Abstract
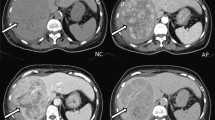
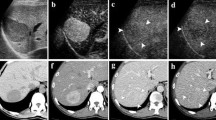
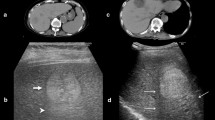
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the detection rate of tumor vessels and vascularity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by contrast-enhanced coded US using Levovist, and to compare with conventional color/power Doppler US (CDUS) and dynamic CT. Ninety nodules (72 hypo/isoechoic nodules, 18 hyperechoic nodules) in 61 patients were studied. We observed tumor vessels by continuous transmission at the early vascular phase (40 s following administration of Levovist) and vascularity by intermittent transmission (intervals of 2–3 s) at the late vascular phase (40 to approximately 120 s). The detection rate of tumor vessels at the early vascular phase was 97% in hypo/isoechoic nodules and 70% in hyperechoic nodules with high density in dynamic CT being higher than that by CDUS. Tumor vascularity at the late vascular phase in hypo/isoechoic and hyperechoic nodules was hyper-enhancement in 78 and 40%, iso-enhancement in 19 and 40%, and hypo-enhancement in 3 and 0%, respectively. The detection rates of tumor vessels and vascularity in hyperechoic nodules were similar to those by CDUS. The detection rates of tumor vessels and vascularity were not affected by the tumor size in HCC tumors with high density in dynamic CT. Contrast-enhanced US with Levovist was superior to CDUS and equal to dynamic CT to assess tumor vessels in hypo/isoechoic nodules. Although it was equal to CDUS for hyperechoic nodules, this modality is useful in evaluating tumor hemodynamics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Winter TC III, Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, Furukawa H, Wakao F, Koga H, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S, Freeny PC (1994) Early advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of CT and MR appearance with pathologic correlation. Radiology 192:379–387
Takayasu K, Furukawa H, Wakao F, Muramatsu Y, Abe H, Terauchi T, Winter TC III, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S (1995) CT diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma: sensitivity, findings, and CT-pathologic correlation. Am J Roentgenol 164:885–890
Tanaka S, Kitamura T, Fujita M, Nakanishi K, Okuda S (1990) Color Doppler flow imaging of liver tumors. Am J Roentgenol 154:509–514
Lencioni R, Pinto F, Armillotta N, Bartolozzi C (1996) Assessment of tumor vascularity in hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of power Doppler US and color Doppler US. Radiology 201:353–358
Matsui O, Kadoya M, Kameyama T, Yoshikawa J, Takashima T, Nakanuma Y, Unoura M, Kobayashi K, Izumi R, Ida M (1991) Benign and malignant nodules in cirrhotic livers: distinction based on blood supply. Radiology 178:493–497
Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, Furukawa H, Wakao F, Moriyama N, Takayama T, Yamasaki S, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S (1995) Early hepatocellular carcinoma: appearance at CT during arterial portography and CT arteriography with pathologic correlation. Radiology 194:101–105
Hayashi M, Matsui O, Ueda K, Kawamori Y, Kadoya M, Yoshikawa J, Gabata T, Takashima T, Nonomura A, Nakanuma Y (1999) Correlation between the blood supply and grade of malignancy of hepatocellular nodules associated with liver cirrhosis: evaluation by CT during intraarterial injection of contrast medium. Am J Roentgenol 172:969–976
Ward J, Robinson PJ (2002) How to detect hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 12:2258–2272
Fujimoto M, Moriyasu F, Nishikawa K, Nada T, Okuma M (1994) Color Doppler sonography of hepatic tumors with a galactose-based contrast agent: correlation with angiographic findings. Am J Roentgenol 163:1099–1104
Kim AY, Choi BI, Kim TK, Han JK, Yun EJ, Lee KY, Han MC (1998) Hepatocellular carcinoma: power Doppler US with a contrast agent—preliminary results. Radiology 209:135–140
Choi BI, Kim TK, Han JK, Kim AY, Seong CK, Park SJ (2000) Vascularity of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment with contrast-enhanced second-harmonic versus conventional power Doppler US. Radiology 214:381–386
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Bartolozzi C (2002) Tissue-harmonic and contrast-specific imaging: back to gray scale in ultrasound. Eur Radiol 12:151–165
Jakobsen JA (2001) Ultrasound contrast agents: clinical applications. Eur Radiol 11:1329–1337
Harvey CJ, Albrecht T (2001) Ultrasound of focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 11:1578–1593
Hirai T, Ohishi H, Tokuno E, Takahashi M, Sakaguchi H, Anai H, Nishimoto Y, Hirohashi S, Kichikawa K (2002) Qualitative diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography using coded harmonic angio with Levovist. J Med Ultrasonics 29:3–9
Ding H, Kudo M, Onda H, Suetomi Y, Minami Y, Chung H, Kawasaki T, Maekawa K (2001) Evaluation of post-treatment response of hepatocellular carcinoma with contrast-enhanced coded phase-inversion harmonic US: comparison with dynamic CT. Radiology 221:721–730
Ding H, Kudo M, Onda H, Suetomi Y, Minami Y, Maekawa K (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma: depiction of tumor parenchymal flow with intermittent harmonic power Doppler US during the early arterial phase in dual-display mode. Radiology 220:349–356
Ding H, Kudo M, Maekawa K, Suetomi Y, Minami Y, Onda H (2001) Detection of tumor parenchymal blood flow in hepatic tumors: value of second harmonic imaging with a galactose-based contrast agent. Hepatol Res 21:242–251
Leen E (2001) The role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the characterisation of focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 11:E27–E34
Dill-Macky MJ, Burns PN, Khalili K, Wilson SR (2002) Focal hepatic masses: enhancement patterns with SH U 508A and pulse-inversion US. Radiology 222:95–102
Quaia E, Bertolotto M, Dalla Palma L (2002) Characterization of liver hemangiomas with pulse-inversion harmonic imaging. Eur Radiol 12:537–544
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Donati F, Franchini C, Giusti S, Bartolozzi C (2002) Ultrasound imaging of focal liver lesions with a second-generation contrast agent. Acad Radiol 9:S371–S374
Fracanzani AL, Burdick L, Borzio M, Roncalli M, Bonelli N, Borzio F, Maraschi A, Fiorelli G, Fargion S (2001) Contrast-enhanced Doppler ultrasonography in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and premalignant lesions in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 34:1109–1112
Blomley MJ, Sidhu PS, Cosgrove DO, Albrecht T, Harvey CJ, Heckemann RA, Butler-Barnes J, Eckersley RJ, Basilico R (2001) Do different types of liver lesions differ in their uptake of the microbubble contrast agent SH U 508A in the late liver phase? Early experience. Radiology 220:661–667
Ding H, Kudo M, Onda H, Suetomi Y, Minami Y, Maekawa K (2001) Contrast-enhanced subtraction harmonic sonography for evaluating treatment response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 176:661–666
Cioni D, Lencioni R, Rossi S, Garbagnati F, Donati F, Crocetti L, Bartolozzi C (2001) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: using contrast-enhanced harmonic power Doppler sonography to assess treatment outcome. Am J Roentgenol 177:783–788
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koda, M., Matsunaga, Y., Ueki, M. et al. Qualitative assessment of tumor vascularity in hepatocellular carcinoma by contrast-enhanced coded ultrasound: comparison with arterial phase of dynamic CT and conventional color/power Doppler ultrasound. Eur Radiol 14, 1100–1108 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2172-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2172-5