Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate for the first time the prognostic significance of female invasive patterns in stage pT4a urothelial carcinoma of the bladder in a large series of women undergoing anterior pelvic exenteration.
Patients and methods
Our series comprised of 92 female patients in total of whom 87 with known invasion patterns were eligible for final analysis. Median follow-up for evaluation of cancer-specific mortality (CSM) was 38 months (interquartile ranges, 21–82 months). The impact on CSM was evaluated using multivariable Cox proportional-hazards regression analysis; predictive accuracy (PA) was assessed by receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Results
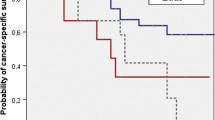
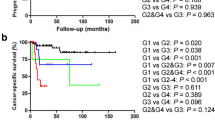
Vaginal invasion was noted in 33 patients (37.9 %; group VAG), uterine invasion in 20 patients (23 %; group UT), and infiltration of both vagina and uterus in 34 patients (39.1 %; group VAG + UT). Groups VAG and UT significantly differed from group VAG + UT with regard to the presence of positive soft tissue margins (STM) only. Five-year-cancer-specific survival probabilities in the groups VAG, UT, and VAG + UT were 21, 20, and 21 %, respectively (p = 0.955). On multivariable analysis, only STM status (HR = 2.02, p = 0.023) independently influenced CSM. C-indices of multivariable models for CSM with and without integration of invasive patterns were 0.570 and 0.567, respectively (PA gain 0.3 %, p = 0.526).
Conclusions
Infiltration of the vagina, the uterus or both is associated with poor 5-year survival rates. With regard to CSM, no difference was detectable between patients with different invasion patterns, thus justifying further collectively including these invasive patterns as stage pT4a.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC et al (2014) EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur Urol 65(4):778–792
Greene FL, Gospodarowicz M, Wittekend C et al (2009) American joint committee on cancer (AJCC) staging manual, 7th edn. Springer, Philadelphia
Novara G, Svatek RS, Karakiewicz PI et al (2010) Soft tissue surgical margin status is a powerful predictor of outcomes after radical cystectomy: a multicenter study of more than 4,400 patients. J Urol 183:2165–2170
Tilki D, Svatek RS, Karakiewicz PI et al (2010) Characteristics and outcomes of patients with pT4 urothelial carcinoma at radical cystectomy: a retrospective international study of 583 patients. J Urol 183:87–93
Liberman D, Alasker A, Sun M et al (2011) Radical cystectomy for patients with pT4 urothelial carcinoma in a large population-based study. BJU Int 107:905–911
Schemper M, Smith TL (1996) A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control Clin Trials 17(4):343–346
Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL, Mark DB (1996) Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med 15:361–387
Ali-El-Dein B, Abdel-Latif M, Mosbah A et al (2004) Secondary malignant involvement of gynecologic organs in radical cystectomy specimens in women: is it mandatory to remove these organs routinely? J Urol 172:885–887
Salem H, El-Mazny A (2011) A clinicopathologic study of gynecologic organ involvement at radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 115:188–190
Djaladat H, Bruins HM, Miranda G, Cai J, Skinner EC, Daneshmand S (2012) Reproductive organ involvement in female patients undergoing radical cystectomy for urothelial bladder cancer. J Urol 188(6):2134–2138
May M, Bastian PJ, Brookman-May S et al (2013) Gender-specific differences in cancer-specific survival after radical cystectomy for patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder in pathologic tumor stage T4a. Urol Oncol 31(7):1141–1147
Zehnder P, Studer UE, Skinner EC et al (2011) Super extended versus extended pelvic lymph node dissection in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a comparative study. J Urol 186:1261–1268
Burger M, Mulders P, Witjes W (2012) Use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer is low among major European centres: results of a Feasibility Questionnaire. Eur Urol 61(5):1070–1071
deVere White RW, Katz MH, Steinberg GD (2009) The case for neoadjuvant chemotherapy and cystectomy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Urol 181:1994–1997
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This study has been approved by the appropriate ethics committee and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Matthias May and Atiqullah Aziz have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
May, M., Aziz, A., Brookman-May, S. et al. Prognostic impact of infiltration of the vagina and/or uterus in women undergoing anterior pelvic exenteration for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: results of a contemporary multicentre series. World J Urol 33, 343–350 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1308-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1308-3