Abstract
Objectives
To define optimal window settings for displaying virtual monoenergetic images (VMI) of dual-energy CT pulmonary angiography (DE-CTPA).
Methods
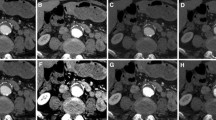
Forty-five patients who underwent clinically-indicated third-generation dual-source DE-CTPA were retrospectively evaluated. Standard linearly-blended (M_0.6), 70-keV traditional VMI (M70), and 40-keV noise-optimised VMI (M40+) reconstructions were analysed. For M70 and M40+ datasets, the subjectively best window setting (width and level, B-W/L) was independently determined by two observers and subsequently related with pulmonary artery attenuation to calculate separate optimised values (O-W/L) using linear regression. Subjective evaluation of image quality (IQ) between W/L settings were assessed by two additional readers. Repeated measures of variance were performed to compare W/L settings and IQ indices between M_0.6, M70, and M40+.
Results
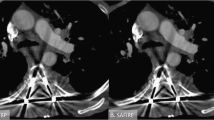
B-W/L and O-W/L for M70 were 460/140 and 450/140, and were 1100/380 and 1070/380 for M40+, respectively, differing from standard DE-CTPA W/L settings (450/100). Highest subjective scores were observed for M40+ regarding vascular contrast, embolism demarcation, and overall IQ (all p<0.001).
Conclusions
Application of O-W/L settings is beneficial to optimise subjective IQ of VMI reconstructions of DE-CTPA. A width slightly less than two times the pulmonary trunk attenuation and a level approximately of overall pulmonary vessel attenuation are recommended.
Key Points
• Application of standard window settings for VMI results in inferior image perception.
• No significant differences between B-W/L and O-W/L for M70/M40+ were observed.
• O-W/L for M70 were 450/140 and were 1070/380 for M40+.
• Improved subjective IQ characteristics were observed for VMI displayed with O-W/L.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belohlavek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A (2013) Pulmonary embolism, part I: epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism. Exp Clin Cardiol 18:129–138
Kurcz J, Garcarek J, Guzinski M, Czarnecka A, Sasiadek MJ (2013) Multislice computed tomography angiography as an imaging modality of choice in patients with suspicion of pulmonary embolism - own experiences and modern imaging techniques. Adv Clin Exp Med 22:705–713
Johnson TR, Krauss B, Sedlmair M et al (2007) Material differentiation by dual energy CT: initial experience. Eur Radiol 17:1510–1517
Johnson TR (2012) Dual-energy CT: general principles. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:s3–s8
Apfaltrer P, Sudarski S, Schneider D et al (2014) Value of monoenergetic low-kV dual energy CT datasets for improved image quality of CT pulmonary angiography. Eur J Radiol 83:322–328
Meier A, Wurnig M, Desbiolles L, Leschka S, Frauenfelder T, Alkadhi H (2015) Advanced virtual monoenergetic images: improving the contrast of dual-energy CT pulmonary angiography. Clin Radiol 70:1244–1251
Lenga L, Albrecht MH, Othman AE et al (2017) Monoenergetic dual-energy computed tomographic imaging: cardiothoracic applications. J Thorac Imaging 32:151–158
Mangold S, Cannao PM, Schoepf UJ et al (2016) Impact of an advanced image-based monoenergetic reconstruction algorithm on coronary stent visualization using third generation dual-source dual-energy CT: a phantom study. Eur Radiol 26:1871–1878
Maturen KE, Kaza RK, Liu PS, Quint LE, Khalatbari SH, Platt JF (2012) “Sweet spot” for endoleak detection: optimizing contrast to noise using low kev reconstructions from fast-switch kvp dual-energy CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 36:83–87
Secchi F, De Cecco CN, Spearman JV et al (2015) Monoenergetic extrapolation of cardiac dual energy CT for artifact reduction. Acta Radiol 56:413–418
Pinho DF, Kulkarni NM, Krishnaraj A, Kalva SP, Sahani DV (2013) Initial experience with single-source dual-energy CT abdominal angiography and comparison with single-energy CT angiography: image quality, enhancement, diagnosis and radiation dose. Eur Radiol 23:351–359
Beeres M, Trommer J, Frellesen C et al (2016) Evaluation of different kev-settings in dual-energy CT angiography of the aorta using advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic imaging. Int J Card Imaging 32:137–144
Grant KL, Flohr TG, Krauss B, Sedlmair M, Thomas C, Schmidt B (2014) Assessment of an advanced image-based technique to calculate virtual monoenergetic computed tomographic images from a dual-energy examination to improve contrast-to-noise ratio in examinations using iodinated contrast media. Investig Radiol 49:586–592
Albrecht MH, Trommer J, Wichmann JL et al (2016) Comprehensive comparison of virtual monoenergetic and linearly blended reconstruction techniques in third-generation dual-source dual-energy computed tomography angiography of the thorax and abdomen. Investig Radiol 51:582–590
Caruso D, Parinella AH, Schoepf UJ et al (2017) Optimization of window settings for standard and advanced virtual monoenergetic imaging in abdominal dual-energy CT angiography. Abdom Radiol (NY) 42:772–780
Henk CB, Grampp S, Linnau KF et al (2003) Suspected pulmonary embolism: enhancement of pulmonary arteries at deep-inspiration CT angiography--influence of patent foramen ovale and atrial-septal defect. Radiology 226:749–755
Wichmann JL, Rw B, Doss M et al (2013) Diagnostic accuracy of late iodine-enhancement dual-energy computed tomography for the detection of chronic myocardial infarction compared with late gadolinium-enhancement 3-t magnetic resonance imaging. Investig Radiol 48:851–856
Schueller-Weidekamm C, Schaefer-Prokop CM, Weber M, Herold CJ, Prokop M (2006) CT angiography of pulmonary arteries to detect pulmonary embolism: improvement of vascular enhancement with low kilovoltage settings. Radiology 241:899–907
Bae KT, Mody GN, Balfe DM et al (2005) CT depiction of pulmonary emboli: display window settings. Radiology 236:677–684
Saba L, Mallarin G (2009) Window settings for the study of calcified carotid plaques with multidetector CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1445–1450
De Cecco CN, Caruso D, Schoepf UJ et al (2016) Optimization of window settings for virtual monoenergetic imaging in dual-energy CT of the liver: a multi-reader evaluation of standard monoenergetic and advanced imaged-based monoenergetic datasets. Eur J Radiol 85:695–699
Weiss J, Notohamiprodjo M, Bongers M et al (2017) Effect of noise-optimized monoenergetic postprocessing on diagnostic accuracy for detecting incidental pulmonary embolism in portal-venous phase dual-energy computed tomography. Investig Radiol 52:142–147
Mangold S, De Cecco CN, Schoepf UJ et al (2016) A noise-optimized virtual monochromatic reconstruction algorithm improves stent visualization and diagnostic accuracy for detection of in-stent re-stenosis in lower extremity run-off CT angiography. Eur Radiol 26:4380–4389
Martin SS, Albrecht MH, Wichmann JL et al (2017) Value of a noise-optimized virtual monoenergetic reconstruction technique in dual-energy CT for planning of transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Eur Radiol 27:705–714
Albrecht MH, Scholtz JE, Husers K et al (2016) Advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic dual-energy CT angiography of the abdomen: optimization of kiloelectron volt settings to improve image contrast. Eur Radiol 26:1863–1870
Wichmann JL, Gillott MR, De Cecco CN et al (2016) Dual-energy computed tomography angiography of the lower extremity runoff: impact of noise-optimized virtual monochromatic imaging on image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Investig Radiol 51:139–146
Liu Y, Hopper KD, Mauger DT, Addis KA (2000) CT angiographic measurement of the carotid artery: optimizing visualization by manipulating window and level settings and contrast material attenuation. Radiology 217:494–500
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Julian L. Wichmann.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: J.L.W. received speakers’ fees from GE Healthcare and Siemens Healthcare. The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• performed at one institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Angelo, T., Bucher, A.M., Lenga, L. et al. Optimisation of window settings for traditional and noise-optimised virtual monoenergetic imaging in dual-energy computed tomography pulmonary angiography. Eur Radiol 28, 1393–1401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5059-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5059-6