Abstract
Key message
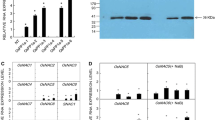
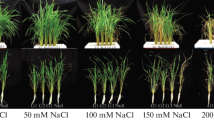
Our results indicate that OsPGK2a-P gene is differentially regulated in contrasting rice cultivars under stress and its overexpression confers salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco.
Abstract
Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK; EC = 2.7.2.3) plays a major role for ATP production during glycolysis and 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate production to participate in the Calvin cycle for carbon fixation in plants. Whole genome analysis of rice reveals the presence of four PGK genes (OsPgks) on different chromosomes. Comparative expression analysis of OsPgks in rice revealed highest level of transcripts for OsPgk2 at most of its developmental stages. Detailed characterization of OsPgk2 transcript and protein showed that it is strongly induced by salinity stress in two contrasting genotypes of rice, i.e., cv IR64 (salt sensitive) and landrace Pokkali (salt tolerant). Ectopic expression of OsPgk2a-P (isolated from Pokkali) in transgenic tobacco improved its salinity stress tolerance by higher chlorophyll retention and enhanced proline accumulation, besides maintaining better ion homeostasis. Ectopically expressing OsPgk2a-P transgenic tobacco plants showed tall phenotype with more number of pods than wild-type plants. Therefore, OsPgk2a-P appears to be a potential candidate for increasing salinity stress tolerance and enhanced yield in crop plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Chl:
-
Chloroplastic
- Cyt:
-
Cytoplasmic
- GA:
-
Gallic acid
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PGK2:
-
Phosphoglycerate kinase protein 2
- PGK2a-P:
-
PGK2a gene from rice landrace Pokkali
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- VC:
-
Vector control
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Aharon R, Shahak Y, Wininger S, Bendov R, Kapulnik Y, Galili G (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane aquaporin in transgenic tobacco improves plant vigor under favorable growth conditions but not under drought or salt stress. Plant Cell 15:439–447
Alam I, Lee DG, Kim KH, Park CH, Sharmin SA, Lee H, Oh KW, Yun BW, Lee BH (2010) Proteome analysis of soybean roots under waterlogging stress at an early vegetative stage. J Biosci 35:49–62
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Anderson LE, Advani VR (1970) Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. Three distinct isoenzymes associated with the reductive pentose phosphate cycle. Plant Physiol 45:583–585
Anderson LE, Carol AA, Bryant JA (2003) Calvin cycle enzymes in the nucleus. PhysiolBiochem Cult Plants 35:309–316
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts.Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bohnert HJ, Ayoubi P, Borchert C, Bressan RA, Burnap RL, Cushman JC, Cushman MA, Deyholos M, Fischer R, Galbraith DW, Hasegawa PM, Jenks M, Kawasaki S, Koiwa H, Kore-eda S, Lee BH, Michalowski CB, Misawa E, Nomura M, Ozturk N, Postier B, Prade R, Song CP, Tanaka Y, Wang H, Zhu JK (2001) A genomics approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant PhysiolBiochem 39:295–311
Bosco MB, Aleanzi MC, Iglesias AA (2012) Plastidicphosphoglycerate kinase from Phaeodactylumtricornutum: on the critical role of cysteine residues for the enzyme function. Protist 163:188–203
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brice DC, Bryant JA, Dambrauskas G, Drury SC, Littlechild JA (2004) Cloning and expression of cytosolic phosphoglycerate kinase from pea (PisumsativumL.). J Expt Bot 55:955–956
Castillejo MA, Maldonado AM, Ogueta S, Jorrín JV (2008) Proteomic analysis of responses to drought stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) leaves by 2DE gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Open Proteom J 1:59–71
Cavell S, Scopes RK (1976) Isolation and characterisation of the ‘Photosynthetic’ phosphoglycerate kinase from Beta vulgaris. Eur J Biochem 63:483–490
Chao S, Raines CA, Longstaff M, Sharp PJ, Gale MD, Dyer TA (1989) Chromosomal location and copy number in wheat and some of its close relatives of genes for enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet 218:423–430
Chiarelli LR, Morera SM, Bianchi P, Fermo E, Zanella A, Galizzi A, Valentini G (2012) Molecular insights on pathogenic effects of mutations causing phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency. Plos One 7(2):e32065
Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ (2004) The jalview java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 20:426–427
Danshina PV, Geyer CB, Dai Q, Goulding EH, Willis WD, Kitto GB, McCarrey JR, Eddy EM, O’Brien DA (2010) Phosphoglycerate kinase 2 (PGK2) is essential for sperm function and male fertility in mice. Biol Rep 82:136–145
Fotopoulos V, De Tullio MC, Barnes J, Kanellis AK (2008) Altered stomatal dynamics in ascorbate oxidase over-expressing tobacco plants suggest a role for dehydroascorbate signaling. J Expt Bot 59:729–737
Fox TC, Green BJ, Kennedy RA, Rumpho ME (1998) Changes in hexokinase activity in Echinochloaphyllopogon and Echinochloa crus-pavonis in response to abiotic stress. Plant Physiol 118:1403–1409
Garg AK, Kim JK, Owens TG, Ranwala AP, Choi YD, Kochian LV, Wu RJ (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abitoic stresses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15898–15903
Ghosh A, Pareek A, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL (2014) A glutathione responsive rice glyoxalase II, OsGLYII-2, functions in salinity adaptation by maintaining better photosynthesis efficiency and anti-oxidant pool. Plant J 80:93–105
Gruber V, Blanchet S, Diet A, Zahaf O, Boualem A, Kakar K et al (2009) Identification of transcription factors involved in root apex responses to salt stress in Medicagotruncatula. Mol Genet Gen 281:55–66
Gupta AK, Kaur N (2005) Sugar signalling and gene expression in relation to carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stresses in plants. J Biosci 30:761–776
Hossain Z, Khatoon A, Komatsu S (2013) Soybean proteomics for unraveling abiotic stress response mechanism. J Proteome Res 12:4670–4684
Houde M, Belcaid M, Ouellet F, Danyluk J, Monroy AF, Dryanova A, Gulick P, Bergeron A, Laroche A, Links MG, MacCarthy L, Crosby WL, Sarhan F (2006) Wheat EST resources for functional genomics of abiotic stress. BMC Genom 7:149
Hruz T, Laule O, Szabo G, Wessendorp F, Bleuler S, Oertle L, Widmayer P, Gruissem W, Zimmermann P (2008) Genevestigator V3: a reference expression database for the meta-analysis of transcriptomes. Adv Bioinfo. Article ID 420747
Jeffery CJ (1999) Moonlighting proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 24:8–11
Joao HC, Williams RJ (1993) The anatomy of a kinase and the control of phosphate transfer. Eur J Biochem 216:1–18
Joao HC, Williams RJP, Littlechild JA, Nagasuma R, Watson HC (1992) An investigation of large inhibitors binding to phosphoglycerate kinase and their effect on anion activation. Eur J Biochem 205:1077–1088
Kaiser WM, Heber U (1981) Photosynthesis under osmotic stress. Effect of high solute concentration on the permeability of the chloroplast envelop and on the activity of stroma enzymes. Planta 153:423–429
Karan R, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2009) Histidine kinase and response regulator genes as they relate to salinity tolerance in rice. Funct Integr Genom 9:411–417
Kaur C, Kumar G, Kaur S, Ansari MW, Pareek A, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL (2015) Molecular cloning and characterization of salt overly sensitive gene promoter from Brassica juncea (BjSOS2). Mol Biol Rep 42:1139–1148
Khatoon A, Rehman S, Hiraga S, Makino T, Komatsu S (2012) Organ-specific proteomics analysis for response mechanism in soybean seedlings under flooding stress. J Proteom 75:5706–5723
Kim DY, Hong MJ, Jang JH, Seo YW (2012) cDNA-AFLP analysis reveals differential gene expression in response to salt stress in Brachypodiumdistachyon. Genes Genom 34:475–484
Komatsu S, Hossain Z (2013) Organ-specific proteome analysis for identification of abiotic stress response mechanism in crop. Front Plant Sci 4:71
Kopke-Secundo E, Molnar I, Schnarrenberger C (1990) Isolation and characterization of the cytosolic and chloroplastic 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from spinach leaves. Plant Physiol 93:40–47
Kostadinova N, Vassilev S, Spasova B, Angelova M (2011) Cold stress in antarctic fungi targets enzymes of the glycolytic pathway and tricarboxylicacid cycle. Biotech Biotechnol Equip 25:50–57
Kumar G, Kushwaha HR, Panjabi-Sabharwal V, Kumari S, Joshi R, Karan R, Mittal S, Singla Pareek SL, Pareek A (2012) Clustered metallothionein genes are co-regulated in rice and ectopic expression of OsMT1e-P confers multiple abiotic stress tolerance in tobacco via ROS scavenging. BMC Plant Biol 12:107
Kumari S, Panjabi Nee Sabharwal V, Kushwaha HR, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2009) Transcriptome map for seedling stage specific salinity stress response indicates a specific set of genes as candidate for saline tolerance in Oryza sativa L. Funct Intgr Genom 9:109–123
Kumari S, Joshi R, Singh K, Roy S, Tripathi AK, Singh P, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2015) Expression of a cyclophilin OsCyp2-P isolated from a salt-tolerant landrace of rice in tobacco alleviates stress via ion homeostasis and limiting ROS accumulation. Funct Integr Genom 15:395–412
Kundu SK, Tigerstedt PMA (1998) Variation in net photosynthesis, stomatal characteristics, leaf area and whole-plant phytomass production among ten provenances of neem (Azadirachtaindica). Tree Physiol 19:47–52
Lakra N, Nutan KK, Das P, Anwar K, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2015) A nuclear-localized histone-gene binding protein from rice (OsHBP1b) functions in salinity and drought stress tolerance by maintaining chlorophyll content and improving the antioxidant machinery. J Plant Physiol 176:36–46
Lay AJ, Jiang XM, Daly E, Sun L, Hogg PJ (2002) Plasmin reduction by phosphoglycerate kinase is a thiol-independent process. J Biol Chem 277:9062–9068
Lin JW, Ding MP, Hsu YH, Tsai CH (2007) Chloroplast phosphoglycerate kinase, a gluconeogenetic enzyme, is required for efficient accumulation of Bamboo mosaic virus. Nucl Acids Res 35:424–432
Longstaff M, Raines CA, McMorrow EM, Bradbeer JW, Dyer TA (1989) Wheat phosphoglycerate kinase: evidence for recombination between the genes for the chloroplastic and cytosolic enzymes. Nucl Acids Res 17:6569–6580
McHarg J, Kelly SM, Price NC, Cooper A, Littlechild JA (1999) Site-directed mutagenesis of proline 204 in the ‘hinge’ region of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. Eur J Biochem 259:939–945
McMorrow EM, Bradbeer JW (1987) The regulation of phosphoglycerate kinase in the chloroplasts and cytoplasm of barley leaves. In J Biggins (ed) Progress in photosynthesis research, pp 333–336, Vol III. MartinusNijhoff, Netherlands
McMorrow EM, Bradbeer JW (1990) Separation, purification, and comparative properties of chloroplast and cytoplasmic phosphoglycerate kinase from barley leaves. Plant Physiol 93:374–383
Ogino T, Iwama M, Kinouchi J, Shibagaki Y, Tsukamoto T, Mizumoto K (1999) Involvement of a cellular glycolytic enzyme, phosphoglycerate kinase, in Sendai virus transcription. J Biol Chem 274:35999–36008
Okuma E, Soeda K, Tada M, Murata Y (2000) Exogenous proline mitigates the inhibition of growth of Nicotianatabacum cultured cells under saline conditions. Soil Sci Pl Nut 46:257–263
Pacold I, Anderson LE (1975) Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. VI. Pea leaf 3-phosphoglycerate kinases. Plant Physiol 55:168–171
Pareek A, Singla SL, Grover A (1995) Immunological evidence for accumulation of two high-molecular-weight (104 and 90 kDa) HSPs in response to different stresses in rice and in response to high temperature stress in diverse plant genera. Plant Mol Biol 29:293–301
Pareek A, Singh A, Kumar M, Kushwaha HR, Lynn AM, Singla-Pareek SL (2006) Whole genome analysis of Oryza sativa L. reveals similar architecture of two-component-signaling-machinery with Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 142:380–397
Pareek A, Sopory SK, Bohnert HJ, Govindjee (2010) Abiotic stress adaptation in plants: physiological, molecular and genomic foundation. Springer, Berlin, pp 503–521
Qing Y, Chen ZZ, Zhou XF, Yin HB, Li X, Xin XF, Hong XH, Zhu JK, Gong ZZ (2009) Overexpression of SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:22–31
Rus A, Yokoi S, Sharkhuu A, Reddy M, Lee BH, Matsumoto TK, Koiwa H, Zhu JK, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2001) AtHKT1 is a salt tolerance determinant that controls Na(+) entry into plant roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14150–14155
Sarowar S, Lee JY, Ahn ER, Pai HS (2008) A role of hexokinases in plant resistance to oxidative stress and pathogen infection. J Plant Biol 51:341–346
Sawyer GM, Monzingo AF, Poteet EC, O’Brien DA, Robertus JD (2008) X-ray analysis of phosphoglycerate kinase 2, a sperm-specific isoform from Musmusculus. Proteins 71:1134–1144
Senadheera P, Singh RK, Maathuis FJM (2009) Differentially expressed membrane transporters in rice roots may contribute to cultivar dependent salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 60:2553–2563
Shah N, Bradbeer JW (1994) The occurrence of chloroplastic and cytosolic isoenzymes of phosphoglycerate kinase in a range of plant species. Planta 193:232–237
Shetty S, Ganachari M, Liu MC, Azghani A, Muniyappa H, Idell S (2005) Regulation of urokinase receptor expression by phosphoglycerate kinase is independent of its catalytic activity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L591–L598
Singh R, Jwa NS (2013) Understanding the responses of rice to environmental stress using proteomics. J Proteome Res 12:4652–4669
Singla-Pareek SL, Reddy MK, Sopory SK (2003) Genetic engineering of the glyoxalase pathway in tobacco leads to enhanced salinity tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 100:14672–14677
Soda N, Kushwaha HR, Soni P, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2013) A suite of new genes defining salinity stress tolerance in seedlings of contrasting rice genotypes. Funct Integr Genom 13:351–365
Sorenson R, Bailey-Serres J (2014) Selective mRNA sequestration by OLIGOURIDYLATE BINDING PROTEIN 1 contributes to translational control during hypoxia in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 111:2373–2378
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tripathi AK, Pareek A, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL (2012) Narrowing down the targets for yield improvement in rice under normal and abiotic stress conditions via expression profiling of yield-related genes. Rice 5:37
Troncoso-Ponce MA, Rivoal J, Venegas-Calerón M, Dorion S, Sánchez R, Cejudo FJ, Garcés R, Martínez-Force E (2012) Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of three phosphoglycerate kinase isoforms from developing sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seeds. Phytochem 79:27–38
Tsukamoto Y, Fukushima Y, Hara S, Hisabori T (2013) Redox control of the activity of phosphoglycerate kinase in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Plant Cell Physiol 54:484–491
Walia H, Wilson C, Wada H, Condamine P, Cui XP, Close TJ (2006) Expression analysis of barley (Hordeumvulgare L.) during salinity stress. Funct Integr Gen 6:143–156
Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P, Ismail AM, Xu J, Cui X, Close TJ (2007) Array-based genotyping and expression analysis of barley cv Maythorpe and Golden promise. BMC Genom 8:87
Walia H, Wilson C, Ismail AM, Close TJ, Cui X (2009) Comparing genomic expression patterns across plant species reveals highly diverged transcriptional dynamics in response to salt stress. BMC Genom 10:398
Xu Z, Zhou G (2008) Responses of leaf stomatal density to water status and its relationship with photosynthesis in a grass. J Expt Bot 59:3317–3325
Zhou S, Wei S, Boone B, Levy S (2007) Microarray analysis of genes affected by salt stress in tomato. Afr J Environ Sci Tech 1:014–026
Acknowledgments
Work carried out in this paper has been supported by funds available from UGC Resource Networking, Capacity building funds from JNU, Department of Science and Technology, Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India. R.K. gratefully acknowledges the award of research fellowship from UGC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by N. Sreenivasulu.
Rohit Joshi and Ratna Karan have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1
Total cDNA sequence of OsPgk2 along with the deduced amino acid sequence. (TIFF 271 kb)
Supplementary material 2
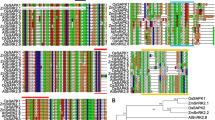
(A) Multiple alignments of IR64 and Pokkali phosphoglycerate kinase amino acid sequence with different isoforms of OsPGK2. (B) The putative gene structure of OsPGK2a, OsPGK2b and OsPGK2c were obtained from TIGR database to show the alternate splicing event between the OsPGK2 isoforms. (TIFF 80895 kb)
Supplementary material 3
Expression pattern of OsPgk1, OsPgk2, OsPgk3 and OsPgk4at various developmental stages of Oryza sativa based on microarray data (www.genevestigator.com). The expression data shown here is normalized, high quality and manually curated data obtained from several hundreds of independent experiments. The stage of development of plant is also shown diagrammatically in the figure. (TIFF 25296 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, R., Karan, R., Singla-Pareek, S.L. et al. Ectopic expression of Pokkali phosphoglycerate kinase-2 (OsPGK2-P) improves yield in tobacco plants under salinity stress. Plant Cell Rep 35, 27–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1864-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1864-z