Abstract
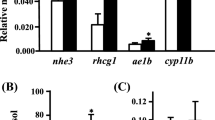
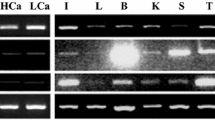
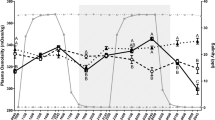
This study investigated endocrine control of branchial ionoregulatory function in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by prolactin (Prl188 and Prl177), growth hormone (Gh) and cortisol. Branchial expression of Na+/Cl− cotransporter (ncc) and Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter (nkcc) genes were employed as specific markers for freshwater- and seawater-type ionocytes, respectively. We further investigated whether Prl, Gh and cortisol direct expression of two Na+, K+-ATPase (nka)-α1 subunit genes, denoted nka-α1a and nka-α1b. Tilapia transferred to fresh water following hypophysectomy failed to adequately activate gill ncc expression; ncc expression was subsequently restored by Prl replacement. Prl188 and Prl177 stimulated ncc expression in cultured gill filaments in a concentration-related manner, suggesting that ncc is regulated by Prl in a gill-autonomous fashion. Tilapia transferred to brackish water (23 ‰) following hypophysectomy exhibited a reduced capacity to up-regulate nka-α1b expression. However, Gh and cortisol failed to affect nka-α1b expression in vivo. Similarly, we found no clear effects of Gh or cortisol on nkcc expression both in vivo and in vitro. When considered with patterns previously described in euryhaline Mozambique tilapia (O. mossambicus), the current study suggests that ncc is a conserved target of Prl in tilapiine cichlids. In addition, we revealed contrasting dependencies upon the pituitary to direct nka-α1b expression in hyperosmotic environments between Nile and Mozambique tilapia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auperin B, Rentier-Delrue F, Martial JA, Prunet P (1994) Evidence that two (Oreochromis niloticus) prolactins have different osmoregulatory functions during adaptation to a hyperosmotic environment. J Mol Endocrinol 12:13–24
Auperin B, Leguen I, Rentier-Delrue F, Smal J, Prunet P (1995) Absence of a tiGH effect on adaptability to brackish water in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 97:145–159
Borski RJ, Hansen MU, Nishioka RS, Grau EG (1992) Differential processing of the two prolactins of the tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus), in relation to environmental salinity. J Exp Zool 264:46–54
Breves JP, Fox BK, Pierce AL, Hirano T, Grau EG (2010a) Gene expression of growth hormone family and glucocorticoid receptors, osmosensors, and ion transporters in the gill during seawater acclimation of Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. J Exp Zool 313:432–441
Breves JP, Hasegawa S, Yoshioka M, Fox BK, Davis LK, Lerner DT, Takei Y, Hirano T, Grau EG (2010b) Acute salinity challenges in Mozambique and Nile tilapia: differential responses of plasma prolactin, growth hormone and branchial expression of ion transporters. Gen Comp Endocrinol 167:135–142
Breves JP, Hirano T, Grau EG (2010c) Ionoregulatory and endocrine responses to disturbed salt and water balance in Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) exposed to confinement and handling stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A 155:294–300
Breves JP, Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Hirano T, Grau EG (2010d) Prolactin restores branchial mitochondrion-rich cells expressing Na+/Cl− cotransporter in hypophysectomized Mozambique tilapia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299:R702–R710
Breves JP, Serizier SB, Goffin V, McCormick SD, Karlstrom RO (2013) Prolactin regulates transcription of the ion uptake Na+/Cl− cotransporter (ncc) gene in zebrafish gill. Mol Cell Endo 369:98–106
Breves JP, McCormick SD, Karlstrom RO (2014) Prolactin and teleost ionocytes: new insights into cellular and molecular targets of prolactin in vertebrate epithelia. Gen Comp Endocrinol. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.12.014
Bystriansky JS, Richards JG, Schulte PM, Ballantyne JS (2006) Reciprocal expression of gill Na+/K+-ATPase α-subunit isoforms α1a and α1b during seawater acclimation of three salmonid fishes that vary in their salinity tolerance. J Exp Biol 209:1848–1858
Bystriansky JS, Frick NT, Richards JG, Schulte PM, Ballantyne JS (2007) Failure to up-regulate gill Na+, K+-ATPase α-subunit isoform α1b may limit seawater tolerance of land-locked Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus). Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:332–338
Dean DB, Whitlow ZW, Borski RJ (2003) Glucocorticoid receptor upregulation during seawater adaptation in a euryhaline teleost, the tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 132:112–118
Dharmamba M, Maetz J (1972) Effects of hypophysectomy and prolactin on the sodium balance of Tilapia mossambica in fresh water. Gen Comp Endocrinol 19:175–183
Evans DH (2011) Freshwater fish gill ion transport: August Krogh to morpholinos and microprobes. Acta Physiol 202:349–359
Fiol DF, Kültz D (2007) Osmotic stress sensing and signaling in fishes. FEBS J 274:5790–5798
Fiol DF, Sanmarti E, Sacchi R, Kültz D (2009) A novel tilapia prolactin receptor is functionally distinct from its paralog. J Exp Biol 212:2007–2015
Herndon TM, McCormick SD, Bern HA (1991) Effects of prolactin on chloride cells in opercular membrane of seawater-adapted tilapia. Gen Comp Endocrinol 83:283–289
Hirano T (1986) The spectrum of prolactin action in teleosts. Prog Clin Biol Res 205:53–74
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Resp Physiol Neurobiol 184:257–268
Hiroi J, Yasumasu S, McCormick SD, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2008) Evidence for an apical Na-Cl cotransporter involved in ion uptake in a teleost fish. J Exp Biol 211:2584–2599
Horng JL, Hwang PP, Shih TH, Wen ZH, Lin CS, Lin LY (2009) Chloride transport in mitochondrion-rich cells of euryhaline tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) larvae. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:C845–C854
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S, Lee KM, Kaneko T (2008) Gene expression and morphological localization of NHE3, NCC and NKCC1a in branchial mitochondria-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) acclimated to a wide range of salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol A 151:151–158
Kaneko T, Watanabe S, Lee KM (2008) Functional morphology of mitochondrion-rich cells in euryhaline and stenohaline teleosts. Aqua-BioSci Monogr 1:1–62
Kiilerich P, Kristiansen K, Madsen SS (2007) Cortisol regulation of ion transporter mRNA in Atlantic salmon gill and the effect of salinity on the signaling pathway. J Endocrinol 194:417–427
Kültz D, Bastrop R, Jurss K, Siebers D (1992) Mitrochondrial-rich (MR) cells and the activities of the Na+/K+-ATPase and carbonic anhydrase in the gill and opercular epithelium of Oreochromis mossambicus adapted to various salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol B 102:293–301
Madsen SS, Kiilerich P, Tipsmark CK (2009) Multiplicity of expression of Na+, K+–ATPase α-subunit isoforms in the gill of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): cellular localisation and absolute quantification in response to salinity change. J Exp Biol 212:78–88
Mancera JM, McCormick SD (1998) Osmoregulatory actions of the GH/IGF-I axis in non-salmonid teleosts. Comp Biochem Physiol B 121:43–48
McCormick SD (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in teleost fish. Am Zool 41:781–794
McCormick SD, Bern HA (1989) In vitro stimulation of Na+-K+-ATPase activity and ouabain binding by cortisol in coho salmon gill. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 256:707–715
McCormick SD, Regish AM, Christensen AK (2009) Distinct freshwater and seawater isoforms of Na+/K+-ATPase in gill chloride cells of Atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol 212:3994–4001
Moriyama S, Oda M, Yamazaki T, Yamaguchi K, Amiya N, Takahashi A, Amano M, Goto T, Nozaki M, Meguro H, Kawauchi H (2008) Gene structure and functional characterization of growth hormone in dogfish, Squalus acanthias. Zool Sci 25:604–613
Nilsen TO, Ebbesson LOE, Madsen SS, McCormick SD, Andersson E, Björnsson BT, Prunet P, Stefansson SO (2007) Differential expression of gill Na+, K+-ATPase α- and β-subunits, Na+, K+, 2Cl- cotransporter and CFTR anion channel in juvenile anadromous and landlocked Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. J Exp Biol 210:2885–2896
Nishioka RS (1994) Hypophysectomy of fish. In: Hochachka PW, Mommsen TP (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes: analytical techniques. Elsevier, New York, pp 49–58
Pelis RM, McCormick SD (2001) Effects of growth hormone and cortisol on Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter localization and abundance in the gills of Atlantic salmon. Gen Comp Endocrinol 124:134–143
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucl Acids Res 29(9):e45
Pierce AL, Fox BK, Davis LK, Visitacion N, Kitashashi T, Hirano T, Grau EG (2007) Prolactin receptor, growth hormone receptor, and putative somatolactin receptor in Mozambique tilapia: tissue specific expression and differential regulation by salinity and fasting. Gen Comp Endocrinol 154:31–40
Pisam M, Auperin B, Prunet P, Rentier-Delrue F, Martial J, Rambourg A (1993) Effects of prolactin on alpha and beta chloride cells in the gill epithelium of the saltwater adapted tilapia “Oreochromis niloticus”. Anat Rec 235:275–284
Rentier-Delrue F, Swennen D, Philippart JC, L’Hoir C, Lion M, Benrubi O, Martial JA (1989a) Tilapia growth hormone: molecular cloning of cDNA and expression in Escherichia coli. DNA 8:271–278
Rentier-Delrue F, Swennen D, Prunet P, Lion M, Martial JA (1989b) Tilapia prolactin: molecular cloning of two cDNAs and expression in Escherichia coli. DNA 8:261–270
Richards JG, Semple JW, Bystriansky JS, Schulte PM (2003) Na+/K+-ATPase α-isoform switching in gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during salinity transfer. J Exp Biol 206:4475–4486
Sakamoto T, McCormick SD, Hirano T (1993) Osmoregulatory actions of growth hormone and its mode of action in salmonids: a review. Fish Physiol Biochem 11:155–164
Sakamoto T, Shepherd BS, Madsen SS, Nishioka RS, Siharath K, Richman NH, Bern HA, Grau EG (1997) Osmoregulatory actions of growth hormone and prolactin in an advanced teleost. Gen Comp Endocrinol 106:95–101
Sandra O, Sohm F, de Luze A, Prunet P, Edery M, Kelly PA (1995) Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a fish prolactin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6037–6041
Seale AP, Riley LG, Leedom TA, Kajimura S, Dores RM, Hirano T, Grau EG (2002) Effects of environmental osmolality on release of prolactin, growth hormone and ACTH from the tilapia pituitary. Gen Comp Endocrinol 128:91–101
Seale AP, Watanabe S, Grau EG (2012a) Osmoreception: perspectives on signal transduction and environmental modulation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 176:354–360
Seale AP, Moorman BP, Stagg JJ, Breves JP, Lerner DT, Grau EG (2012b) Prolactin 177, prolactin 188 and prolactin receptor 2 in the pituitary of the euryhaline tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, are differentially osmosensitive. J Endocrinol 213:89–98
Specker JL, King DS, Nishioka RS, Shirahata K, Yamaguchi K, Bern HA (1985) Isolation and partial characterization of a pair of prolactins released in vitro by the pituitary of cichlid fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7490–7494
Stickney RR (1986) Tilapia tolerance of saline waters: a review. Prog Fish Cult 48:161–167
Tipsmark CK, Madsen SS (2009) Distinct hormonal regulation of Na+, K+-atpase genes in the gill of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J Endocrinol 203:301–310
Tipsmark CK, Breves JP, Seale AP, Lerner DT, Hirano T, Grau EG (2011) Switching of Na+, K+-ATPase isoforms by salinity and prolactin in the gill of a cichlid fish. J Endocrinol 209:237–244
Trewavas E (1983) Tilapiine fishes of the Genera Sarotherodon, Oreochromis and Danakilia. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca, p 583
Uchida K, Kaneko T, Miyazaki H, Hasegawa S, Hirano T (2000) Excellent salinity tolerance of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus): elevated chloride cell activity in the branchial and opercular epithelia of the fish adapted to concentrated seawater. Zool Sci 17:149–160
Uchida K, Moriyama S, Breves JP, Fox BK, Pierce AP, Borski RJ, Hirano T, Grau EG (2009) cDNA cloning and isolation of somatolactin in Mozambique tilapia and effects of seawater acclimation, confinement stress, and fasting on its pituitary expression. Gen Comp Endocrinol 161:162–170
Watanabe WO, Kuo CM, Huang MC (1985) Salinity tolerance of Nile tilapia fry (Oreochromis niloticus), spawned at various salinities. Aquaculture 48:159–176
Weng CF, Lee TH, Hwang PP (1997) Immune localization of prolactin receptor in the mitochondria-rich cells of the euryhaline teleost (Oreochromis mossambicus) gill. FEBS Lett 405:91–94
Whitehead A, Roach JL, Zhang S, Galvez F (2011) Genomic mechanisms of evolved physiological plasticity in killifish distributed along an environmental salinity gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:6193–6198
Yada T, Hirano T, Grau EG (1994) Changes in plasma levels of the two prolactins and growth hormone during adaptation to different salinities in the euryhaline tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 93:214–223
Yamaguchi K, Specker JL, King DS, Yokoo Y, Nishioka RS, Hirano T, Bern HA (1988) Complete amino acid sequences of a pair of fish (tilapia) prolactins, tPRL177 and tPRL188. J Biol Chem 263:9113–9121
Yamaguchi K, King DS, Specker JL, Nishioka RS, Hirano T, Bern HA (1991) Amino acid sequence of growth hormone isolated from medium of incubated pituitary glands of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 81:323–331
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the encouragement and guidance provided by Prof. Tetsuya Hirano during the course of this study. We also thank Mr. Matt Barton, Mr. Jacob Stagg, and Ms. Elly Breves for laboratory assistance. This work was supported by NSF (IOS-1119693; E.G.G.), USDA (2008-35206-18785 and -18787; E.G.G. and D.T.L.), the Binational Agricultural Research Development (BARD) fund (IS-4296-10) and the Edwin W. Pauley Summer Program in Marine Biology (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breves, J.P., Seale, A.P., Moorman, B.P. et al. Pituitary control of branchial NCC, NKCC and Na+, K+-ATPase α-subunit gene expression in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus . J Comp Physiol B 184, 513–523 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-014-0817-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-014-0817-0