Abstract
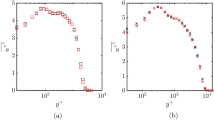
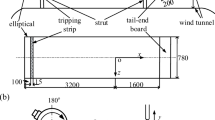
Experiments were carried out to study the effects of imperfect spatial resolution on turbulence measurements in the very near-wall region using hot wires of different lengths, l + (in wall units). Previous works have indicated that the distributions of the longitudinal velocity rms value, skewness and flatness factors are independent of l + in the buffer region and beyond provided l +<20–25. Our results obtained using l +=3, 6, and 22 in the viscous sublayer region show that generally the said distributions are dependent on l + and attentuate in magnitude with increasing l +. Further experiments were also carried out at different Reynolds numbers (Re c , based on centerline velocity and channel’s height) but with measurements made using hot wire of the same l +. The latter shows that the rms value and other higher order moments of longitudinal velocity fluctuations are independent of Re c , thereby extending similar findings by Johansson and Alfredsson (1983), valid in the buffer region into the viscous sublayer region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 January 1996 / Accepted: 10 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoo, B., Chew, Y. & Li, G. Effects of imperfect spatial resolution on turbulence measurements in the very near-wall viscous sublayer region. Experiments in Fluids 22, 327–335 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050055
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050055