Abstract
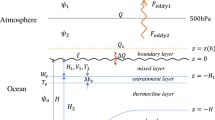
The wave-CISK (cumulus convection heating feedback), the air-sea interaction and the evaporation-wind feedback are together introduced into a simple theoretical model, in order to understand their effect on driving tropical atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation (ISO). The results showed that among the introduced dynamical processes the wave-CISK plays a major role in reducing phase speed of the wave to be closer to the observed tropical ISO. While the evaporation-wind feedback plays a major role in unstabilizing the wave. The air-sea interaction has certain effect on slowing down the phase speed of the wave. Therefore, the wave-CISK and evaporation-wind feedback can be regarded as fundamental dynamical mechanism of the tropical ISO. This study also shows that since the effects of the evaporation-wind feedback and the air-sea interaction were introduced, the excited wave is zonally dispersive, which can dynamically explain the activity feature of the observed ISO in the tropical atmosphere very well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battisti, D. S., and A. C. Hirst, 1989: Interannual variability in a tropical atmosphere-ocean model: influence of the basic state, ocen geometry and nonlinearity. J. Atmos. Sci., 46, 1687–1712.
Chang, C. P., and H. Lim, 1988: Kelvin wave-CISK: a possible mechanism for 3(H50 day oscillatios. J, Atmos. Sci., 45, 1709–1720.
Cho, H. R., K. Fraedrich, and J. T. Wang, 1994: Cloud clusters, Kelvin wave-CISK and the Madden Julian Oscillation in the equatorial troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 51, 68–76.
Cho, H. R., and D. Pendlebury, 1997: Wave CISK of equatorial waves and the vertical distribution of cumulus heat-ing. J. Atmos. Sci., 54, 2429–2440.
Cho, H. R., and C. Y. Li, 1999: Equatorial Kelvin wave and intraseasonal oscillation in the equatorial troposphere. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 23, 237–244.
Crum, F. X., and T. J. Dunkerton, 1994: CISK and evaporation-wind feedback with conditional heating on an equatorial beta-plane. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 72, 11–18.
Emanual, K. A., 1987: An air-sea interaction model of intraseasonal oscillation in the tropics. J. Atmos. Sci., 44, 2324–2340.
Hirst, A. C, and K. M. Lau, 1990: Intraseasonal and interannual oscillations in coupled ocean-atmosphere models. J. Climate, 3, 713–725.
Kirtman, B., and A. Vernekar, 1993: On wave-CISK and the evaporation-wind feedback for the Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci., 50, 2811–2814.
Knuston, T. R., and K. M. Weickmann, 1987: 30-60 day atmospheric oscillation: composite life cyclones of convec-tion and circulation anomalies. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 1407–1436.
Krishnamurti, T. N., and D. Subrahmanyam, 1982: The 30-50 day mode at 850 mb during MONEX. J. Atoms. Sci., 39,2088–2095.
Lau, N. C, and K. M. Lau, 1986: The structure and propagation of oacillation appearing in a GFDL general circula-tion model. J. Atmos. Sci., 43, 2023–2047.
Lau, K. M., and P. H. Chan, 1985: Aspects of the 40-50 day oscillation during the northern winter as inferred from outgoing longwave radiation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 113, 1889–1909.
Lau, K. M., and L. Peng, 1987: Origin of low-frequency (intraseasonal) oscillation in the tropical atmosphere, Part I: Basic theory. J. Atmos. Sci., 44, 850–972.
Lau, K. M., and S. Shen, 1988: On the dynamics of intraseasonal oscillation and ENSO. J. Atmos. Sci., 45, 1781–1791.
Li Chongyin, 1985: Actions of summer monsoon troughs (ridges) and tropical cyclones over South Asia and the mov-ing CISK mode. Scientia Siniea (B), 28, 1197–1207.
Li Chongyin, 1988: On the feedback role of tropical convection. Tropical Rainfall Measurements, A. Deepak Pub-lishing, New York 141–146.
Li Chongyin, 1990: Dynamical study on 30-60 day oscillation in the tropical atmosphere outside equator. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci, 14, 101–112.
Li Chongyin, 1991: Low-Frequency Oscillation in the Atmosphere, China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 276pp (in Chinese).
Li Chongyin, 1993: A further inquiry on the mechanism of 30-60 day oscillation in the tropical atmosphere. Ad-vances in Atmospheric Science, 10, 41–53.
Li Chongyin, 1995: Introduction to Climate Dynamics, China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 254–268 (in Chinese).
Li Chongyin, and Q. H. Liao, 1996: Behaviour of coupled modes in a simple nonlinear air-sea interaction model. Advances in Atmospheric Science, 13, 183–195.
Li G. L., and Liu S. K., 1993: Wave-CISK, evaporation-wind feedback and low-frequency oscillation. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 17,696–702.
Lim, H., T. K. Lim, and C. P. Chang, 1990: Reexamination of wave-CISK theory: Existence and properties of nonlinear wave-CISK modes. J. Atmos. Sci., 47, 3078–3091.
Madden, R. A., and P. R. Julian, 1971: Detection of 40-50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci., 28, 702–708.
Madden, R. A., and P. R. Julian, 1972: Description of global scale circulation cells in the tropics with 40-50 day pe-riod. J. Atmos. Sci., 29, 1109–1123.
Madden, R. A., and P. R. Julian, 1994: Observations of the 40-50 day tropical oscillation-A review. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112,814–837.
Murakami, M., 1984: Analysis of the deep convective activity over the western Pacific and Southeast Asia, Part II: Seasonal and intraseasonal variations during Northern Summer. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 62, 88–108.
Neelin, J. D., I. M. Held, and K. H. Cook, 1987: Evaporation-wind feedback and low-frequency variability in the tropical atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 44, 2341–2348.
Philander, S. G. H., T. Yamagata, and R. C. Pacanowski, 1984: Unstable air-sea interactions in the tropics. J. Atmos. Sci., 41,604–613.
Wang, B., 1988: Dynamics of tropical low-frequency waves: An analysis of the moist Kelvin wave. J. Atmos. Sci., 45,2051–2065.
Wang, B., and X. Xie, 1998: Coupled modes in the warm pool climate system, Part I: The role of air-sea interaction in maintaining Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Climate, 11, 2116–2135.
Takahashi, M., 1987: A slow phase speed of the intraseasonal oscillation using the wave-CISK. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 65, 43–49.
Zhao Qiang, and Liu Shikuo, 1996: CISK and Evaporation-wind feedback mechanism and 30-60 day oscillations in the tropical atmosphere. Acta Meteor. Sinica., 54, 417–426 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Cho, HR. & Wang, JT. CISK kelvin wave with evaporation-wind feedback and air-sea interaction-A further study of tropical intraseasonal oscillation mechanism. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 19, 379–390 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0073-1
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0073-1