Abstract
Introduction and objectives
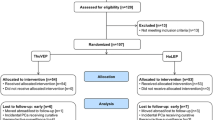
To compare the perioperative outcomes of thulium vapoenucleation of the prostate (ThuVEP) with holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) for patients with symptomatic benign prostatic obstruction (BPO).
Methods
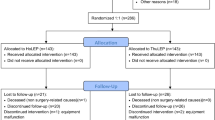
Forty-eight and 46 patients were prospectively randomized to ThuVEP and HoLEP. All patients were assessed preoperatively and 4-week postoperatively. The complications were noted and classified according to the modified Clavien classification system. Patient data were expressed as median (interquartile range) or numbers (%).
Results
Median age at surgery was 73 (67–76) years and median prostate volume was 80 (46.75–100) cc and not different between the groups (p = 0.207). The median operative time was 60 (41–79) minutes without significant differences between both groups (p = 0.275). There were no significant differences between the groups regarding catheterization time [2 (2–2) days, p = 0.966] and postoperative stay [2 (2–3) days, p = 0.80]). Clavien 1 (13.8%), Clavien 2 (3.2%), Clavien 3a (2.1%), and Clavien 3b (4.3%) complications occurred without significant differences between the groups. However, the occurrence of acute postoperative urinary retention was higher after HoLEP compared to ThuVEP (15.2 vs. 2.1%, p ≤ 0.022). At 1-month follow-up, peak urinary flow rates (10.7 vs. 22 ml/s), post-void residual volumes (100 vs. 20 ml), International Prostate Symptom Score (20 vs. 10) and Quality of Life (4 vs. 3) had improved significantly (p ≤ 0.005) without significant differences between the groups.
Conclusions
ThuVEP and HoLEP are safe and effective procedures for the treatment of symptomatic BPO. Both procedures give equivalent and satisfactory immediate micturition improvement with low perioperative morbidity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gratzke C, Schlenker B, Seitz M, Karl A, Hermanek P, Lack N, Stief CG, Reich O (2007) Complications and early postoperative outcome after open prostatectomy in patients with benign prostatic enlargement: results of a prospective multicenter study. J Urol 177:1419–1422
Reich O, Gratzke C, Bachmann A, Seitz M, Schlenker B, Hermanek P, Lack N, Stief CG, Urology Section of the Bavarian Working Group for Quality Assurance (2008) Morbidity, mortality and early outcome of transurethral resection of the prostate: a prospective multicenter evaluation of 10,654 patients. J Urol 180:246–249
Fraundorfer MR, Gilling PJ (1998) Holmium:YAG laser enucleation of the prostate combined with mechanical morcellation: preliminary results. Eur Urol 33:69–72
Ahyai SA, Gilling P, Kaplan SA, Kuntz RM, Madersbacher S, Montorsi F, Speakman MJ, Stief CG (2010) Meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic enlargement. Eur Urol 58:384–397
Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A, de la Rosette J, Gilling P, Gratzke C, McVary K, Novara G, Woo H, Madersbacher S (2015) A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic obstruction: an update. Eur Urol 67:1066–1096
Gilling PJ (2013) Laser enucleation is increasingly becoming the standard of care for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia of all sizes. Eur Urol 63:868–869
Bach T, Wendt-Nordahl G, Michel MS, Herrmann TRW, Gross AJ (2009) Feasibility and efficacy of Thulium:YAG laser enucleation (VapoEnucleation) of the prostate. World J Urol 27:541–545
Netsch C, Engbert A, Bach T, Gross AJ (2014) Long-term outcome following Thulium VapoEnucleation of the prostate. World J Urol 32:1551–1558
Bach T, Netsch C, Pohlmann L, Herrmann TR, Gross AJ (2011) Thulium:YAG vapoenucleation in large volume prostates. J Urol 186:2323–2327
Gross AJ, Netsch C, Knipper S, Hölzel J, Bach T (2013) Complications and early postoperative outcome in 1080 patients after thulium vapoenucleation of the prostate: results at a single institution. Eur Urol 63:859–867
Gilling P (2008) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP). BJU Int. 101:131–142
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Mamoulakis C, Efthimiou I, Kazoulis S, Christoulakis I, Sofras F (2011) The modified Clavien classification system: a standardised platform for reporting complications in transurethral resection of the prostate. World J Urol 29:205–210
Gravas S, Bach T, Bachmann A, Drake M, Gacci M, Gratzke C, Madersbacher S, Mamoulakis S, Tikkinen KAO (2016) Guidelines on the management of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), incl. benign prostatic obstruction (BPO) EAU; http://uroweb.org/guideline/treatment-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts/. Accessed Mar 2016
Neill MG, Gilling PJ, Kennett KM, Frampton CM, Westenberg AM, Fraundorfer MR, Wilson LC (2006) Randomized trial comparing holmium laser enucleation of prostate with plasmakinetic enucleation of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 68:1020–1024
Zhu L, Chen S, Yang S, Wu M, Ge R, Wu W, Liao L, Tan J (2013) Electrosurgical enucleation versus bipolar transurethral resection for prostates larger than 70 ml: a prospective, randomized trial with 5-year followup. J Urol 189:1427–1431
Rao JM, Yang JR, Ren YX, He J, Ding P, Yang JH (2013) Plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate versus transvesical open prostatectomy for benign prostatic hyperplasia >80 mL: 12-month follow-up results of a randomized clinical trial. Urology 82:176–181
Geavlete B, Stanescu F, Iacoboaie C, Geavlete P (2013) Bipolar plasma enucleation of the prostate vs open prostatectomy in large benign prostatic hyperplasia cases—a medium term, prospective, randomized comparison. BJU Int 111:793–803
Ou R, Deng X, Yang W, Wei X, Chen H, Xie K (2013) Transurethral enucleation and resection of the prostate vs transvesical prostatectomy for prostate volumes >80 mL: a prospective randomized study. BJU Int 112:239–245
Chen S, Zhu L, Cai J, Zheng Z, Ge R, Wu M, Deng Z, Zhou H, Yang S, Wu W, Liao L, Tan J (2014) Plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate compared with open prostatectomy for prostates larger than 100 grams: a randomized noninferiority controlled trial with long-term results at 6 years. Eur Urol 66:284–291
Geavlete B, Bulai C, Ene C, Checherita I, Geavlete P (2015) Bipolar vaporization, resection, and enucleation versus open prostatectomy: optimal treatment alternatives in large prostate cases? J Endourol 29:323–331
Wu G, Hong Z, Li C, Bian C, Huang S, Wu D (2016) A comparative study of diode laser and plasmakinetic in transurethral enucleation of the prostate for treating large volume benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized clinical trial with 12-month follow-up. Lasers Med Sci 31:599–604
Elshal AM, Elkoushy MA, El-Nahas AR, Shoma AM, Nabeeh A, Carrier S, Elhilali MM (2015) GreenLightTM laser (XPS) photoselective vapo-enucleation versus holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized controlled study. J Urol 193:927–934
Zhang F, Shao Q, Herrmann TR, Tian Y, Zhang Y (2012) Thulium laser versus holmium laser transurethral enucleation of the prostate: 18-month follow-up data of a single center. Urology 79:869–874
Yang Z, Wang X, Liu T (2013) Thulium laser enucleation versus plasmakinetic resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial with 18-month follow-up. Urology 81:396–400
Lusuardi L, Myatt A, Sieberer M, Jeschke S, Zimmermann R, Janetschek G (2011) Safety and efficacy of eraser laser enucleation of the prostate: preliminary report. J Urol 186:1967–1971
Xu A, Zou Y, Li B, Liu C, Zheng S, Li H, Xu Y, Chen B, Xu K, Shen H (2013) A randomized trial comparing diode laser enucleation of the prostate with plasmakinetic enucleation and resection of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Endourol 27:1254–1260
El Tayeb MM, Jacob JM, Bhojani N, Bammerlin E, Lingeman JE (2016) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate in patients requiring anticoagulation. J Endourol 30:805–809
Netsch C, Stoehrer M, Brüning M, Gabuev A, Bach T, Herrmann TR, Gross AJ (2014) Safety and effectiveness of Thulium VapoEnucleation of the prostate (ThuVEP) in patients on anticoagulant therapy. World J Urol 32:165–172
Bach T, Xia SJ, Yang Y, Mattioli S, Watson GM, Gross AJ, Herrmann TR (2010) Thulium: YAG 2 mum cw laser prostatectomy: where do we stand? World J Urol 28:163–168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CN: Project development, data collection, manuscript writing, data analysis and interpretation. BB: Data collection and manuscript writing. CT: Data collection. CM: Data collection. AVB: Data collection. TRWH: Manuscript writing, data analysis and interpretation. AJG: Project development, manuscript writing, data analysis and interpretation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
All patients were treated after obtaining informed consent, following institutional review board approval.
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Netsch, C., Becker, B., Tiburtius, C. et al. A prospective, randomized trial comparing thulium vapoenucleation with holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic obstruction: perioperative safety and efficacy. World J Urol 35, 1913–1921 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2071-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2071-z