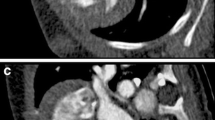
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the potential of advanced modeled iterative reconstruction (ADMIRE) for optimizing radiation dose of high-pitch coronary CT angiography (CCTA).
Methods
High-pitch 192-slice dual-source CCTA was performed in 25 patients (group 1) according to standard settings (ref. 100 kVp, ref. 270 mAs/rot). Images were reconstructed with filtered back projection (FBP) and ADMIRE (strength levels 1–5). In another 25 patients (group 2), high-pitch CCTA protocol parameters were adapted according to results from group 1 (ref. 160 mAs/rot), and images were reconstructed with ADMIRE level 4. In ten patients of group 1, vessel sharpness using full width at half maximum (FWHM) analysis was determined. Image quality was assessed by two independent, blinded readers.
Results
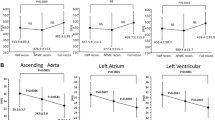
Interobserver agreements for attenuation and noise were excellent (r = 0.88/0.85, p < 0.01). In group 1, ADMIRE level 4 images were most often selected (84 %, 21/25) as preferred data set; at this level noise reduction was 40 % compared to FBP. Vessel borders showed increasing sharpness (FWHM) at increasing ADMIRE levels (p < 0.05). Image quality in group 2 was similar to that of group 1 at ADMIRE levels 2–3. Radiation dose in group 2 (0.3 ± 0.1 mSv) was significantly lower than in group 1 (0.5 ± 0.3 mSv; p < 0.05).
Conclusions
In a selected population, ADMIRE can be used for optimizing high-pitch CCTA to an effective dose of 0.3 mSv.
Key points
• Advanced modeled IR (ADMIRE) reduces image noise up to 50 % as compared to FBP.
• Coronary artery vessel borders show an increasing sharpness at higher ADMIRE levels.
• High-pitch CCTA with ADMIRE is possible at a radiation dose of 0.3 mSv.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamm EP, Rong XJ, Cody DD, Ernst RD, Fitzgerald NE, Kundra V (2011) Quality initiatives: CT radiation dose reduction: how to implement change without sacrificing diagnostic quality. Radiographics 31:1823–1832
Layritz C, Muschiol G, Flohr T et al (2013) Automated attenuation-based selection of tube voltage and tube current for coronary CT angiography: reduction of radiation exposure versus a BMI-based strategy with an expert investigator. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 7:303–310
Vardhanabhuti V, Riordan RD, Mitchell GR, Hyde C, Roobottom CA (2014) Image comparative assessment using iterative reconstructions: clinical comparison of low-dose abdominal/pelvic computed tomography between adaptive statistical, model-based iterative reconstructions and traditional filtered back projection in 65 patients. Invest Radiol 49:209–216
Meyer M, Haubenreisser H, Schoepf UJ et al (2014) Closing in on the K edge: coronary CT angiography at 100, 80, and 70 kV-initial comparison of a second- versus a third-generation dual-source CT system. Radiology. doi:10.1148/radiol.14140244:140244
Morsbach F, Gordic S, Desbiolles L et al (2014) Performance of turbo high-pitch dual-source CT for coronary CT angiography: first ex vivo and patient experience. Eur Radiol 24:1889–1895
Gordic S, Husarik DB, Desbiolles L, Leschka S, Frauenfelder T, Alkadhi H (2014) High-pitch coronary CT angiography with third generation dual-source CT: limits of heart rate. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 30:1173–1179
Gordic S, Morsbach F, Schmidt B et al (2014) Ultralow-dose chest computed tomography for pulmonary nodule detection: first performance evaluation of single energy scanning with spectral shaping. Invest Radiol 49:465–473
Gordic S, Desbiolles L, Stolzmann P et al (2014) Advanced modelled iterative reconstruction for abdominal CT: qualitative and quantitative evaluation. Clin Radiol 69:e497–e504
Pontana F, Pagniez J, Flohr T et al (2011) Chest computed tomography using iterative reconstruction vs filtered back projection (Part 1): evaluation of image noise reduction in 32 patients. Eur Radiol 21:627–635
Thibault JB, Sauer KD, Bouman CA, Hsieh J (2007) A three-dimensional statistical approach to improved image quality for multislice helical CT. Med Phys 34:4526–4544
Taylor AJ, Cerqueira M, Hodgson JM et al (2010) ACCF/SCCT/ACR/AHA/ASE/ASNC/NASCI/SCAI/SCMR 2010 appropriate use criteria for cardiac computed tomography. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Circulation 122:e525–e555
Pontana F, Duhamel A, Pagniez J et al (2011) Chest computed tomography using iterative reconstruction vs filtered back projection (Part 2): image quality of low-dose CT examinations in 80 patients. Eur Radiol 21:636–643
Morsbach F, Desbiolles L, Plass A et al (2013) Stenosis quantification in coronary CT angiography: impact of an integrated circuit detector with iterative reconstruction. Invest Radiol 48:32–40
Wang R, Schoepf UJ, Wu R et al (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of coronary CT angiography: comparison of filtered back projection and iterative reconstruction with different strengths. J Comput Assist Tomogr 38:179–184
Richard S, Husarik DB, Yadava G, Murphy SN, Samei E (2012) Towards task-based assessment of CT performance: system and object MTF across different reconstruction algorithms. Med Phys 39:4115–4122
Menzel HG, Schibilla H, Teunen D (eds) (2000) European guidelines on quality criteria for computed tomography, EUR 16262 EN. European Commission, Luxembourg
Einstein AJ, Elliston CD, Arai AE et al (2010) Radiation dose from single-heartbeat coronary CT angiography performed with a 320-detector row volume scanner. Radiology 254:698–706
Boone JM, Strauus KJ, Cody DD, McCollough CH, McNitt-Gray MF, Toth TL (2011) Size specific dose estimates (SSDE) in pediatric and adult CT examinations. American Association of Physicists in Medicine, report of AAPM Task Group 204. AAPM, College Park, MD
Hou Y, Liu X, Xv S, Guo W, Guo Q (2012) Comparisons of image quality and radiation dose between iterative reconstruction and filtered back projection reconstruction algorithms in 256-MDCT coronary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:588–594
Leipsic J, Labounty TM, Heilbron B et al (2010) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: assessment of image noise and image quality in coronary CT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:649–654
Schuhbaeck A, Achenbach S, Layritz C et al (2013) Image quality of ultra-low radiation exposure coronary CT angiography with an effective dose <0.1 mSv using high-pitch spiral acquisition and raw data-based iterative reconstruction. Eur Radiol 23:597–606
Singh S, Khawaja RD, Pourjabbar S, Padole A, Lira D, Kalra MK (2013) Iterative image reconstruction and its role in cardiothoracic computed tomography. J Thorac Imaging 28:355–367
Yin WH, Lu B, Hou ZH et al (2013) Detection of coronary artery stenosis with sub-milliSievert radiation dose by prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch spiral CT angiography and iterative reconstruction. Eur Radiol 23:2927–2933
Ebersberger U, Tricarico F, Schoepf UJ et al (2013) CT evaluation of coronary artery stents with iterative image reconstruction: improvements in image quality and potential for radiation dose reduction. Eur Radiol 23:125–132
Renker M, Nance JW Jr, Schoepf UJ et al (2011) Evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography: comparison of iterative and filtered back projection image reconstruction. Radiology 260:390–399
Husarik DB, Schindera ST, Morsbach F et al (2014) Combining automated attenuation-based tube voltage selection and iterative reconstruction: a liver phantom study. Eur Radiol 24:657–667
Winklehner A, Goetti R, Baumueller S et al (2011) Automated attenuation-based tube potential selection for thoracoabdominal computed tomography angiography: improved dose effectiveness. Invest Radiol 46:767–773
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is H. Alkadhi. The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: M. Sedlmair and B. Schmidt with Siemens Healthcare.
All other authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was waived by the institutional review board. Methodology: retrospective, case-control study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordic, S., Desbiolles, L., Sedlmair, M. et al. Optimizing radiation dose by using advanced modelled iterative reconstruction in high-pitch coronary CT angiography. Eur Radiol 26, 459–468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3862-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3862-5