Abstract
Key message
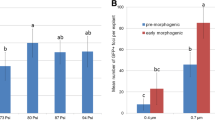
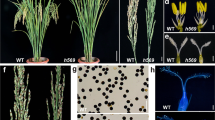
An engineered selectable marker combining herbicide resistance and yellow fluorescence contributes to the characterization of male-sterile phenotype in wheat, the severity of which correlates with expression levels of a synthetic Ms2 gene.
Abstract
Genetic transformation of wheat is conducted using selectable markers, such as herbicide and antibiotic resistance genes. Despite their proven effectiveness, they do not provide visual control of the transformation process and transgene status in progeny, which creates uncertainty and prolongs screening procedures. To overcome this limitation, this study developed a fusion protein by combining gene sequences encoding phosphinothricin acetyltransferase and mCitrine fluorescent protein. The fusion gene, introduced into wheat cells by particle bombardment, enabled herbicide selection, and visual identification of primary transformants along with their progeny. This marker was then used to select transgenic plants containing a synthetic Ms2 gene. Ms2 is a dominant gene whose activation in wheat anthers leads to male sterility, but the relationship between the expression levels and the male-sterile phenotype is unknown. The Ms2 gene was driven either by a truncated Ms2 promoter containing a TRIM element or a rice promoter OsLTP6. The expression of these synthetic genes resulted in complete male sterility or partial fertility, respectively. The low-fertility phenotype was characterized by smaller anthers than the wild type, many defective pollen grains, and low seed sets. The reduction in the size of anthers was observed at earlier and later stages of their development. Consistently, Ms2 transcripts were detected in these organs, but their levels were significantly lower than those in completely sterile Ms2TRIM::Ms2 plants. These results suggested that the severity of the male-sterile phenotype was modulated by Ms2 expression levels and that higher levels may be key to activating total male sterility.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
References
Ali GS, Golovkin M, Reddy AS (2003) Nuclear localization and in vivo dynamics of a plant-specific serine/arginine-rich protein. Plant J 36:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01932.x
Aliaga-Franco N, Zhang C, Presa S, Srivastava AK, Granell A, Alabadí D, Sadanandom A, Blázquez MA, Minguet EG (2019) Identification of transgene-free CRISPR-edited plants of rice, tomato, and arabidopsis by monitoring DsRED fluorescence in dry seeds. Front Plant Sci 10:1150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01150
Altpeter F, Vasil V, Srivastava V, Vasil IK (1996) Integration and expression of the high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit 1Ax1 gene into wheat. Nat Biotechnol 14:1155–1159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0996-1155
An X, Ma B, Duan M, Dong Z, Liu R, Yuan D, Hou Q, Wu S, Zhang D, Liu D, Yu D, Zhang Y, Xie K, Zhu T, Li Z, Zhang S, Tian Y, Liu C, Li J, Yuan L, Wan X (2020) Molecular regulation of ZmMs7 required for maize male fertility and development of a dominant male-sterility system in multiple species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:23499–23509. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2010255117
Bahieldin A, Hesham HH, Eissa HH, Saleh OO, Ramadan AA, Ahmed II, Dyer WW, El-Itriby HH, Madkour MA (2005) Field evaluation of transgenic wheat plants stably expressing the HVA1 gene for drought tolerance. Physiol Plant 123:421–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00470.x
Barro F, Cannell ME, Lazzeri PA, Barcelo P (1998) The influence of auxins on transformation of wheat and tritordeum and analysis of transgene integration patterns in transformants. Theor Appl Genet 97:684–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050944
Bell MR, Engleka MJ, Malik A, Strickler JE (2013) To fuse or not to fuse: What is your purpose? Protein Sci 22:1466–1477. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2356
Bhowmik P, Ellison E, Polley B, Bollina V, Kulkarni M, Ghanbarnia K, Song H, Gao C, Voytas DF, Kagale S (2018) Targeted mutagenesis in wheat microspores using CRISPR/Cas9. Sci Rep 8:6502. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24690-8
Bilichak A, Sastry-Dent L, Sriram S, Simpson M, Samuel P, Webb S, Jiang F, Eudes F (2020) Genome editing in wheat microspores and haploid embryos mediated by delivery of ZFN proteins and cell-penetrating peptide complexes. Plant Biotechnol J 18:1307–1316. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13296
Borisjuk N, Kishchenko O, Eliby S, Schramm C, Anderson P, Jatayev S, Kurishbayev A, Shavrukov Y (2019) Genetic modification for wheat improvement: from transgenesis to genome editing. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6216304
Chang Z, Chen Z, Wang N, Xie G, Lu J, Yan W, Zhou J, Tang X, Deng XW (2016) Construction of a male sterility system for hybrid rice breeding and seed production using a nuclear male sterility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:14145–14150. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1613792113
Chen X, Zaro JL, Shen WC (2013) Fusion protein linkers: property, design and functionality. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1357–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.039
de Oliveira MLP, Stover E, Thomson JG (2015) The codA gene as a negative selection marker in Citrus. Springerplus 4:264. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-1047-y
Debernardi JM, Tricoli DM, Ercoli MF, Hayta S, Ronald P, Palatnik JF, Dubcovsky J (2020) A GRF–GIF chimeric protein improves the regeneration efficiency of transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 38:1274–1279. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0703-0
Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1349. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/19.6.1349
Ferrie AMR, Bhowmik P, Rajagopalan N, Kagale S (2020) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in wheat doubled haploids. Methods Mol Biol 2072:183–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9865-4_15
Fu J, Ristic Z (2010) Analysis of transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) harboring a maize (Zea mays L.) gene for plastid EF-Tu: segregation pattern, expression and effects of the transgene. Plant Mol Biol 73:339–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9622-7
Gadaleta A, Giancaspro A, Blechl A, Blanco A (2006) Phosphomannose isomerase, pmi, as a selectable marker gene for durum wheat transformation. J Cereal Sci 43:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2005.06.004
Gao X, Chen J, Dai X, Zhang D, Zhao Y (2016) An Effective strategy for reliably isolating heritable and Cas9-free arabidopsis mutants generated by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. Plant Physiol 171:1794–1800. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00663
Gasparis S, Kala M, Przyborowski M, Lyznik LA, Orczyk W, Nadolska-Orczyk A (2018) A simple and efficient CRISPR/Cas9 platform for induction of single and multiple, heritable mutations in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Methods 14:111. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-018-0382-8
Gautam R, Shukla P, Kirti PB (2019) Targeted expression of a cysteine protease (AdCP) in tapetum induces male sterility in Indian mustard, Brassica juncea. Funct Integr Genomics 19:703–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00674-3
Griesbeck O, Baird GS, Campbell RE, Zacharias DA, Tsien RY (2001) Reducing the environmental sensitivity of yellow fluorescent protein. Mech Appl J Biol Chem 276:29188–29194. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M102815200
Haruta M, Tan LX, Bushey DB, Swanson SJ, Sussman MR (2018) Environmental and genetic factors regulating localization of the plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Physiol 176:364–377. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01126
Hayta S, Smedley MA, Demir SU, Blundell R, Hinchliffe A, Atkinson N, Harwood WA (2019) An efficient and reproducible agrobacterium-mediated transformation method for hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Methods 15:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0503-z
He Y, Jones HD, Chen S, Chen XM, Wang DW, Li KX, Wang DS, Xia LQ (2010) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum cv Stewart) with improved efficiency. J Exp Bot 61:1567–1581. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq035
Hensel G, Marthe C, Kumlehn J (2017) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of wheat using immature embryos. In: Bhalla P, Singh M (eds) Wheat biotechnology. Methods in molecular biology, vol 1679. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7337-8_8
Ishida Y, Tsunashima M, Hiei Y, Komari T (2015) Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) transformation using immature embryos. In: Wang K (ed) Agrobacterium protocols. Methods in molecular biology, vol 1223. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1695-5_15
Itakura K, Hirose T, Crea R, Riggs AD, Heyneker HL, Bolivar F, Boyer HW (1977) Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science 198:1056–1063. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.412251
Ji Q, Xu X, Wang K (2013) Genetic transformation of major cereal crops. Int J Dev Biol 57:495–508. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.130244kw
Jordan MC (2000) Green fluorescent protein as a visual marker for wheat transformation. Plant Cell Rep 19:1069–1075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990000246
Li Z, Jayasankar S, Gray DJ (2001) Expression of a bifunctional green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion marker under the control of three constitutive promoters and enhanced derivatives in transgenic grape (Vitis vinifera). Plant Sci 160:877–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00336-3
Li J, Zhang S, Zhang R, Gao J, Qi Y, Song G, Li W, Li Y, Li G (2021a) Efficient multiplex genome editing by CRISPR/Cas9 in common wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 19:427–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13508
Li JY, Jiao G, Sun Y, Chen J, Zhong Y, Yan L, Jiang D, Ma Y, Xia L (2021b) Modification of starch composition, structure and properties through editing of TaSBEIIa in both winter and spring wheat varieties by CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Biotechnol J 19:937–951. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13519
Liang Z, Chen K, Zhang Y, Liu J, Yin K, Qiu JL, Gao C (2018) Genome editing of bread wheat using biolistic delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 in vitro transcripts or ribonucleoproteins. Nat Protoc 13:413–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.145
Liu X, Shangguan Y, Zhu J, Lu Y, Han B (2013) The rice OsLTP6 gene promoter directs anther-specific expression by a combination of positive and negative regulatory elements. Planta 238:845–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1934-9
Liu J, Xia C, Dong H, Liu P, Yang R, Zhang L, Liu X, Jia J, Kong X, Sun J (2022) Wheat Male sterile 2 reduces the ROS levels to inhibit anther development by deactivating ROS modulator 1. Mol Plant 15:1428–1439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2022.07.010
Ni F, Qi J, Hao Q, Lyu B, Luo MC, Wang Y, Chen F, Wang S, Zhang C, Epstein L, Zhao X, Wang H, Zhang X, Chen C, Sun L, Fu D (2017) Wheat Ms2 encodes for an orphan protein that confers male sterility in grass species. Nat Commun 8:15121. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15121
Pallotta MA, Warner P, Kouidri A, Tucker EJ, Baes M, Suchecki R, Watson-Haigh N, Okada T, Garcia M, Sandhu A, Singh M, Wolters P, Albertsen MC, Cigan AM, Baumann U, Whitford R (2019) Wheat ms5 male-sterility is induced by recessive homoeologous A and D genome non-specific lipid transfer proteins. Plant J 99:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14350
Qi X, Zhang C, Zhu J, Liu C, Huang C, Li X, Xie C (2020) Genome editing enables next-generation hybrid seed production technology. Mol Plant 13:1262–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.003
Quaedvlieg NE, Schlaman HR, Admiraal PC, Wijting SE, Stougaard J, Spaink HP (1998) Fusions between green fluorescent protein and beta-glucuronidase as sensitive and vital bifunctional reporters in plants. Plant Mol Biol 37:715–727. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006068129255
Rooke L, Steele SH, Barcelo P, Shewry PR, Lazzeri PA (2003) Transgene inheritance, segregation and expression in bread wheat. Euphytica 129:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022296017801
Sanchez-Leon S, Gil-Humanes J, Ozuna CV, Gimenez MJ, Sousa C, Voytas DF, Barro F (2017) Low-gluten, nontransgenic wheat engineered with CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Biotechnol J 16:902–910. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12837
Sheen J, Hwang S, Niwa Y, Kobayashi H, Galbraith DW (1995) Green-fluorescent protein as a new vital marker in plant cells. Plant J 8:777–784. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.08050777.x
Smedley MA, Harwood WA (2015) Gateway®-compatible plant transformation vectors. In: Wang K (ed) Agrobacterium protocols. Methods in molecular biology, vol 1223. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1695-5_1
Sparks CA, Jones HD (2014) Genetic transformation of wheat via particle bombardment. In: Henry R, Furtado A (eds) Cereal genomics. Methods in molecular biology, vol 1099. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-715-0_17
Tang H, Liu H, Zhou Y, Liu H, Du L, Wang K, Ye X (2021) Fertility recovery of wheat male sterility controlled by Ms2 using CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Biotechnol J 19:224–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13482
Tanz SK, Castleden I, Small ID, Millar AH (2013) Fluorescent protein tagging as a tool to define the subcellular distribution of proteins in plants. Front Plant Sci 24(4):214. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00214
Thompson MV, Wolniak SM (2008) A plasma membrane-anchored fluorescent protein fusion illuminates sieve element plasma membranes in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant Physiol 146:1599–1610. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.113274
Tian B, Navia-Urrutia M, Chen Y, Brungardt J, Trick HN (2019) Biolistic transformation of wheat. In: Kumar S, Barone P, Smith M (eds) Transgenic plants. Methods in molecular biology, vol 1864. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8778-8_9
Tucker EJ, Baumann U, Kouidri A, Suchecki R, Baes M, Garcia M, Okada T, Dong C, Wu Y, Sandhu A, Singh M, Langridge P, Wolters P, Albertsen MC, Cigan AM, Whitford R (2017) Molecular identification of the wheat male fertility gene Ms1 and its prospects for hybrid breeding. Nat Commun 8:869. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00945-2
Wan Y, Layton J (2006) Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). In: Wang K (ed) Agrobacterium protocols. Methods in molecular biology, vol 343. Humana Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59745-130-4:245
Wang Y, Cheng X, Shan Q, Zhang Y, Liu J, Gao C, Qiu JL (2014) Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew. Nat Biotechnol 32:947–951. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2969
Wang K, Liu H, Du L, Ye X (2017a) Generation of marker-free transgenic hexaploid wheat via an agrobacterium-mediated co-transformation strategy in commercial Chinese wheat varieties. Plant Biotechnol J 15:614–623. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12660
Wang Z, Li J, Chen S, Heng Y, Chen Z, Yang J, Zhou K, Peic J, He H, Xing Deng W, Mac L (2017b) Poaceaespecific MS1 encodes a phospholipid-binding protein for male fertility in bread wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:12614–12619. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1715570114
Wang K, Shi L, Liang X, Zhao P, Wang W, Liu J, Chang Y, Hiei Y, Yanagihara C, Du L, Ishida Y, Ye X (2022) The gene TaWOX5 overcomes genotype dependency in wheat genetic transformation. Nat Plants 8:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-021-01085-8
Whitford R, Fleury D, Reif JC, Garcia M, Okada T, Korzun V, Langridge P (2013) Hybrid breeding in wheat: technologies to improve hybrid wheat seed production. J Exp Bot 64:5411–5428. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert333
Wright M, Dawson J, Dunder E, Suttie J, Reed J, Kramer C, Chang Y, Novitzky R, Wang H, Artim-Moore L (2001) Efficient biolistic transformation of maize (Zea mays L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using the phosphomannose isomerase gene, pmi, as the selectable marker. Plant Cell Rep 20:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990100318
Xia C, Zhang L, Zou C, Gu Y, Duan J, Zhao G, Wu J, Liu Y, Fang X, Gao L, Jiao Y, Sun J, Pan Y, Liu X, Jia J, Kong X (2017) A TRIM insertion in the promoter of Ms2 causes male sterility in wheat. Nat Commun 8:15407. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15407
Zacharias DA, Violin JD, Newton AC, Tsien RY (2002) Partitioning of lipid-modified monomeric GFPs into membrane microdomains of live cells. Science 296:913–916. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1068539
Zhang D, Wu S, An X, Xie K, Dong Z, Zhou Y, Xu L, Fang W, Liu S, Liu S, Zhu T, Li J, Rao L, Zhao J, Wan X (2018) Construction of a multicontrol sterility system for a maize male-sterile line and hybrid seed production based on the ZmMs7 gene encoding a PHD-finger transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol J 16:459–471
Zhang Z, Hua L, Gupta A, Tricoli D, Edwards KJ, Yang B, Li W (2019) Development of an agrobacterium-delivered CRISPR/Cas9 system for wheat genome editing. Plant Biotechnol J 17:1623–1635. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13088
Zhang S, Zhang R, Gao J, Song G, Li J, Li W, Qi Y, Li Y, Li G (2021) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing for wheat grain quality improvement. Plant Biotechnol J 19:1684–1686. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13647
Zhou X, Carranco R, Vitha S, Hall TC (2005) The dark side of green fluorescent protein. New Phytol 168:313–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01489.x
Zhou W, Huang J, Watson AM, Hong Y (2012) W:: Neo: a novel dual-selection marker for high efficiency gene targeting in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31997. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031997
Acknowledgements
Prof. Leszek A. Łyżnik is acknowledged for his valuable comments on the manuscript. The author thanks Stefan Smoleński for technical assistance in the growth chamber. Prof. Wacław Orczyk, Institute of Plant Breeding, Radzików, is acknowledged for a gift of pBract211-derived vectors.
Funding
This work was supported by the NCBR Grant BIOSTRATEG3/343665/6/NCBR/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author designed and performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author states no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Rachel Wells.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Szabała, B.M. A bifunctional selectable marker for wheat transformation contributes to the characterization of male-sterile phenotype induced by a synthetic Ms2 gene. Plant Cell Rep 42, 895–907 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-02998-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-02998-8