Abstract
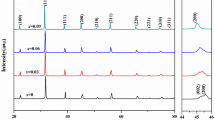
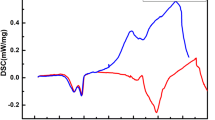
(1 − x)BaTiO3–xBiAlO3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics were prepared by the conventional sintering (CS) and the microwave sintering (MWS) methods, respectively. The microstructure, the dielectric properties, the relaxation characteristic, the ferroelectric and the energy storage properties were investigated in detail. The results show that a single perovskite phase exists in ceramic samples sintered by CS and MWS. The addition of BiAlO3 into BaTiO3 and the MWS method result in the reduction of the grain size and the porosity of BaTiO3 ceramic. This leads to the enhanced diffuse transition and frequency dispersion. The dielectric constant and loss decrease with increasing the BiAlO3 content, and the temperature and the frequency stabilities are enhanced by introducing BiAlO3 into BaTiO3. The remnant polarization (Pr) increases initially and then decreases with the increase of BiAlO3 content, the maximum values of Pr (9.5 μC/cm2 for CS and 7.27 μC/cm2 for MWS) are obtained at x = 0.02. The addition of BiAlO3 can elevate the variation of polarization ΔP (Pmax − Pr), its maximum values (12.56 μC/cm2 for CS ceramic and 12.2 μC/cm2 for MWS ceramic) are acquired at x = 0.04, 0.08, respectively. The energy storage properties indicate that the energy storage density (Wrec) increases, while the energy storage efficiency (η) firstly decreases and then increases with the increase of x.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Smolenskii, A.I. Agranovskaya, Dielectric polarization and losses of some complex compounds. Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 28, 1380–1382 (1958)
H. Ogihara, C.A. Randall, S.T. McKinstry, Weakly coupled relaxor behavior of BaTiO3–BiScO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 024112 (2007)
M. Wei, J. Zhang, M. Zhang, Z. Yao, H. Chen, C. Yang, Relaxor behavior of BaTiO3–BiYO3 perovskite materials for high energy density capacitors. Ceram. Int. 43, 4768–4774 (2017)
M. Liu, H. Hao, Y. Zhen, T. Wang, D. Zhou, H. Liu, M. Cao, Z. Yao, Temperature stability of dielectric properties for xBiAlO3–(1 − x) BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 2303–2311 (2015)
Z. Shen, X. Wang, B. Luo, L. Li, BaTiO3–BiYbO3 perovskite materials for energy storage applications. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 18146–18153 (2015)
M.A. Beuerlein, N. Kumara et al., Current understanding of structure-processing-property relationships in BaTiO3–Bi(M)O3 dielectrics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2849–2870 (2016)
N. Triamnak, R. Yimnirun, J. Pokorny, D.P. Cann, Relaxor characteristics of the phase transformation in (1 − x)BaTiO3–xBi(Zn1/2Ti1/2)O3 perovskite ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 3176–3182 (2013)
Y.D. Hou, L. Cui, S. Wang, C. Wang, M.K. Zhu, H. Yan, Progress in research on BiAlO3-based high temperature lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J. Inorg. Mater. 25, 225–229 (2010)
Y. Wang, Y. Pu, X. Li, H. Zheng, Structural evolution, relaxation behaviors and dielectric properties of BaTiO3–BiAlO3 perovskite solid solutions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 11565–11571 (2016)
G. Chen, X.D. Peng, C.L. Fu, W. Cai, R.L. Gao, P.G. Fan, X. Yi, H.Q. Yang, C. Ji, H.L. Yong, Effects of sintering method and BiFeO3 dopant on the dielectric and ferroelectric properties of BaTiO3–BiYbO3 based solid solution ceramics. Ceram. Int. 44, 16880–16889 (2018)
G. Chen, X.D. Peng, C.L. Fu, W. Cai, R.L. Gao, P.G. Fan, X.Y. Zhang, X. Yi, C. Ji, H.Q. Yang, H.L. Yong, Microstructure, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (1−x)BaTiO3–xBiYbO3 ceramics fabricated by conventional and microwave sintering methods. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 20017–20032 (2018)
C. Chen, H.R. Zhuang, X.N. Zhu, D. Zhang, K.C. Zhou, H.X. Yan, Effect of Ca substitution sites on dielectric properties and relaxor behavior of Ca doped barium strontium titanate ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 2486–2492 (2015)
Y. Wang, Y. Pu, X. Li, H. Zheng, Structural evolution, relaxation behaviors and dielectric properties of BaTiO3–BiAlO3 perovskite solid solutions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 1–7 (2016)
Z. Song, H. Liu, S. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Shi, H. Hao, M. Cao, Z. Yao, Z. Yu, Effect of grain size on the energy storage properties of (Ba0.4Sr0.6)TiO3 paraelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 1209–1217 (2014)
H.C. Yu, Z.G. Ye, Dielectric properties and relaxor behavior of a new (1 − x)BaTiO3–xBiAlO3 solid solution. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 034114 (2008)
S. Mahajan, O.P. Thakur, D.K. Bhattacharya, K. Sreenivas, A comparative study of Ba0.95Ca0.05Zr0.25Ti0.75O3 relaxor ceramics prepared by conventional and microwave sintering techniques. Mater. Chem. Phys. 3, 858–862 (2008)
X.G. Tang, J. Wang, X.X. Wang, H.L.W. Chan, Effects of grain size on the dielectric properties and tunabilities of sol–gel derived Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 ceramics. Solid State Commun. 131, 163–168 (2004)
W. Cai, C.L. Fu, J.C. Gao, H.Q. Chen, Effects of grain size on domain structure and ferroelectric properties of barium zirconate titanate ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 480, 870–873 (2009)
W.L. Shu, J. Wang, T.Y. Zhang, Effect of grain boundary on the electromechanical response of ferroelectric polycrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 064108 (2012)
T. Wang, Y. Wang, H. Yang, Y. Lin, L. Kong, S. Gao, F. Wang, Structure, dielectric properties of low-temperature-sintering BaTiO3-based glass–ceramics for energy storage. J. Adv. Dielectr. 8, 1850041 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (cstc2016jcyjA0175, cstc2016jcyjA0349, cstc2018jcyjAX0416); the Leading Talents of Scientific and Technological Innovation in Chongqing (CSTCCXLJRC201919); the Excellent Talent Project in University of Chongqing (2017-35); the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Social Undertakings and People’s Livelihood Guarantee of Chongqing (cstc2017shmsA0192); the Program for Innovation Teams in University of Chongqing (CXTDX201601032) and the Scientific and Technological Research Young Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJQN201801509).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and the manuscript is approved by all authors and the institutes for publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Fan, T., Yang, H. et al. Effects of BiAlO3 dopant and sintering method on microstructure, dielectric relaxation characteristic and ferroelectric properties of BaTiO3-based ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 125, 433 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2729-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2729-z