Abstract
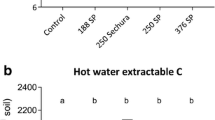
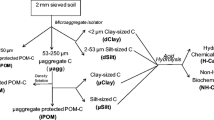
This study was conducted to determine whether separation of particulate organic matter (POM) that is biologically labile from aggregate entrapped material improves the usefulness of POM as an index of soil C and N dynamics. The effects of conventional (CT) and no-tillage (NT) practices on POM were assessed using soils from three 10-year trials in Illinois. Loose and occluded POM in the 0–5 cm depth were separated from 1994 samples. Use of NT practices increased C and N contents at 0–5 cm relative to CT practices and those increases were most apparent in the occluded POM fraction. The correlation between total POM-N and potentially mineralizable N (PMN) was stronger than that between PMN and either the loose or occluded-POM fractions. In 1995, both the microbial biomass, estimated as chloroform-labile C (CFEC), and PMN were correlated with POM-C and N, but the relationship was weak when data (from different tillage and depth combinations) were not treated in aggregate. POM-C and CFEC were most strongly correlated in surface depths and in CT treatments. In NT 0–5 cm samples, PMN contents were similar (≈27 mg N kg–1 soil) at all sites despite notable differences in POM-N concentrations; PMN was not related to POM-N in CT samples. There was no consistent relationship between PMN and POM-N contents in 5–30 cm samples. DRFTIR spectra indicated that carbohydrates were most abundant in POM at 0–5 cm. Relatively low PMN rates and enrichment of polysaccharides in POM in the sicl soil suggest that physical protection of labile organic substrates was more important at that site than at sites with lighter textured soils. Improved fractionation and incubation techniques and alleviation of laboratory artifacts will improve our ability to relate POM quantity, distribution and composition to biologically mediated C and N dynamics occurring in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wander, M., Bidart, M. Tillage practice influences on the physical protection, bioavailability and composition of particulate organic matter. Biol Fertil Soils 32, 360–367 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000260
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000260