240–2249
Matsukawa R, Kubota T, Okabe M, Yamamoto Y (2015) Early use of V2 receptor antagonists is associated with a shorter hospital stay and reduction in in-hospital death in patients with decompensated heart failure. Heart Vessels 31:1650–1658
Felker GM, Mentz RJ (2012) Diuretics and ultrafiltration in acute decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:2145–2153
Paterna S, Di Pasquale P, Parrinello G, Amato P, Cardinale A, Follone G, Giubilato A, Licata G (2000) Effects of high-dose furosemide and small-volume hypertonic saline solution infusion in comparison with a high dose of furosemide as a bolus, in refractory congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2:305–313
Watanabe K, Dohi K, Sugimoto T, Yamada T, Sato Y, Ichikawa K, Sugiura E, Kumagai N, Nakamori S, Nakajima H, Hoshino K, Machida H, Okamoto S, Onishi K, Nakamura M, Nobori T, Ito M (2012) Short-term effects of low-dose tolvaptan on hemodynamic parameters in patients with chronic heart failure. J Cardiol 60:462–469
Kinugawa K, Sato N, Inomata T, Shimakawa T, Iwatake N, Mizuguchi K (2014) Efcacy and safety of tolvaptan in heart failure patients with volume overload—an interim result of post-marketing surveillance in Japan. Circ J 78:844–852
Hirai K, Shimomura T, Moriwaki H, Ishii H, Shimoshikiryo T, Tsuji D, Inoue K, Kadoiri T, Itoh K (2016) Risk factors for hypernatremia in patients with short- and long-term tolvaptan treatment. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72:1177–1183
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was not financially supported from any company, grant or fund, and all authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The values of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and plasma renin activity (PRA) have been corrected in this article.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-1102-4.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kogure, T., Jujo, K., Hamada, K. et al. Good response to tolvaptan shortens hospitalization in patients with congestive heart failure. Heart Vessels 33, 374–383 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-1072-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-1072-6