Abstract
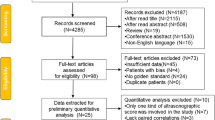
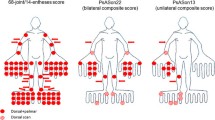
With the aim to develop and validate a clinical + ultrasound (US) inflammation score in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for use in clinical practice, a mixed-method study was conducted. The theoretical development of the index was achieved with qualitative methodology (discussion group and Delphi survey). Subsequently, a cross-sectional study was carried out to analyse issues related to scoring and validation of the new index. RA patients underwent clinical [28 swollen and tender joints count, patient and physician global assessment (PhGA), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP)], and US assessments [synovitis or tenosynovitis by grey-scale (GS) and power Doppler (PD) of 42 structures]. An index was created based on statistical models and expert interaction. Construct validity was tested by correlation with DAS28, SDAI, CDAI, and PhGA. Reliability was evaluated in a subgroup of patients with the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). US assessment, CRP, and swollen joints were the items that passed the prioritization phase (Delphi study). For the cross-sectional study, 281 patients were randomly divided into design (n = 141) and validation samples (n = 140). The combination of US sites chosen (7 bilaterally) detected the maximum proportion of synovitis and PD present. Three scoring methods were tested: semiquantitative (0–3 GS + 0–3 PD), dichotomous (0/1 GS + 0/1 PD), and qualitative (0/1 based on algorithm). All showed strong correlation with activity measures (ρ ≥ 0.60), and reliability (ICC 0.89–0.93). The index with best parameters of validity, feasibility, and reliability was the qualitative. The final index chosen was the sum of swollen joint count, US qualitative score, and CRP. The UltraSound Activity score is a valid and reliable measure of inflammation in RA equal to the sum of 28 SJC, a simplified (0/1) US assessment of 11 structures and CRP. It is necessary further investigation to demonstrate additional value over existing indices.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data sets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Buchbinder R, Bombardier C, Yeung M, Tugwell P (1995) Which outcome measures should be used in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials? Clinical and quality-of-life measures’ responsiveness to treatment in a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 38(11):1568–1580 (PubMed PMID: 7488277)
Kirwan JR (1993) Outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials: assessing improvement. J Rheumatol 20(3):543–545 (PubMed PMID: 8478868)
van der Heijde DM, van’t Hof MA, van Riel PL, Theunisse LA, Lubberts EW, van Leeuwen MA et al (1990) Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis 49(11):916–920 (PubMed PMID: 2256738. Epub 1990/11/01. Eng)
van der Heijde DM, van’t Hof M, van Riel PL, van de Putte LB (1993) Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol 20(3):579–581 (PubMed PMID: 8478878. Epub 1993/03/01. Eng)
Prevoo ML, van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38(1):44–48 (PubMed PMID: 7818570. Epub 1995/01/01. Eng)
Inoue E, Yamanaka H, Hara M, Tomatsu T, Kamatani N (2007) Comparison of Disease Activity Score (DAS)28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate and DAS28-C-reactive protein threshold values. Ann Rheum Dis 66(3):407–409 (PubMed PMID: 16926186. Epub 2006/08/24. Eng)
Matsui T, Kuga Y, Kaneko A, Nishino J, Eto Y, Chiba N et al (2007) Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) using C-reactive protein underestimates disease activity and overestimates EULAR response criteria compared with DAS28 using erythrocyte sedimentation rate in a large observational cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Japan. Ann Rheum Dis 66(9):1221–1226 (PubMed PMID: 17369281. Epub 2007/03/21. Eng)
Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Schiff MH, Kalden JR, Emery P, Eberl G et al (2003) A simplified disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis for use in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42(2):244–257 (PubMed PMID: 12595618. Epub 2003/02/22. Eng)
Aletaha D, Nell VP, Stamm T, Uffmann M, Pflugbeil S, Machold K et al (2005) Acute phase reactants add little to composite disease activity indices for rheumatoid arthritis: validation of a clinical activity score. Arthritis Res Ther 7(4):R796–R806 (PubMed PMID: 15987481. Epub 2005/07/01. Eng)
Aletaha D, Smolen J (2005) The Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI): a review of their usefulness and validity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23(5 Suppl 39):S100–S108 (PubMed PMID: 16273793. Epub 2005/11/09. Eng)
Bakker MF, Jacobs JW, Verstappen SM, Bijlsma JW (2007) Tight control in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: efficacy and feasibility. Ann Rheum Dis 66(Suppl 3: iii):56–60 (PubMed PMID: 17934098. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2095293. Epub 2007/11/21. Eng)
Taylor WJ, Harrison AA, Highton J, Chapman P, Stamp L, Dockerty J et al (2008) Disease Activity Score 28-ESR bears a similar relationship to treatment decisions across different rheumatologists, but misclassification is too frequent to replace physician judgement. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(4):514–518 (PubMed PMID: 18321947. Epub 2008/03/07. Eng)
Szkudlarek M, Court-Payen M, Strandberg C, Klarlund M, Klausen T, Ostergaard M (2001) Power Doppler ultrasonography for assessment of synovitis in the metacarpophalangeal joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum 44(9):2018–2023 (PubMed PMID: 11592362. Epub 2001/10/11. Eng)
Backhaus M, Ohrndorf S, Kellner H, Strunk J, Backhaus TM, Hartung W et al (2009) Evaluation of a novel 7-joint ultrasound score in daily rheumatologic practice: a pilot project. Arthritis Rheum 61(9):1194–1201 (PubMed PMID: 19714611. Epub 2009/08/29. Eng)
Naredo E, Rodriguez M, Campos C, Rodriguez-Heredia JM, Medina JA, Giner E et al (2008) Validity, reproducibility, and responsiveness of a twelve-joint simplified power doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59(4):515–522 (PubMed PMID: 18383408. Epub 2008/04/03. Eng)
Hameed B, Pilcher J, Heron C, Kiely PD (2008) The relation between composite ultrasound measures and the DAS28 score, its components and acute phase markers in adult RA. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(4):476–480 (PubMed PMID: 18281367. Epub 2008/02/19. Eng)
Mandl P, Naredo E, Wakefield RJ, Conaghan PG, D’Agostino MA (2011) A systematic literature review analysis of ultrasound joint count and scoring systems to assess synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis according to the OMERACT filter. J Rheumatol 38(9):2055–2062 (PubMed PMID: 21885517. Epub 2011/09/03. Eng)
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62(9):2569–2581 (PubMed PMID: 20872595. Epub 2010/09/28. Eng)
D’Agostino MA, Wakefield RJ, Berner-Hammer H, Vittecoq O, Filippou G, Balint P et al (2016) Value of ultrasonography as a marker of early response to abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: results from the APPRAISE study. Ann Rheum Dis 75(10):1763–1769 (PubMed PMID: 26590174. Pubmed Central PMCID: 5036216. Epub 2015/11/22. Eng)
van Riel PL, van Gestel AM (2000) Clinical outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 59(Suppl 1):i28–i31 (PubMed PMID: 11053082. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC1766622)
Zammurrad S, Munir W, Farooqi A (2013) Disease activity score in rheumatoid arthritis with or without secondary fibromyalgia. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 23(6):413–417 (PubMed PMID: 23763802)
Leeb BF, Haindl PM, Maktari A, Nothnagl T, Rintelen B (2007) Disease activity score-28 values differ considerably depending on patient’s pain perception and sex. J Rheumatol 34(12):2382–2387 (PubMed PMID: 17985407)
Balsa A, Carmona L, Gonzalez-Alvaro I, Belmonte MA, Tena X, Sanmarti R et al (2004) Value of Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) and DAS28-3 compared to American College of Rheumatology-defined remission in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 31(1):40–46 (PubMed PMID: 14705217)
Naredo E, Collado P, Cruz A, Palop MJ, Cabero F, Richi P et al (2007) Longitudinal power Doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis: predictive value in disease activity and radiologic progression. Arthritis Rheum 57(1):116–124 (PubMed PMID: 17266071)
Backhaus TM, Ohrndorf S, Kellner H, Strunk J, Hartung W, Sattler H et al (2013) The US7 score is sensitive to change in a large cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis over 12 months of therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 72(7):1163–1169 (PubMed PMID: 22956596. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC3686255)
Ohrndorf S, Backhaus M (2013) Advances in sonographic scoring of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 72(Suppl 2):ii69–ii75 (PubMed PMID: 23253922)
Yoshimi R, Ihata A, Kunishita Y, Kishimoto D, Kamiyama R, Minegishi K et al (2015) A novel 8-joint ultrasound score is useful in daily practice for rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 25(3):379–385 (PubMed PMID: 25401228)
Leng XF, Zhu Y, Wang GP, Jin J, Xian L, Zhang YH (2016) Accuracy of ultrasound for the diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis 8(8):2146–2157 (PubMed PMID: 27621871. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC4999759)
Dougados M, Jousse-Joulin S, Mistretta F, d’Agostino MA, Backhaus M, Bentin J et al (2010) Evaluation of several ultrasonography scoring systems for synovitis and comparison to clinical examination: results from a prospective multicentre study of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(5):828–833 (PubMed PMID: 19740905)
Hartung W, Kellner H, Strunk J, Sattler H, Schmidt WA, Ehrenstein B et al (2012) Development and evaluation of a novel ultrasound score for large joints in rheumatoid arthritis: one year of experience in daily clinical practice. Arthritis Care Res 64(5):675–682 (PubMed PMID: 22183834)
Boesen M, Ellegaard K, Boesen L, Cimmino MA, Jensen PS, Terslev L et al (2012) Ultrasound Doppler score correlates with OMERACT RAMRIS bone marrow oedema and synovitis score in the wrist joint of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ultraschall Med 33(7):E166–E172 (PubMed PMID: 21259184)
de Miguel E, Pecondon-Espanol A, Castano-Sanchez M, Corrales A, Gutierrez-Polo R, Rodriguez-Gomez M et al (2017) A reduced 12-joint ultrasound examination predicts lack of X-ray progression better than clinical remission criteria in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 37(8):1347–1356 (PubMed PMID: 28389854)
Damjanov N, Radunovic G, Prodanovic S, Vukovic V, Milic V, Simic Pasalic K et al (2012) Construct validity and reliability of ultrasound disease activity score in assessing joint inflammation in RA: comparison with DAS-28. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51(1):120–128 (PubMed PMID: 22072084. Epub 2011/11/11. Eng)
Han J, Geng Y, Deng X, Zhang Z (2016) Subclinical synovitis assessed by ultrasound predicts flare and progressive bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis patients with clinical remission: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheumatol 43(11):2010–2018 (PubMed PMID: 27803342)
Nguyen H, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Gandjbakhch F, Constantin A, Foltz V, Cantagrel A (2014) Prevalence of ultrasound-detected residual synovitis and risk of relapse and structural progression in rheumatoid arthritis patients in clinical remission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53(11):2110–2118 (PubMed PMID: 24929634)
Raffeiner B, Grisan E, Botsios C, Stramare R, Rizzo G, Bernardi L et al (2017) Grade and location of power Doppler are predictive of damage progression in rheumatoid arthritis patients in clinical remission by anti-tumour necrosis factor α. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56(8):1320–1325 (PubMed PMID: 28431141)
Naredo E, Gamero F, Bonilla G, Uson J, Carmona L, Laffon A (2005) Ultrasonographic assessment of inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of extended versus reduced joint evaluation. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23(6):881–884 (PubMed PMID: 16396709)
Alcalde M, D’Agostino MA, Bruyn GA, Moller I, Iagnocco A, Wakefield RJ et al (2012) A systematic literature review of US definitions, scoring systems and validity according to the OMERACT filter for tendon lesion in RA and other inflammatory joint diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51(7):1246–1260 (PubMed PMID: 22378717)
Aga AB, Berner Hammer H, Christoffer Olsen I, Uhlig T, Kvien TK, van der Heijde D et al (2016) Development of a feasible and responsive ultrasound inflammation score for rheumatoid arthritis through a data-driven approach. RMD Open 2(2):e000325 (PubMed PMID: 28074154. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC5174791)
Hammer HB, Kvien TK (2011) Ultrasonography shows significant improvement in wrist and ankle tenosynovitis in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with adalimumab. Scand J Rheumatol 40(3):178–182 (PubMed PMID: 21091275)
Salaffi F, Di Carlo M, Iannone F, Fedele AL, Epis OM, Pellerito R et al (2018) The UltraSound-CLinical ARthritis Activity (US-CLARA) index: properties of a new composite disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 47(5):619–629 (PubMed PMID: 29102157)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge all rheumatologists participants in the study: Andrea Cuervo Aguilera (Hospital Clinic), Anne Riveros (Hospital de Granollers), Basilio Rodríguez Díez (Hospital Vall d´Hebron), Elena Leonor Sirvent Alierta (Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu), Elisabet Montori (Hospital Plató), Jose Miguel Ruiz Martín (Hospital Viladecans), Laura López Vives (Hospital San Rafael), Maria Bonet (Hospital Vilafranca), Melania Martínez Morillo (Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol), Mireia Castillo (Hospital Universitari Mútua Terrassa), Mireia Moreno Martínez-Losa (Hospital Parc Tauli), Patricia Moya (Hospital Sant Pau), Paula Estrada Alarcón (Hospital Moisés Broggi), Sandra Farietta Varela (Hospital Vall d´Hebron), Susana Holgado Pérez (Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol). Also we are thankful to Rafael Curbelo Rodríguez who at the time was working at InMusc and helped with the design of materials and logistics, as well as the help of Esther Martín-Blas (InMusc), who acted as technical secretariat.
Funding
The study was funded by the Societat Catalana de Reumatologia with a grant from Abbvie. The funding body had no role in the design of the study, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was designed by JJdA, LC, and MJGY. MB, SFV, ACA, AR, SHP, DRS, EM, CDT, MPB, BRD, JMRM, PSP, EC, MMML, AED, LLV, JRG, AP, LMS, MMM, PEA, CMP, PM, MC, SRE, EM, and ELSA contributed as panellists for the qualitative part, recruited the patients, and collected the data. Analyses were carried out by MJGY. The manuscript was drafted by JJdA, MJGY, and LC. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the ethics committee of research (ECR) of the Vall d’Hebron hospital (ID-RTF080) as reference and then by all other ECR involved. All patients signed an informed consent prior to their participation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Agustín, J.J., Erra, A., Ponce, A. et al. Measuring inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis with a new clinical and ultrasound index: development and initial validation. Rheumatol Int 39, 2137–2145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04383-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04383-9