Abstract
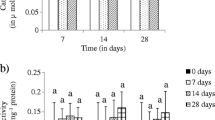
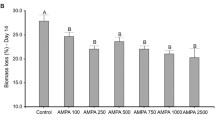
The chemical imidacloprid is the major component of many widely used insecticides and is relatively persistent in soils. A set of experiments was carried out to estimate the lethal (mortality) and sublethal (weight loss) effects of one of these insecticides, Confidor, on two earthworm species commonly found in agricultural soils. A preliminary experiment in the absence of earthworms showed that imidacloprid was not rapidly degraded, with a decrease of less than 10% after 2 weeks, and that it was distributed in a reasonably homogeneous manner throughout the soil (less than 10% of variation between samples). The LC50 of imidacloprid for the anecic species Aporrectodea nocturna and the endogeic species Allolobophora icterica was between 2 and 4 mg kg−1 dry soil. This result is consistent with previous findings obtained with other earthworm species and natural soils. When sublethal effects were examined, significant decreases in weight were observed at concentrations of 0.5 and 1 mg kg−1 dry soil for the two earthworm species whereas no effect was observed at a concentration of 0.1 mg kg−1 dry soil (NOEC value). These concentrations are close to 0.33 mg kg−1 which is the Predictive Environmental Concentration. Weight loss appears to be a valuable endpoint that can be used with worms freshly collected in the field as long as variability in the response of a control is taken into account.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrust KL, Peeler HB (2002) Effects of formulation on the run-off of imidacloprid from turf. Pestic Manage Sci 58:702–706
Bai D, Lummis SCR, Leicht V, Breer H, Satelle BD (1991) Actions of imidacloprid and a related nitromethylene on cholinergic receptors of an identified insect motor neurone. Pestic Sci 33:197–204
Bauer C, Römbke J (1997) Factors influencing the toxicity of two pesticides on three lumbricid species in laboratory tests. Soil Biol Biochem 29:705–708
Bembridge JD (1998) Recommendations from the second international workshop on earthworm ecotoxicology, Amsterdam, Netherlands (April 1997). In: Sheppard SC, Bembridge JD, Holmstrup M, Posthuma L (eds) Advances in earthworm ecotoxicology. SETAC, Pensacola, pp 389–398
Bouché MB (1977) Stratégies lombriciennes. Ecol Bull 25:122–132
Bouché MB (1992) Earthworm species and ecotoxicological studies. In: Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (eds) Ecotoxicology of earthworms. Intercept, Andover, pp 20–35
Capowiez Y (2000) Difference in burrowing behaviour and spatial interaction between the two earthworm species Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora chlorotica. Biol Fertil Soils 30:341–346
Capowiez Y, Belzunces L (2001) Dynamic study of the burrowing behaviour of Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora chlorotica: interactions between earthworms and spatial avoidance of burrows. Biol Fertil Soils 33:310–316
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Mazzia C, Belzunces L (2003) Earthworm behaviour as a biomarker: a study case with imidacloprid. Pedobiologia 47:542–547
Capri E, Camisa MG, Flores-Céspedes F, Glass CR, Gonzalez-Pradas E, Trevisan M (2001) Imidacloprid and pyrimethanil soil sorption. Agronomie 21:57–64
Cox C (2001) Insecticide factsheet: imidacloprid. J Pestic Reform 21:15–21
Cox L, Koskinen WC, Yen PY (1997) Sorption-desorption of imidacloprid and its metabolites in soils. J Agric Food Chem 45:1468–1472
Dalby PR, Baker GH, Smith E (1996) “Filter paper method” to remove soil from earthworm intestines and to standardize the water content of earthworm tissue. Soil Biol Biochem 28:685–687
EEC (1984) Directive 79/931 annex V, part C: methods for the determination of ecotoxicity—level 1, earthworms—artificial soil. Commission of the European Communities, DG, X1/128/82. Rev. 5. EEC, Brussels
EEC (2003) SANCO/10329. Guidance document on terrestrial ecotoxicology. Under Council Directive 91/414/EEC. Rev 2. EEC, Brussels
Edwards PJ, Coulson JM (1992) Choice of earthworm species for laboratory tests. In: Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (eds) Ecotoxicology of earthworms. Intercept, Andover, pp 36–43
Gupta S, Gajbhiye VT, Kalpana, Agnihotri NP (2002) Leaching behavior of imidacloprid formulations in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:502–508
Hans RK, Gupta SC, Beg U (1990) Toxicity assessment of four insecticides to earthworm, Pheretima posthuma. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:358–364
Idinger J (2002) Laboratory studies to detect effects of selected plant protection products on Folsomia candida (Collembola: Isotomidae). Z Pflanzenkr Pflanzenschutz 109:512–529
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386
Kula C (1998) Endpoints in laboratory testing with earthworms: experience with regard to regulatory decisions for plant protection products. In: Sheppard SC, Bembridge JD, Holmstrup M, Posthuma L (eds) Advances in earthworm ecotoxicology. SETAC, Pensacola, pp 3–14
Lal OP, Palta RK, Srivastava YNS (2001) Impact of imidacloprid and carbofuran on earthworm castings in Okra field. Ann Plant Prot Sci 9:137–138
Lavelle P (1997) Faunal activities and soil processes: adaptative strategies that determine ecosystem function. Adv Ecol Res 27:93–132
Leland JE, Mullins DE, Berry DF (2001) Evaluating environmental hazards of land applying composted diazinon using earthworm bioassays. J Environ Sci Health B 36:821–834
Luo Y, Zang Y, Zhong Y, Kong Z (1999) Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere 39:2347–2356
Ma Y, Dickinson NM, Wong MH (2002) Toxicity of Pb/Zn mine tailings to the earthworm Pheretima and the effects of burrowing on metal availability. Biol Fertil Soils 36:79–86
McIndoe EC, Bembridge JD, Martin P (1998) Improving the accuracy and precision of earthworm laboratory experiments though the use of pretreatment measurements. In: Sheppard SC, Bembridge JD, Holmstrup M, Posthuma L (eds) Advances in earthworm ecotoxicology. SETAC, Pensacola, pp 27–34
Mostert MA, Schoeman AS, van der Merwe M (2000) The toxicity of five insecticides to earthworms of the Pheretima group, using an artificial soil test. Pest Manage Sci 56:1093–1097
Mostert MA, Schoeman AS, van der Merwe M (2002) The relative toxicity of insecticides to earthworms of the Pheretima group (Oligochaeta). Pest Manage Sci 58:446–450
Ndongo B, Leroux GD, Fortin J (2000) Transport de linuron, de l’imidaclopride et du bromure au travers de colonnes de sol et de lysimètres drainants. Biotechnol Agron Soc Environ 4:33–40
Nemeth-Konda L, Füleky G, Morovjan G, Csokan P (2002) Sorption behaviour of acetochlor, atrazine, carbendazim, diazinon, imidacloprid and isoproturon on Hungarian agricultural soil. Chemosphere 48:545–552
Northcott GL, Jones KC (2000a) Developing a standard spiking procedure for the introduction of hydrophobic organic compounds into field-wet soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2409–2417
Northcott GL, Jones KC (2000b) Spiking hydrophobic organic compounds into soil and sediment: a review and critique of adopted procedures. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2418–2430
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals. Test 207: earthworm acute toxicity tests. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Oi M (1999) Time-dependent sorption of imidacloprid in two different soils. J Agric Food Chem 47:327–332
Oliveira RS, Koskinen WC, Werdin NR, Yen PY (2000) Sorption of imidacloprid and its metabolites on tropical soils. J Environ Sci Health B 35:39–49
Paoletti MG (1999) The role of earthworms for assessment of sustainability and as bioindicators. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:137–155
Quillin KJ (1999) Kinematic scaling of locomotion by hydrostatic animals: ontogeny of peristaltic crawling by the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. J Exp Biol 202:661–674
Raymond M, Prato G, Ratsira D (1993) PROBIT CNRS-UMII. License L93019. Praxem, 34680 St Georges d’Orques, France
Ribera D, Saint Denis M (1999) Le ver Eisenia foetida: intérêts et perspectives en écotoxicologie terrestre. Bull Soc Zool Fr 124:411–420
Rouchaud J, Thirion A, Wauters A, van der Steene F, Benoit F, Ceustermans N, Gillet J, Marchand S (1996) Effects of fertilizer on insecticides adsorption and biodegradation in crop soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:98–106
Sarkar MA, Roy S, Kole RK, Chowdhury A (2001) Persistence and metabolism of imidacloprid in different soils of West Bengal. Pest Manage Sci 57:598–602
Sheppard SC, Evende WG (1992) Optimized design for earthworm survival tests in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 49:648–655
Skillings JH, Mack GA (1981) On the use of a Friedman-type statistic in balanced and unbalanced block designs. Technometrics 23:171–177
Spurgeon DJ, Weeks JM (1998) Evaluation of factors influencing results from laboratory toxicity tests with earthworms. In: Sheppard SC, Bembridge JD, Holmstrup M, Posthuma L (eds) Advances in earthworm ecotoxicology. SETAC, Pensacola, pp 15–25
Tomlin AD (1992) Behaviour as a source of earthworm susceptibility to ecotoxicants. In: Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (eds) Ecotoxicology of earthworms. Intercept, Andover, pp 116–125
Tu CM (1995) Effect of five insecticides on microbial and enzymatic activities in sandy soil. Z Pflanzenkr Pflanzenschutz 30:289–306
Venkateswara Rao J, Surya Pavan Y, Madhavendra SS (2003a) Toxic effects of chlorpyrifos on morphology and acetylcholinesterase activity in the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 54:296–301
Venkateswara Rao J, Kavitha P, Padmanabha Rao A (2003b) Comparative toxicity of tetra ethyl lead and lead oxide to earthworms, Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Environ Res 92:271–276
Vermeulen LA, Reinecke AJ, Reinecke SA (2001) Evaluation of the fungicide manganese-zinc ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) (Mancozeb) for sublethal and acute toxicity to Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 48:183–189
Zang Y, Zhong Y, Luo Y, Kong ZM (2000) Genotoxicity of two novel pesticides for the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. Environ Pollut 108:271–278
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Zwahlen C, Hilbeck A, Howald R, Nentwig W (2003) Effects of transgenic Bt corn litter on the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Mol Ecol 12:1077–1086
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Leigh Gebbie for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capowiez, Y., Rault, M., Costagliola, G. et al. Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora icterica). Biol Fertil Soils 41, 135–143 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0829-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0829-0