Abstract
Objectives
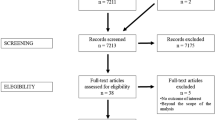
The purpose of our study was to distinguish the different components of a brain arteriovenous malformation (bAVM) on 3D rotational angiography (3D-RA) using a semi-automated segmentation algorithm.
Materials and methods
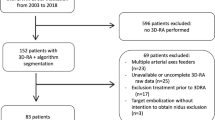
Data from 3D-RA of 15 patients (8 males, 7 females; 14 supratentorial bAVMs, 1 infratentorial) were used to test the algorithm. Segmentation was performed in two steps: (1) nidus segmentation from propagation (vertical then horizontal) of tagging on the reference slice (i.e., the slice on which the nidus had the biggest surface); (2) contiguity propagation (based on density and variance) from tagging of arteries and veins distant from the nidus. Segmentation quality was evaluated by comparison with six frame/s DSA by two independent reviewers. Analysis of supraselective microcatheterisation was performed to dispel discrepancy.
Results
Mean duration for bAVM segmentation was 64 ± 26 min. Quality of segmentation was evaluated as good or fair in 93 % of cases. Segmentation had better results than six frame/s DSA for the depiction of a focal ectasia on the main draining vein and for the evaluation of the venous drainage pattern.
Conclusion
This segmentation algorithm is a promising tool that may help improve the understanding of bAVM angio-architecture, especially the venous drainage.
Key points
• The segmentation algorithm allows for the distinction of the AVM’s components
• This algorithm helps to see the venous drainage of bAVMs more precisely
• This algorithm may help to reduce the treatment-related complication rate


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3D-RA:
-
Three dimensional-rotational angiography
- bAVM:
-
Brain arteriovenous malformation
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- TOF:
-
Time of flight
- TR MRA:
-
Time-resolved magnetic resonance angiography
References
Lasjaunias P, Manelfe C, Chiu M (1986) Angiographic architecture of intracranial vascular malformations and fistulas − pretherapeutic aspects. Neurosurg Rev 9:253–263
Cognard C, Spelle L, Pierot L (2004) Pial arteriovenous malformations. In: M Forsting (Ed), Intracranial malformations and aneurysms 39-40
Combaz X, Levrier O, Moritz J et al (2011) Three-dimensional rotational angiography in the assessment of the angioarchitecture of brain arteriovenous malformations. J Neuroradiol 38:167–174
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Kirbas C, Quek FKH (2004) A review of vessel extraction techniques and algorithms ACM Comput Surv 36:81-121
Yaniv Z, Cleary K (2006) Image guided procedures: a review. Computer aided intervention and medical robotics CAIMR TR-2006-3
Babin D, Vansteenkiste E, Pizurica A, Philips W (2011) Segmentation of brain blood vessels using projections in 3-D CT angiography images. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc:8475–8478
Forkert ND, Illies T, Goebell E, Fiehler J, Saring D, Handels H (2013) Computer-aided nidus segmentation and angiographic characterization of arteriovenous malformations. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8:775–786
Naganawa S, Ito T, Iwayama E et al (1999) Magnitude subtraction vs. complex subtraction in dynamic contrast-enhanced 3D-MR angiography: basic experiments and clinical evaluation. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:813–820
Bock M, Schoenberg SO, Floemer F, Schad LR (2000) Separation of arteries and veins in 3D MR angiography using correlation analysis. Magn Reson Med 43:481–487
Santini F, Patil S, Meckel S, Scheffler K, Wetzel SG (2008) Double-reference cross-correlation algorithm for separation of the arteries and veins from 3D MRA time series. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:646–654
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Prof. Charbel Mounayer. The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies:
Dr Nader Sourour is proctor for the Covidien Company. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has received funding from the AVRUL (Agence pour la Valorisation de la Recherche Universitaire du Limousin), Limoges. FRANCE. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board. Methodology: retrospective, experimental, multicentre study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional material 1
(DOCX 87 kb)
Additional material 2
(DOCX 102 kb)
Additional material 3
(DOCX 78 kb)
(MP4 42028 kb)
ESM 5
(JPEG 32 kb)
High resolution image
(TIFF 4615 kb)
ESM 6
(JPEG 109 kb)
High resolution image
(TIFF 2807 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clarençon, F., Maizeroi-Eugène, F., Bresson, D. et al. Elaboration of a semi-automated algorithm for brain arteriovenous malformation segmentation: initial results. Eur Radiol 25, 436–443 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3421-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3421-5