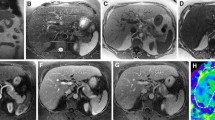
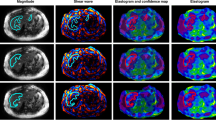
Abstract
Objectives
To compare the diagnostic performance and image quality of state-of-the-art 2D MR elastography (MRE) and 3D MRE in the basic application of liver fibrosis staging.
Methods
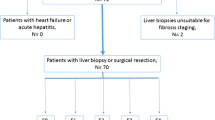
This retrospective study assessed data from 293 patients who underwent 2D and 3D MRE examinations. MRE image quality was assessed with a qualitative 2-point grading system by evaluating artifacts. Two experienced analysts independently measured mean liver stiffness values. The interobserver agreement of liver stiffness measurement was assessed by the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to assess the diagnostic performance of 2D and 3D MRE and blood-based markers for fibrosis staging using the pathology-proven liver fibrosis stage as the gold standard.
Results
The image quality provided by 3D MRE was graded as significantly higher than that obtained with the 2D MRE method (p < 0.01). Interobserver agreement in liver stiffness measurements was higher for 3D MRE (ICC: 3D 0.979 vs 2D 0.955). The AUC values for discriminating ≥ F1, ≥ F2, ≥ F3, and F4 fibrosis for 3D MRE (0.89, 0.92, 0.95, and 0.93) were similar to those for 2D MRE (0.89, 0.91, 0.94, and 0.92). Both the 2D and 3D MRE methods provided superior accuracy to the blood-based biomarkers, including APRI, FIB-4, and Forns index, especially for ≥ F2, ≥ F3, and F4 fibrosis stages (all p < 0.01).
Conclusions
While 3D MRE offers certain advantages and opportunities for new applications of MRE, current widely deployed 2D MRE technology has comparable performance in the basic application of detecting and staging liver fibrosis.
Key Points
• 2D MRE and 3D MRE have comparable diagnostic performance in detecting and staging liver fibrosis.
• 3D MRE has superior image quality and interobserver agreement compared to 2D MRE.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- APRI:
-
Aspartate transaminase-to-platelet ratio index
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- FIB-4:
-
Fibrosis index based on four factors
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- GRE:
-
Gradient recalled echo
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- MRE:
-
Magnetic resonance elastography
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- ROI:
-
Regions of interest
- SE-EPI:
-
Spin-echo echo-planar imaging
References
Castera L (2012) Noninvasive methods to assess liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology 142:1293–1302
Seeff LB, Everson GT, Morgan TR et al (2010) Complication rate of percutaneous liver biopsies among persons with advanced chronic liver disease in the HALT-C trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:877–883
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ et al (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97:2614–2618
Lefebvre T, Wartelle-Bladou C, Wong P et al (2019) Prospective comparison of transient, point shear wave, and magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis. Eur Radiol 29:6477–6488
Hoodeshenas S, Yin M, Venkatesh SK (2018) Magnetic resonance elastography of liver: current update. Top Magn Reson Imaging 27:319–333
Venkatesh SK, Yin M, Ehman RL (2013) Magnetic resonance elastography of liver: technique, analysis, and clinical applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 37:544–555
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ et al (2007) Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:1207–1213
Zhan C, Kannengiesser S, Chandarana H, Fenchel M, Ream J, Shanbhogue KP (2019) MR elastography of liver at 3 Tesla: comparison of gradient-recalled echo (GRE) and spin-echo (SE) echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequences and agreement across stiffness measurements. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44:1825–1833
Shi Y, Xia F, Li QJ et al (2016) Magnetic resonance elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis b and c by using both gradient-recalled echo and spin-echo echo planar imaging: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 111:823–833
Kim YS, Jang YN, Song JS (2018) Comparison of gradient-recalled echo and spin-echo echo-planar imaging MR elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 28:1709–1718
Chang W, Lee JM, Yoon JH et al (2016) Liver fibrosis staging with MR elastography: comparison of diagnostic performance between patients with chronic hepatitis b and those with other etiologic causes. Radiology 280:88–97
Wang J, Glaser KJ, Zhang T et al (2018) Assessment of advanced hepatic MR elastography methods for susceptibility artifact suppression in clinical patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 47:976–987
Wagner M, Corcuera-Solano I, Lo G et al (2017) Technical failure of MR elastography examinations of the liver: experience from a large Single-Center study. Radiology 284:401–412
Felker ER, Choi KS, Sung K et al (2018) Liver MR elastography at 3 T: agreement across pulse sequences and effect of liver R2* on image quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol 211:588–594
Wagner M, Besa C, Bou AJ et al (2016) Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver: qualitative and quantitative comparison of gradient echo and spin echo echoplanar imaging sequences. Invest Radiol 51:575–581
Mariappan YK, Dzyubak B, Glaser KJ et al (2017) Application of modified spin-echo-based sequences for hepatic MR elastography: evaluation, comparison with the conventional gradient-echo sequence, and preliminary clinical experience. Radiology 282:390–398
Choi SL, Lee ES, Ko A et al (2020) Technical success rates and reliability of spin-echo echo-planar imaging (SE-EPI) MR elastography in patients with chronic liver disease or liver cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 30:1730–1737
Kim DW, Kim SY, Yoon HM, Kim KW, Byun JH (2020) Comparison of technical failure of MR elastography for measuring liver stiffness between gradient-recalled echo and spin-echo echo-planar imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging 51:1086–1102
Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Ehman RL (2012) Review of MR elastography applications and recent developments. J Magn Reson Imaging 36:757–774
Allen AM, Shah VH, Therneau TM et al (2020) The role of three-dimensional magnetic resonance elastography in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Hepatology 71:510–521
Wang J, Shan Q, Liu Y et al (2019) 3D MR elastography of hepatocellular carcinomas as a potential biomarker for predicting tumor recurrence. J Magn Reson Imaging 49:719–730
Plaikner M, Kremser C, Zoller H et al (2019) Does gadoxetate disodium affect MRE measurements in the delayed hepatobiliary phase? Eur Radiol 29:829–837
Yin M, Glaser KJ, Talwalkar JA, Chen J, Manduca A, Ehman RL (2016) Hepatic MR elastography: clinical performance in a series of 1377 consecutive examinations. Radiology 278:114–124
Dzyubak B, Venkatesh SK, Manduca A, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL (2016) Automated liver elasticity calculation for MR elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging 43:1055–1063
Kottner J, Audige L, Brorson S et al (2011) Guidelines for Reporting Reliability and Agreement Studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J Clin Epidemiol 64:96–106
Morisaka H, Motosugi U, Ichikawa S et al (2018) Magnetic resonance elastography is as accurate as liver biopsy for liver fibrosis staging. J Magn Reson Imaging 47:1268–1275
Bedossa P, Poynard T (1996) An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 24:289–293
Yoshimitsu K, Mitsufuji T, Shinagawa Y et al (2016) MR elastography of the liver at 3.0 T in diagnosing liver fibrosis grades; preliminary clinical experience. Eur Radiol 26:656–663
Loomba R, Cui J, Wolfson T et al (2016) Novel 3D magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in NAFLD: A prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 111:986–994
Imajo K, Kessoku T, Honda Y et al (2016) Magnetic resonance imaging more accurately classifies steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease than transient elastography. Gastroenterology 150:626–637
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E et al (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135:32–40
Bohte AE, de Niet A, Jansen L et al (2014) Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis: a comparison of ultrasound-based transient elastography and MR elastography in patients with viral hepatitis B and C. Eur Radiol 24:638–648
Morisaka H, Motosugi U, Glaser KJ et al (2017) Comparison of diagnostic accuracies of two- and three-dimensional MR elastography of the liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 45:1163–1170
Castera L, Forns X, Alberti A (2008) Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography. J Hepatol 48:835–847
Serai SD, Obuchowski NA, Venkatesh SK et al (2017) Repeatability of MR elastography of liver: a meta-analysis. Radiology 285:92–100
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Jing Zhou for assessment of pathologic specimens.
Funding
The authors state that this study has received funding by the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 91959118 (JW), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China 201704020016 (JW), Clinical Research Foundation of the 3rd Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University YHJH201901 (JW), and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No.2021A1515010582) (JW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Jin Wang.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• diagnostic or prognostic study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Yang, H., Liu, Y. et al. Comparison of the diagnostic performance of 2D and 3D MR elastography in staging liver fibrosis. Eur Radiol 31, 9468–9478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08053-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08053-y