Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the feasibility and time saving of fusing CT and MR enterography with ultrasound for ultrasound molecular imaging (USMI) of inflammation in an acute small bowel inflammation of swine.
Methods
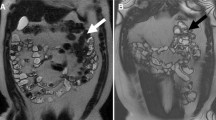
Nine swine with ileitis were scanned with either CT (n = 3) or MR (n = 6) enterography. Imaging times to load CT/MR images onto a clinical ultrasound machine, fuse them to ultrasound with an anatomical landmark-based approach, and identify ileitis were compared to the imaging times without anatomical road mapping. Inflammation was then assessed by USMI using dual selectin-targeted (MBSelectin) and control (MBControl) contrast agents in diseased and healthy control bowel segments, followed by ex vivo histology.
Results
Cross-sectional image fusion with ultrasound was feasible with an alignment error of 13.9 ± 9.7 mm. Anatomical road mapping significantly reduced (P < 0.001) scanning times by 40%. Localising ileitis was achieved within 1.0 min. Subsequently performed USMI demonstrated significantly (P < 0.001) higher imaging signal using MBSelectin compared to MBControl and histology confirmed a significantly higher inflammation score (P = 0.006) and P- and E-selectin expression (P ≤ 0.02) in inflamed vs. healthy bowel.
Conclusions
Fusion of CT and MR enterography data sets with ultrasound in real time is feasible and allows rapid anatomical localisation of ileitis for subsequent quantification of inflammation using USMI.
Key Points
• Real-time fusion of CT/MRI with ultrasound to localise ileitis is feasible.
• Anatomical road mapping using CT/MRI significantly decreases the scanning time for USMI.
• USMI allows quantification of inflammation in swine, verified with ex vivo histology.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loftus EV Jr (2004) Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 126:1504–1517
Danese S (2012) New therapies for inflammatory bowel disease: from the bench to the bedside. Gut 61:918–932
Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM et al (2012) Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology 142:46–54 e42; quiz e30
Malaty HM, Fan X, Opekun AR, Thibodeaux C, Ferry GD (2010) Rising incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among children: a 12-year study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 50:27–31
Benchimol EI, Mack DR, Nguyen GC et al (2014) Incidence, outcomes, and health services burden of very early onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 147:803–813 e807; quiz e814-805
Ahluwalia JP (2012) Immunotherapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Med Clin North Am 96:525–544
Speight RA, Mansfield JC (2013) Drug advances in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Med 13:378–382
Vilela EG, Torres HO, Martins FP, Ferrari Mde L, Andrade MM, Cunha AS (2012) Evaluation of inflammatory activity in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 18:872–881
Kiessling F, Fokong S, Bzyl J, Lederle W, Palmowski M, Lammers T (2014) Recent advances in molecular, multimodal and theranostic ultrasound imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 72:15–27
Pysz MA, Willmann JK (2011) Targeted contrast-enhanced ultrasound: an emerging technology in abdominal and pelvic imaging. Gastroenterology 140:785–790 e786
Kircher MF, Willmann JK (2012) Molecular body imaging: MR imaging, CT, and US. Part II. Applications. Radiology 264:349–368
Kircher MF, Willmann JK (2012) Molecular body imaging: MR imaging, CT, and US. part I. principles. Radiology 263:633–643
Kamaya A, Machtaler S, Safari Sanjani S et al (2013) New technologies in clinical ultrasound. Semin Roentgenol 48:214–223
Abou-Elkacem L, Bachawal SV, Willmann JK (2015) Ultrasound molecular imaging: Moving toward clinical translation. Eur J Radiol 84:1685–1693
Kiessling F, Huppert J, Palmowski M (2009) Functional and molecular ultrasound imaging: concepts and contrast agents. Curr Med Chem 16:627–642
Lindner JR (2009) Contrast ultrasound molecular imaging of inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res 84:182–189
Deshpande N, Lutz AM, Ren Y et al (2012) Quantification and monitoring of inflammation in murine inflammatory bowel disease with targeted contrast-enhanced US. Radiology 262:172–180
Wang H, Felt SA, Machtaler S et al (2015) Quantitative assessment of inflammation in a porcine acute terminal ileitis model: US with a molecularly targeted contrast agent. Radiology 276:809–817
Wang H, Machtaler S, Bettinger T et al (2013) Molecular imaging of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease with a clinically translatable dual-selectin-targeted US contrast agent: comparison with FDG PET/CT in a mouse model. Radiology 267:818–829
Machtaler S, Knieling F, Luong R, Tian L, Willmann JK (2015) Assessment of inflammation in an acute on chronic model of inflammatory bowel disease with ultrasound molecular imaging. Theranostics 5:1175–1186
Haas K, Rubesova E, Bass D (2016) Role of imaging in the evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease: How much is too much? World J Radiol 8:124–131
Ewertsen C, Saftoiu A, Gruionu LG, Karstrup S, Nielsen MB (2013) Real-time image fusion involving diagnostic ultrasound. AJR American Journal of Roentgenology 200:W249–W255
Lee MW (2014) Fusion imaging of real-time ultrasonography with CT or MRI for hepatic intervention. Ultrasonography 33:227–239
Diana M, Halvax P, Mertz D et al (2015) Improving echo-guided procedures using an ultrasound-CT image fusion system. Surg Innov 22:217–222
Burke CJ, Bencardino J, Adler R (2017) The potential use of ultrasound-magnetic resonance imaging fusion applications in musculoskeletal intervention. J Ultrasound Med 36:217–224
Kilcoyne A, Kaplan JL, Gee MS (2016) Inflammatory bowel disease imaging: current practice and future directions. World J Gastroenterol 22:917–932
Puylaert CA, Tielbeek JA, Bipat S, Stoker J (2015) Grading of Crohn's disease activity using CT, MRI, US and scintigraphy: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 25:3295–3313
Deepak P, Kolbe AB, Fidler JL, Fletcher JG, Knudsen JM, Bruining DH (2016) Update on magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound evaluation of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 12:226–236
Al-Bawardy B, Hansel SL, Fidler JL, Barlow JM, Bruining DH (2017) Endoscopic and radiographic assessment of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 46:493–513
Moran CP, Neary B, Doherty GA (2016) Endoscopic evaluation in diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc 8:723–732
Stanley E, Moriarty HK, Cronin CG (2016) Advanced multimodality imaging of inflammatory bowel disease in 2015: an update. World J Radiol 8:571–580
Kljucevsek D, Vidmar D, Urlep D, Dezman R (2016) Dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the bowel wall with quantitative assessment of Crohn's disease activity in childhood. Radiol Oncol 50:347–354
Ripolles T, Rausell N, Paredes JM, Grau E, Martinez MJ, Vizuete J (2013) Effectiveness of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for characterisation of intestinal inflammation in Crohn's disease: a comparison with surgical histopathology analysis. J Crohns Colitis 7:120–128
Wong DD, Forbes GM, Zelesco M, Mason R, Pawlik J, Mendelson RM (2012) Crohn's disease activity: quantitative contrast-enhanced ultrasound assessment. Abdom Imaging 37:369–376
Bachmann C, Klibanov AL, Olson TS et al (2006) Targeting mucosal addressin cellular adhesion molecule (MAdCAM)-1 to noninvasively image experimental Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 130:8–16
Eppihimer MJ, Wolitzky B, Anderson DC, Labow MA, Granger DN (1996) Heterogeneity of expression of E- and P-selectins in vivo. Circ Res 79:560–569
Homeister JW, Zhang M, Frenette PS et al (1998) Overlapping functions of E- and P-selectin in neutrophil recruitment during acute inflammation. Blood 92:2345–2352
Henseleit U, Steinbrink K, Goebeler M et al (1996) E-selectin expression in experimental models of inflammation in mice. J Pathol 180:317–325
Labow MA, Norton CR, Rumberger JM et al (1994) Characterization of E-selectin-deficient mice: demonstration of overlapping function of the endothelial selectins. Immunity 1:709–720
Bhatti M, Chapman P, Peters M, Haskard D, Hodgson HJ (1998) Visualising E-selectin in the detection and evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 43:40–47
Schurmann GM, Bishop AE, Facer P et al (1995) Increased expression of cell adhesion molecule P-selectin in active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 36:411–418
Jubeli E, Moine L, Vergnaud-Gauduchon J, Barratt G (2012) E-selectin as a target for drug delivery and molecular imaging. J Control Release 158:194–206
Magro F, Araujo F, Pereira P, Meireles E, Diniz-Ribeiro M, Velosom FT (2004) Soluble selectins, sICAM, sVCAM, and angiogenic proteins in different activity groups of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 49:1265–1274
Willmann JK, Bonomo L, Carla Testa A et al (2017) Ultrasound molecular imaging with BR55 in patients with breast and ovarian lesions: first-in-human results. J Clin Oncol 35:2133–2140
Kim AY, Lee MW, Cha DI et al (2016) Automatic registration between real-time ultrasonography and pre-procedural magnetic resonance images: a prospective comparison between two registration methods by liver surface and vessel and by liver surface only. Ultrasound Med Biol 42:1627–1636
Hakime A, Deschamps F, De Carvalho EG, Teriitehau C, Auperin A, De Baere T (2011) Clinical evaluation of spatial accuracy of a fusion imaging technique combining previously acquired computed tomography and real-time ultrasound for imaging of liver metastases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:338–344
Walter U, Muller JU, Rosche J et al (2016) Magnetic resonance-transcranial ultrasound fusion imaging: A novel tool for brain electrode location. Mov Disord 31:302–309
Prada F, Del Bene M, Mattei L et al (2014) Fusion imaging for intra-operative ultrasound-based navigation in neurosurgery. J Ultrasound 17:243–251
Maxeiner A, Stephan C, Durmus T, Slowinski T, Cash H, Fischer T (2015) Added value of multiparametric ultrasonography in magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography fusion-guided biopsy of the prostate in patients with suspicion for prostate cancer. Urology 86:108–114
Baek J, Huh J, Kim M et al (2013) Accuracy of volume measurement using 3D ultrasound and development of CT-3D US image fusion algorithm for prostate cancer radiotherapy. Med Phys 40:021704
Kousaka J, Nakano S, Ando T et al (2016) Targeted sonography using an image fusion technique for evaluation of incidentally detected breast lesions on chest CT: a pilot study. Breast Cancer 23:301–309
Pickles MD, Gibbs P, Hubbard A et al (2015) Registration of supine MR mammography with breast ultrasound for surgical planning of breast conserving surgery: a feasibility study. Ultraschall Med. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-108008
Helck A, Notohamiprodjo M, Danastasi M, Meinel F, Reiser M, Clevert DA (2012) Ultrasound image fusion - clinical implementation and potential benefits for monitoring of renal transplants. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 52:179–186
Amalou H, Wood BJ (2012) Multimodality fusion with MRI, CT, and ultrasound contrast for ablation of renal cell carcinoma. Case Rep Urol 2012:390912
Iagnocco A, Perella C, D'Agostino MA, Sabatini E, Valesini G, Conaghan PG (2011) Magnetic resonance and ultrasonography real-time fusion imaging of the hand and wrist in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 50:1409–1413
Liu J, Zhan W, Zhou M, Zhang X, Hu Y, Zhu Y (2012) The feasibility study of US-MRI virtual navigation in the shoulder. Clin Imaging 36:803–809
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Rebecca Fahrig, PhD, and the Zeego Laboratory at Stanford University for the C-arm CT imaging technical support.
Funding
This study has received funding by NIH R01DK092509 grant (JKW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Jürgen K. Willmann.
Conflict of interest:
The authors of this manuscript except T.B. declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. T.B. is an employee of Bracco Suisse SA. Bracco Suisse SA only provided the contrast agents used in this study, but was not involved in planning and performing of the study, nor in analyzing or interpretation of the data.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors has significant statistical expertise.
Ethical approval
Approval from the institutional animal care committee was obtained.
Methodology
• prospective
• experimental
• performed at one institution
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Felt, S.A., Guracar, I. et al. Anatomical Road Mapping Using CT and MR Enterography for Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Small Bowel Inflammation in Swine. Eur Radiol 28, 2068–2076 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5148-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5148-6