Abstract
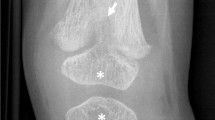
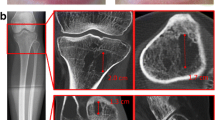
Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is a rare inborn error of bone metabolism caused by various defects in the gene coding for the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSAP). It results in a reduced activity of the TNSAP and elevated concentrations of its substrates, including inorganic pyrophosphate. Clinical features of HPP include defective bone mineralisation with bone deformities, fractures and chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis. Renal damage due to calcification, craniosynostosis and dental abnormalities with premature loss of dentition are further complications. Until now, detailed descriptions of whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) in HPP do not exist. Here, we analysed WB-MRIs of 4 children with the childhood form of HPP. Deformities and defects of the long bones could be seen. All patients showed radiological lesions in the metaphyses of the long bones predominantly in the lower extremities being consistent with hyperaemia and oedema. Differential diagnosis includes an inflammatory process being active in these locations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mornet E (2007) Hypophosphatasia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2:40
Akahoshi T, Murakami Y, Kitasato H (2007) Recent advances in crystal-induced acute inflammation. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19(2):146–150
Beck C, Morbach H, Richl P, Stenzel M, Girschick HJ (2008) How can calcium pyrophosphate crystals induce inflammation in hypophosphatasia or chronic inflammatory joint diseases? Rheumatol Int 29:229–238
Bouchard L, de Medicis R, Lussier A, Naccache PH, Poubelle PE (2002) Inflammatory microcrystals alter the functional phenotype of human osteoblast-like cells in vitro: synergism with IL-1 to overexpress cyclooxygenase-2. J Immunol 168(10):5310–5317
Chuck AJ, Pattrick MG, Hamilton E, Wilson R, Doherty M (1989) Crystal deposition in hypophosphatasia: a reappraisal. Ann Rheum Dis 48(7):571–576
Beck C, Morbach H, Stenzel M, Schneider P, Collmann H, Girschick G, Girschick HJ (2009) Hypophosphatasie. Klin Padiatr 221:219–226
Liu-Bryan R, Pritzker K, Firestein GS, Terkeltaub R (2005) TLR2 signaling in chondrocytes drives calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate and monosodium urate crystal-induced nitric oxide generation. J Immunol 174(8):5016–5023
Mariathasan S, Weiss DS, Newton K, McBride J, O’Rourke K, Roose-Girma M, Lee WP, Weinrauch Y, Monack DM, Dixit VM (2006) Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to toxins and ATP. Nature 440:228–232
Whyte MP (1995) Hypophosphatasia. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly S (eds) The metabolic and molecular basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 4095–4111
Girschick HJ, Schneider P, Kruse K, Huppertz HI (1999) Bone metabolism and bone mineral density in childhood hypophosphatasia. Bone 25(3):361–367
Collmann H, Mornet E, Gattenlohner S, Beck C, Girschick H (2008) Neurosurgical aspects of childhood hypophosphatasia. Childs Nerv Syst 25:217–223
Girschick HJ, Schneider P, Haubitz I, Hiort O, Collmann H, Beer M, Shin YS, Seyberth HW (2006) Effective NSAID treatment indicates that hyperprostaglandinism is affecting the clinical severity of childhood hypophosphatasia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 1:24
Girschick HJ, Seyberth HW, Huppertz HI (1999) Treatment of childhood hypophosphatasia with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Bone 25(5):603–607
Kozlowski K, Sutcliffe J, Barylak A, Harrington G, Kemperdick H, Nolte K, Rheinwein H, Thomas PS, Uniecke W (1976) Hypophosphatasia. Review of 24 cases. Pediatr Radiol 15:103–117
Girschick HJ, Mornet E, Beer M, Warmuth-Metz M, Schneider P (2007) Chronic multifocal non-bacterial osteomyelitis in hypophosphatasia mimicking malignancy. BMC Pediatr 7:3
Whyte MP, Wenkert D, McAlister WH et al (2009) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis mimicked in childhood hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 24(8):1493–1505
Darge K, Jaramillo D, Siegel MJ (2008) Whole-body MRI in children: current status and future applications. Eur J Radiol 68:289–298
Beer M, Stenzel M, Girschick H, Schlegel PG, Darge K (2008) Ganzkörper-MRT bei Kindern mit Verdacht auf Osteonekrose nach intensiver Chemotherapie. Fortschr Röntgenstr 180:238–245
Girschick HJ, Raab P, Surbaum S, Trusen A, Kirschner S, Schneider P, Papadopoulos T, Muller-Hermelink HK, Lipsky PE (2005) Chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis in children. Ann Rheum Dis 64(2):279–285
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to Etienne Mornet for performing the genetic analysis in patients 1, 2 and 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, C., Morbach, H., Wirth, C. et al. Whole-body MRI in the childhood form of hypophosphatasia. Rheumatol Int 31, 1315–1320 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1493-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1493-3