Abstract
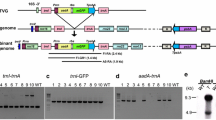
Uniparental inheritance of the chloroplast genome has been observed in a wide variety of green plants. In Chlamydomonas this phenomenon, which can be selectively inhibited by UV irradiation of mt + gametes, has been shown cytologically to be due to the preferential degradation of mt −-derived chloroplast nucleoids in young zygotes. The zygote-specific pair of zys1 genes, zys1A and zys1B, is expressed earliest among five genes isolated from a “10-min” zygote library. We report here that the ZYS1 protein, which is encoded by the invertedly duplicated zys1 gene, accumulates in zygotes and is localized in nuclei. In addition, when mt + gametes (but not mt − gametes) are UV-irradiated before mating, only very limited accumulation of ZYS1 protein can be detected in the resulting zygotes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 July 1998 / 30 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchida, H., Suzuki, L., Anai, T. et al. A pair of invertedly repeated genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii encodes a zygote-specific protein whose expression is UV-sensitive. Curr Genet 36, 232–240 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940050495
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940050495