Abstract
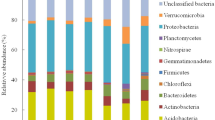
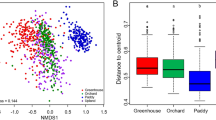
Soil bacterial diversity at environmentally distinct locations on Signy Island, South Orkney Islands was examined using the denaturing gradient gel profiling approach. A range of chemical variables in soils at each site was determined in order to describe variation between locations. No apparent differences in Shannon Diversity Index (H′) were observed. However, as revealed in an analysis of similarity (ANOSIM), the dominant bacterial communities of all eight studied locations were significantly different. Within this, higher levels of similarity were observed between penguin rookeries, seal wallows and vegetated soils, all of which share varying levels of impact from vertebrate activity, in contrast with more barren soil. In addition, the lowest H′ value was detected from the latter soil which also has the most extreme environmental conditions, and its bacterial community has the greatest genetic distance from the other locations. DGGE analyses indicated that the majority of the excised and sequenced bands were attributable to the Bacteroidetes. Across a range of ten environmental variables, multivariate correlation analysis suggested that a combination of pH, conductivity, copper and lead content potentially contributed explanatory value to the measured soil bacterial diversity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams BJ, Bardgett RB, Ayres E, Wall DH, Aislabie J, Bamforth S, Bargagli R, Cary C, Cavacini P, Connell L, Convey P, Fell JW, Frati F, Hogg ID, Newsham KK, O’Donnell A, Russell N, Seppelt RD, Stevens MI (2006) Diversity and distribution of Victoria Land biota. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3003–3018. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.04.030
Aislabie JM, Chhour K, Saul DJ, Miyauchi S, Ayton J, Paetzold RF, Balks MR (2006) Dominant bacteria in soils of Marble Point and Wright Valley, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3041–3056. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.02.018
Aislabie JM, Jordan S, Barker GM (2008) Relation between soil classification and bacterial diversity in soils of the Ross Sea region, Antarctica. Geoderma 144:9–20. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.10.006
Arnold RJ, Convey P, Hughes KA, Wynn-Williams DD (2003) Seasonal periodicity of physical factors, inorganic nutrients and microalgae in Antarctic fellfields. Polar Biol 26:396–403. doi:10.1007/s00300-003-0503-2
Barrett JE, Virginia RA, Wall DH, Cary SC, Adams BJ, Hacker AL, Aislabie JM (2006) Co-variation in soil biodiversity and biogeochemistry in northern and southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 18:535–548. doi:10.1017/S0954102006000587
Bokhorst S, Huiskes A, Convey P, Aerts R (2007) External nutrient inputs into terrestrial ecosystems of the Falkland Islands and the Maritime Antarctic region. Polar Biol 30:1315–1321. doi:10.1007/s00300-007-0256-4
Bokhorst S, Huiskes A, Convey P, van Bodegom PM, Aerts R (2008) Climate change effects on soil arthropod communities from the Falkland Islands and the Maritime Antarctic. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1547–1556. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.01.017
Bölter M, Blume HP, Schneider D, Beyer L (1997) Soil properties and distributions of invertebrates and bacteria from King George Island (Arctowski Station), Maritime Antarctic. Polar Biol 18:295–304. doi:10.1007/s003000050191
Caulkett AP, Ellis-Evans JC (1997) Chemistry of streams of Signy Island, maritime Antarctic: sources of major ions. Antarct Sci 9:3–11. doi:10.1017/S0954102097000023
CCAMLR (1997) CCAMLR ecosystem monitoring program: standard methods for monitoring studies. Commission for the Conservation of Antarctica Living Resources (CCAMLR), Hobart
Chong CW, Tan GYA, Wong RCS, Riddle MJ, Tan IKP (2009) DGGE fingerprinting of bacteria in soils from eight ecologically different sites around Casey Station, Antarctica. Polar Biol 32:853–860. doi:10.1007/s00300-009-0585-6
Chown SL, Convey P (2007) Spatial and temporal variability across life’s hierarchies in the terrestrial Antarctic. Philos Trans R Soc B 362:2307–2331. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1949
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Convey P (2001) Antarctic ecosystems. In: Levin SA (ed) Encyclopedia of biodiversity, vol 1. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 171–184
Davey MC, Rothery P (1993) Primary colonization by microalgae in relation to spatial variation in edaphic factors on Antarctic fellfield soils. J Ecol 81:335–343. doi:10.2307/2261503
Deheyn DD, Gendreau P, Baldwin RJ, Latz MI (2005) Evidence for enhanced bioavailability of trace elements in the marine ecosystem of Deception Island, a volcano in Antarctica. Mar Environ Res 60:1–33. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.08.001
Dick LK, Field KG (2004) Rapid estimation of numbers of fecal bacteroidetes by use of a quantitative PCR assay for 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5695–5697. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.9.5695-5697.2004
Engelen A, Convey P, Hodgson DA, Worland MR, Ott S (2008) Soil properties of an Antarctic inland site: implications for ecosystem development. Polar Biol 31:1453–1460. doi:10.1007/s00300-008-0486-0
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:626–631. doi:10.1073_pnas.0507535103
Flint HJ, Duncan SH, Scott KP, Louis P (2007) Interactions and competition within the microbial community of the human colon: links between diet and health. Environ Microbiol 9:1101–1111. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01281.x
Frenot Y, Chown SL, Whinam J, Selkirk PM, Convey P, Skotnicki M, Bergstrom DM (2005) Biological invasions in the Antarctic: extent, impacts and implications. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 80:45–72. doi:10.1017/S1464793104006542
Gafan GP, Lucas VS, Roberts GJ, Petrie A, Wilson M, Spratt DA (2005) Statistical analyses of complex denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles. J Clin Microbiol 43:3971–3978. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.8.3971-3978.2005
Green K, Williams R (1985) Observations on food remains in faeces of elephant, leopard and crabeater seals. Polar Biol 6:1432–2056. doi:10.1007/BF00446239
Holdgate MW (1977) Life sciences: terrestrial ecosystem in Antarctic. Philos Trans R Soc B 279:5–25. doi:10.1098/rstb.1977.0068
Honda K, Yamamoto Y, Tatsukawa R (1987) Distribution of heavy metals in Antarctic marine ecosystem. Proc NIPR Symp Polar Biol 1:184–197
Kowalchuk GA, Drigo B, Yergeau E, van Veen JA (2006) Assessing bacterial and fungal community structure in soil using ribosomal RNA and other structural gene markers. In: Nannipieri P, Smalla K (eds) Nucleic Acids and Proteins in Soil, Soil Biology, vol 8, pp 159–188
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163. doi:10.1093/bib/5.2.150
Li S, Xiao X, Yin X, Wang F (2006) Bacterial community along a historic lake sediment core of Ardley Island, west Antarctica. Extremophiles 10:461–467. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0523-2
Lynnes AS, Reid K, Crozall JP, Trathan PN (2002) Conflict or co-existence? Foraging distribution and competition for prey between Adélie and chinstrap penguins. Mar Biol (Berl) 141:1165–1174. doi:10.1007/s00300-004-0617-1
Melick DR, Hovenden MJ, Seppelt RD (1994) Phytogeography of bryophyte and lichen vegetation in the Windmill Islands, Wilkes Land, Continental Antarctica. Plant Ecol 111:71–87. doi:10.1007/BF00045578
Michel RFM, Schaefer CEGR, Dias LE, Simas FNB, Benites VDM, Mendonça EDS (2006) Ornithogenic Gelisols (Cryosols) from maritime Antarctica: pedogenesis, vegetation, and carbon studies. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1370–1376. doi:10.2136/sssaj2005.0178
Mizutani H, Wada E (1988) Nitrogen and carbon isotope ratios in seabird rookeries and their ecological implications. Ecology 69:340–349. doi:10.2307/1940432
Moosvi SA, McDonald IR, Pearce DA, Kelly DP, Wood AP (2005) Molecular detection and isolation from Antarctica of methylotrophic bacteria able to grow with methylated sulfur compounds. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:541–554. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2005.03.002
Nakatsu CH (2007) Soil microbial community analysis using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:562–571. doi:10.2136/sssaj2006.0080
Newberry CJ, Webster G, Cragg BA, Parkes RJ, Weightman AJ, Fry JC (2004) Diversity of prokaryotes and methanogenesis in deep subsurface sediments from the Nankai Trough, Ocean Drilling Program Leg 190. Environ Microbiol 6:274–287. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00568.x
Pearce DA (2003) Bacterioplankton community structure in a maritime Antarctic Oligotrophic Lake during a period of Holomixis, as determined by Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis (DGGE) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Microb Ecol 46:92–105. doi:1007/S00248-002-2039-3
Pearce DA, van der Gast CJ, Lawley B, Ellis-Evans JC (2003) Bacterioplankton community diversity in a maritime Antarctic lake, determined by culture-dependent and culture-independent techniques. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:59–70. doi:10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00110-7
Powell SM, Bowman JP, Snape I, Stark JS (2003) Microbial community in pristine and polluted nearshore Antarctic sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:135–145. doi:10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00135-1
Powell SM, Snape I, Bowman JP, Thompson BAW, Stark JS, McCammon SA, Riddle MJ (2005) A comparison of the short term effects of diesel fuel and lubricant oils on Antarctic benthic microbial communities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 322:53–65. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2005.02.005
Reid K (1995) The diet of Antarctic fur seals (Arctocephalus gazella Peters 1875) during winter at South Georgia. Antarct Sci 7:241–249. doi:10.1017/S0954102095000344
Santos IR, Silva-Filho EV, Schaefer CEGR, Albuqueque-Filho MR, Campos LS (2005) Heavy metal contamination in coastal sediments and soils near the Brazilian Antarctic Station, King George Island. Mar Pollut Bull 50:185–194. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.10.009
Santos IR, Silva-Filho EV, Schaefer C, Sella SM, Silva CA, Gomes V, Passos MJACR, Ngan PV (2006) Baseline mercury and zinc concentrations in terrestrial and coastal organisms of Admiralty Bay, Antarctica. Environ Pollut 140:304–311. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.07.007
Scouller RC, Snape I, Stark JS, Gore DB (2006) Evaluation of geochemical methods for discrimination of metal contamination in Antarctic marine sediments: a case study from Casey Station. Chemosphere 65:294–309. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.062
Simas FNB, Schaefer CEGR, Melo VF, Albuquerque-Filho MR, Michel FM, Pareira VV, Gomes MRM, Da Costa LM (2007) Ornithogenic cryosols from maritime Antarctica: phosphatization as a soil forming process. Geoderma 138:191–203. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.11.011
Smith RIL (1972) Vegetation of the South Orkney Islands with particular reference to Signy Island. Br Antarct Surv Sci Rep 68:124
Smith RIL (1998) Destruction of Antarctic terrestrial ecosystems by rapidly increasing fur seal population. Biol Conserv 45:55–72
Smith VR (2005) Moisture, carbon and inorganic nutrient controls of soil respiration at a sub-Antarctic island. Soil Biol Biochem 37:81–91. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.026
Snape I, Scouller RC, Stark SC, Stark J, Riddle MJ, Gore DB (2004) Characterisation of the dilute HCl extraction method for the identification of metal contamination in Antarctic marine sediments. Chemosphere 57:491–504. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.040
Stark JS, Riddle MJ, Snape I, Scouller RC (2003) Human impacts in Antartic marine soft-sediment assemblages: correlations between multivariate biological patterns and environmental variables at Casey Station. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 56:717–734. doi:10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00291-3
Tin T, Fleming ZL, Hughes KA, Ainley DG, Convey P, Moreno CA, Pfeiffer S, Scott J, Snape I (2009) Review: impacts of local human activities on the Antarctic environment. Antarct Sci 21:3–33. doi:10.1017/S0954102009001722
Usher MB, Booth RG (1986) Arthropod communities in a maritime Antarctic moss-turf habitat: multiple scales of pattern in the mites and Collembola. J Anim Ecol 55:155–170. doi:10.2307/4699
Vincent WF (1988) Microbial ecosystems of Antarctica. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 303
Wall DH (2005) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in terrestrial habitats of Antarctica. Antarct Sci 17:523–531. doi:10.1017/S0954102005002944
Wynn-Williams DD (1996) Antarctic microbial diversity: the basis of polar ecosystem processes. Biodivers Conserv 5:1271–1293. doi:10.1007/BF00051979
Yamamoto Y, Honda K, Tatsukawa R (1987) Heavy metal accumulation in Antarctic krill Euphausia Superba. Proc NIPR Symp Polar Biol 1:198–204
Yergeau E, Bokhorst S, Huiskes AHL, Boschker HTS, Aerts R, Kowalchuk GA (2007a) Size and structure of bacterial, fungal and nematode communities along an Antarctic environmental gradient. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:436–451. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00200.x
Yergeau E, Newsham KE, Pearce DA, Kowalchuk GA (2007b) Patterns of bacterial diversity across a range of Antarctic terrestrial habitats. Environ Microbiol 9:2670–2682. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01379.x
Yin X, Xia L, Sun L, Luo H, Wang Y (2008) Animal excrement: a potential biomonitor of heavy metal contamination in the marine environment. Sci Total Environ 399:179–185. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.03.005
Zdanowski MK, Weglenski P, Golik P, Sasin JM, Borsuk P, Zmuda MJ, Stankovic A (2004) Bacterial diversity in Adélie penguin, Pygoscelis adeliae, guano: molecular and morpho-physiological approaches. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50:163–173. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2004.06.012
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Malaysian Antarctic Research Programme (MARP), and the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) provided logistic support and field training. It also forms a contribution to the BAS BIOFLAME and SCAR EBA research programmes. We thank Roger Worland and David Routledge for assistance in sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, C.W., Dunn, M.J., Convey, P. et al. Environmental influences on bacterial diversity of soils on Signy Island, maritime Antarctic. Polar Biol 32, 1571–1582 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-009-0656-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-009-0656-8