Abstract
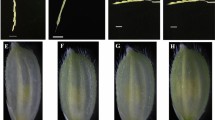
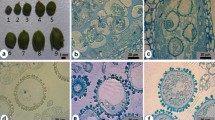
We report high-frequency embryogenesis and plantlet development from microspores isolated from anthers of two indica (IR-43, IR-54) and a japonica (T-309) rice cultivars, without prior nutrient preculture of anthers. Pretreatment stress of anthers with mannitol or a sugar-starvation medium, and use of maltose as the carbohydrate source in the microspore culture medium were found to be critical. Co-culture of microspores with rice ovaries was found beneficial but not essential. More than 60% of the microspores of the japonica variety Taipai-309 and 25–45% of the indica cultivars IR-54 and IR-43 showed induction of non-gametophytic development. Consequently, in the best treatments for IR-43 and T-309, more than 500 microspore-derived embryos could be obtained from a single dish (35 mm) containing about 80,000 microspores. Among the indica cultivars, the maximum response was obtained in the basal medium M-019. Plantlet regeneration occurred in about 9% (T-309), 7% (IR-43) and 2% (IR-54) of the transferred embryo-like structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 November 1996 / Revision received: 18 June 1997 / Accepted: 20 August 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raina, S., Irfan, S. High-frequency embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from isolated microspores of indica rice. Plant Cell Reports 17, 957–962 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050517
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050517