Abstract
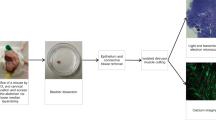
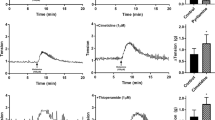
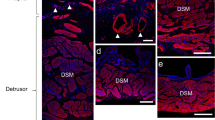
The potent inflammatory mediator histamine is released from activated mast cells in interstitial cystitis (IC). Here, we report on the histamine receptor subtypes involved in the intracellular calcium response of cultured smooth muscle cells (cSMC). Fura-2 was used to monitor the calcium response in cSMC, cultured from human detrusor biopsies. The distribution of histamine receptor subtypes was addressed by immunocytochemistry in situ and in vitro. Histamine stimulated a maximum of 92% of the cells (n=335), being more effective than carbachol (70%, n=920). HTMT (H1R-agonist), dimaprit (H2R) and MTH (H3R) lead to significant lower numbers of reacting cells (60, 48 and 54%). Histamine receptor immunoreactivity (H1R, H2R, H3R, H4R) was found in situ and in vitro. Histamine-induced calcium increase is mediated by distinct histamine receptors. Thus, pre-therapeutic evaluation of histamine receptor expression in IC patients may help to optimize therapy by using a patient-specific cocktail of subtype-specific histamine receptor antagonists.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkmann OA, Hertle L (2000) The pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis—many hypotheses, but etiology remains uncertain. Urologe A 39:520–526
Chiang G, Patra P, Letourneau R, Jeudy S, Boucher W, Green M, Sant GR, Theoharides TC (2000) Pentosanpolysulfate inhibits mast cell histamine secretion and intracellular calcium ion levels: an alternative explanation of its beneficial effect in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 164(6):2119–2125
Dasgupta P, Sharma SD, Womack C, Blackford HN, Dennis P (2001) Cimetidine in painful bladder syndrome: a histopathological study. Brit J Urol Int 88:183–186
Elbadawi A (1997) Interstitial cystitis: a critique of current concepts with a new proposal for pathologic diagnosis and pathogenesis. Urology 49(5A Suppl):14–40
El-Mansoury M, Boucher W, Sant GR, Theoharides TC (1994) Increased urine histamine and methylhistamine in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 152:350–353
Gomez-Viquez L, Guerrero-Serna G, Garcia U, Guerrero-Hernandez (2003) A SERCA pump optimizes Ca(2+) release by a mechanism independent of store filling in smooth muscle cells. Biophys J 85:370–380
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of calcium indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Pang X, Marchand J, Sant GR, Kream RM, Theoharides TC (1995) Increased number of substance P positive nerve fibres in interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 75:744–750
Patra PB, Westfall DP (1994) Potentiation of purinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig urinary bladder by histamine. J Urol 151:787–790
Peeker R, Aldenborg F, Dahlstrom A, Johansson SL, Li JY, Fall M (2000) Increased tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in bladder tissue from patients with classic and nonulcer interstitial cystitis. J Urol 163:1112–1115
Poli E, Coruzzi G, Bertaccini G (1988) Pre- and postjunctional effects of histamine on the guinea pig urinary bladder: evidence for heterogeneity in the H1-receptor population? Agents Actions 23:241–243
Rubinstein R, Nissenkorn I, Cohen S (1987) Acetylcholine mediation of the contractile response to histamine in human bladder detrusor muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 142:45–50
Sant GR, Theoharides TC (1994) The role of the mast cell in interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am 21:41–53
Thastrup O, Cullen PJ, Drøbak BK, Hanley MR, Dawson AP (1990) Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2466–2470
Theoharides TC (1994) Hydroxyzine in the treatment of interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am 21:113–119
Theoharides TC, Sant GR (1997) Hydroxyzine therapy for interstitial cystitis. Urology 49(5A Suppl):108–110
Theoharides TC, Kempuraj D, Sant GR (2001) Mast cell involvement in interstitial cystitis: a review of human and experimental evidence. Urology 57(6 Suppl 1):47–55
Thilgarajah R, Walker MW, Witherow RO’N (1998) Oral cimetidine for symptomatic relief in painful bladder syndrome; a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Urol 81 (Suppl 4):43
Wellendorph P, Goodman MW, Burstein ES, Nash NR, Brann MR, Weiner DM (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of functionally distinct isoforms of the human histamine H3 receptor. Neuropharmacology 42:929–940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuhaus, J., Weimann, A., Stolzenburg, JU. et al. Histamine receptors in human detrusor smooth muscle cells: physiological properties and immunohistochemical representation of subtypes. World J Urol 24, 202–209 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-006-0079-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-006-0079-x