Abstract.
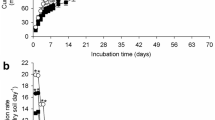
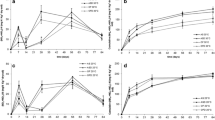
Environmental conditions may modify pesticide effects on non-target soil micro-organisms due to their influence on pesticide persistence, bioavailability and interactions with microbial metabolism. This study investigated the relationship between effects of the herbicide metazachlor and its degradation and availability in soils with different organic C contents (soil A=1.3%, soil B=7.1%), incubated at 20°C and 30°C. Relative differences between dehydrogenase activity (DHA) in soil treated with metazachlor and untreated soil ranged from –16.6 to +18.9% with a greater impact for soil A, probably due to greater pesticide availability and potential for the microflora to recover from adverse effects. Relative effects on substrate-induced, short-term respiration (SIR, –11.8 to +6.0%) and N mineralisation (Nmin, –24.4 to +35.8%) were similar in both soils. Soil temperature did not consistently influence the effects of metazachlor on DHA and SIR. Nmin was more strongly affected at 20°C than at 30°C, which was potentially caused by larger pesticide concentrations at 20°C or a smaller potential for the microflora to reproduce destroyed biomass. Additional studies with the herbicide dinoterb showed stronger effects on DHA, SIR and Nmin than for metazachlor (–57.7 to +78.2%) and no clear influence of soil and temperature. Results showed that environmental factors may influence pesticide effects on micro-organisms. Clear relationships are not always found due to interactions between these factors, pesticide persistence, bioavailability and microbial metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beulke, S., Malkomes, HP. Effects of the herbicides metazachlor and dinoterb on the soil microflora and the degradation and sorption of metazachlor under different environmental conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 33, 467–471 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740100354
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740100354