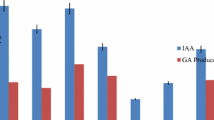
Abstract
The presence of small amount of soluble forms of Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K) and Zinc (Zn) in most soils is one of the limiting factors for agronomic crop production. The current study focuses on Macrotyloma uniflorum (horse gram or gahat), the most commonly cultivated crop in Uttarakhand. The current initiative and study were started, because there is a little information available on the impact of co-inoculation of beneficial fungi on crops in agricultural fields. Aspergillus niger K7 and Penicillium chrysogenum K4 were isolated and selected for the study on the basis of in vitro P, K and Zn-solubilizing activity. The solubilizing efficiency of K4 strain was 140% and K7 was 173.9% for P. However, the solubilizing efficiencies of K4 and K7 were 160% and 138.46% for Zn and 160% and 466% for K, respectively. The field trials were performed for two consecutive years, and growth and yield related parameters were measured for evaluation of the effect of P, K and Zn-solubilizing fungal strains on the crop. All the treatments showed a significant (P < 0.05) increase in growth and yield of M. uniflorum plants over uninoculated control; however, the best treatment was found to be soil inoculated with P. chrysogenum K4 + A. niger K7 in which the yield was enhanced by 71% over control. Thus, the co-inoculation of K4 and K7 strains showed a great potential to improve the growth and yield of plants. Both the fungal strains simultaneously solubilized three important nutritional elements in soil, which is a rare trait. Moreover, the capacity of these fungal strains to enhance the plant root nodulation and microbial count in soil makes the co-inoculation practice quite beneficial for sustainable agriculture.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Rawat J, Sanwal P, Saxena J (2018) Towards the mechanisms of nutrient solubilization and fixation in soil system. In: Meena VS (ed) Role of rhizospheric microbes in soil. Springer, Singapore, pp 229–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0044-8_8
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MHMB, Nahar K, Hossain MS, Mahmud JA, Hossen MS, Masud AAC, Moumita FM (2018) Potassium: a vital regulator of plant responses and tolerance to abiotic stresses. Agronomy 8(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8030031
Suganya A, Saravanan A, Manivannan N (2020) Role of zinc nutrition for increasing zinc availability, uptake, yield, and quality of maize (Zea Mays L.) grains: an overview. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 51(15):2001–2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1820030
Su L, Xie J, Wen W, Li J, Zhou P, An Y (2020) Interaction of zinc and IAA alleviate aluminum-induced damage on photosystems via promoting proton motive force and reducing proton gradient in alfalfa. BMC Plant Biol 20(433):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02643-6
Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP (2014) Does a rhizospheric microorganism enhance K+ availability in agricultural soils. Microbiol Res 169:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.09.003
Dey P, Santhi R, Subramaniam SM, Sellamuthu K (2017) Status of phosphorus and potassium in the indian soils vis-à-vis world soils. Indian J Fertil 13:44–59
Singh VK, Dwivedi BS, Rathore SS, Mishra RP, Satyanarayana T, Majumdar K (2021) Timing potassium applications to synchronize with plant demand. In: Murrell TS, Mikkelsen RL, Sulewski G, Norton R, Thompson ML (eds) Improving potassium recommendations for agricultural crops. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59197-7_13
Shukla AK, Behera SK, Prakash C, Tripathi A, Patra AK, Dwivedi BS, Trivedi V, Rao CS, Chaudhari SK, Das S, Singh AK (2021) Deficiency of phyto-available sulphur, zinc, boron, iron, copper and manganese in soils of India. Sci Rep 11(19760):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-99040-2
Johan PD, Ahmed OH, Omar L, Hasbullah NA (2021) Phosphorus transformation in soils following co-application of charcoal and wood ash. Agronomy 11:1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102010
Manzoor M, Abbasi MK, Sultan T (2017) Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from maize rhizosphere and their potential for rock phosphate solubilization-mineralization and plant growth promotion. Geomicrobiol J 34(1):81–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2016.1146373
Tian J, Ge F, Zhang D, Deng S, Liu X (2021) Roles of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from managing soil phosphorus deficiency to mediating biogeochemical P cycle. Biology (Basel) 10(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020158
Alaylar B, Egamberdieva D, Gulluce M, Karadayi M, Arora NK (2020) Integration of molecular tools in microbial phosphate solubilization research in agriculture perspective. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36(93):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02870-x
Devi R, Kaur T, Kour D, Rana KL, Yadav A, Yadav AN (2020) Beneficial fungal communities from different habitats and their roles in plant growth promotion and soil health. Microb Biosyst 5(1):21–47. https://doi.org/10.21608/mb.2020.32802.1016
Styriakova I, Styriak I, Sasvari T (2004) Extraction of elements from sulphide and silicate concentrates by selected bacillus isolates. Metalurgija 43(4):293–297
Mohamed AH, Abd El-Megeed FH, Hassanein NM, Youseif SH, Farag PF, Saleh SA, Abdel-Wahab BA, Alsuhaibani AM, Helmy YA, Abdel-Azeem AM (2022) Native rhizospheric and endophytic fungi as sustainable sources of plant growth promoting traits to improve wheat growth under low nitrogen input. J Fungi 8(2):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020094
Kumari DS, Saxena N (2017) Seed borne mycoflora of Macrotyloma uniflorum L (Horse gram). Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6(1):373–378. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.045
Ingle KP, Al-Khayri JM, Chakraborty P, Narkhede GW, Suprasanna P (2020) Bioactive compounds of horse gram (Macrotyloma uniflorum Lam. [Verdc.]). In: Murthy HN, Paek KY (eds) Bioactive compounds in underutilized vegetables and legumes. Reference series in phytochemistry. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44578-2_36-1
Nautiyal CS (1999) An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170(1):265–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13383.x
Nguyen C, Yan W, Tacon FL, Lapyire F (1992) Genetic variability of phosphate solubilizing activity by monocaryotic and dicaryotic mycelia of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor (Maire) P D Orton. Plant Soil 143:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007873
Hu XF, Chen J, Guo JF (2006) Two phosphate- and potassium-solubilizing bacteria isolated from Tianmu Mountain, Zhejiang, China. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:983–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9144-2
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus in methods of soil analysis. In: Page AL (ed) Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties. ASA and SSSA, Madison, pp 403–430
Lindsay WL, Norwell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Saxena J, Rawat J, Sanwal P (2017) Enhancement of growth and yield of Glycine max plants with inoculation of phosphate solubilizing fungus Aspergillus niger K7 and biochar amendment in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 47(20):2334–2347. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2016.1243708
Allen SC (1989). In: Steward SE (ed) Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Blackman Scientific, Oxford, p 368
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available p in soil by extraction with sodium bicarbonate, USDA circulation no. 939, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp19–27
AOAC (1965) Official methods of analysis, 10th edn. Association of Official Agricultural Chemist(s), Washington, DC
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37(1):29–38
Jain R, Saxena J, Sharma V (2012) Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by Aspergillus awamori S19 isolated from agricultural soil of semi-arid region. Ann Microbiol 62:725–735
Jain R, Saxena J, Sharma V (2014) Differential effects of immobilized and free forms of phosphate-solubilizing fungal strains on the growth and phosphorus uptake of mung bean plants. Ann Microbiol 64:1523–1534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0795-6
Vibha, Kumari G, Nidhi (2014) Impact of phosphate solubilizing fungi on the soil nutrient status and yield mungbean (Vigna radiate L) crop. Ann Agric Res 35(2):136–143
Rawat J, Sanwal P, Saxena J (2021) Utilization of pressmud waste as a carrier for enhancing agronomic traits of finger millet. Clean- Soil, Air, Water 49(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.202000260
Pandey A, Dhakar K, Jain R, Pandey N, Gupta VK, Kooliyottil R, Dhyani A, Malviya MK, Adhikari P (2019) Cold adapted fungi from indian himalaya: untapped source for bioprospecting. Proc Natl Acad Sci India B 89:1125–1132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-018-1002-0
Gaind S, Nain L (2015) Soil-phosphorus mobilization potential of phytate mineralizing fungi. J Plant Nutr 38(14):2159–2175. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1014561
Yadav J, Verma JP, Tiwari KN (2011) Solubilization of tricalcium phosphate by fungus Aspergillus niger at different carbon source and salinity. Trends Appl Sci Res 6(6):606–613. https://doi.org/10.3923/tasr.2011.606.613
Patel AK, Ghosh JK, Sayyad SU (2022) Fractional abundances study of macronutrients in soil using hyperspectral remote sensing. Geocarto Int 37(2):474–493. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1720315
Antonios C, Evgenia M, Nikos T (2018) Physiological and biochemical responses of Lavandula angustifolia to salinity under mineral foliar application. Front Plant Sci 9(489):7–29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00489
Sun F, Ou Q, Wang N, Guo ZX, Ou Y, Li N, Peng C (2020) Isolation and identification of potassium-solubilizing bacteria from Mikania micrantha rhizospheric soil and their effect on M. micrantha plants. Glob Ecol Conserv 23:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01141
Etesami H, Emami S, Alikhani HA (2017) Potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB): mechanisms, promotion of plant growth, and future prospects a review. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 17(4):897–911. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162017000400005
Marra LM, de Oliveira-Longatti SM, Soares CRFS, de Lima JM, Olivares FL, Moreira FMS (2015) Initial pH of medium affects organic acids production but do not affect phosphate solubilisation. Braz J Microbiol 46(2):367–375. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838246246220131102
Xue X, Zhang L, Peng Y, Li P, Yu J (2018) Effects of mineral structure and microenvironment on K release from potassium aluminosilicate minerals by Cenococcum geophilum fr. Geomicrobiol J 36(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2018.1485064
Lian B, Wang B, Pan M, Liu C, Teng HH (2008) Microbial release of potassium from K-bearing minerals by thermophilic fungus Aspergillus fumigates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72(1):87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.10.005
Babu-Khan S, Yeo TC, Martin WL, Duron MR, Rogers RD, Goldstein AH (1995) Cloning of a mineral phosphate-solubilizing gene from Pseudomonas cepacia. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(3):972–978. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.3.972-978.1995
Williams SG, Greenwood JA, Jones CW (1996) Physiological and biochemical changes accompanying the loss of mucoidy by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 142:881–888. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-142-4-881
Saravanan VS, Madhaiyan M, Thangaraju M (2007) Solubilization of zinc compounds by the diazotrophic, plant growth promoting bacterium Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Chemosphere 66:1794–1798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.067
Franz A, Burgstaller W, Schinner F (1991) Leaching with Penicillium simplicissimum: influence of metals and buffers on proton extrusion and citric acid production. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:769–774. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.57.3.769-774.1991
Rudresh DL, Shivaprakash MK, Prasad RD (2005) Tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities of Trichoderma spp. in relation to P uptake and growth and yield parameters of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Can J Microbiol 51:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1139/w04-127
Zayed G, Motaal HA (2005) Bioactive compost from rice straw enriched with rock phosphate and their effect on the phosphorus nutrition and microbial community in rhizosphere of cowpea. Bioresour Technol 96(8):929–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.08.002
El-Azouni IM (2008) Effect of phosphate solubilizing fungi on growth and nutrient uptake of soyabean plants. J Appl Sci Res 4(6):592–598
Mittal V, Singh O, Nayyar H, Kaur J, Tewari R (2008) Stimulatory effect of phosphate-solubilizing fungal strains (Aspergillus awamori and Penicillium citrinum) on the yield of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L. cv. GPF2). Soil Biol Biochem 40:718–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.10.008
Jain R, Saxena J, Sharma V (2010) The evaluation of free and encapsulated A. awamori for phosphate solubilization in fermentation and soil-plant system. Appl Soil Ecol 46:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.06.008
Prajapati K, Sharma MC, Modi HA (2013) Growth promoting effect of potassium solubilizing microorganisms on okra (Abelmoscus Esculantus). Int J Agric Sci 3(1):181–188
Singh H, Reddy MS (2011) Effect of inoculation with phosphate solubilizing fungus on growth and nutrient uptake of wheat and maize plants fertilized with rock phosphate in alkaline soils. Eur J Soil Biol 47:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2010.10.005
Zaidi A, Khan MS (2007) Stimulatory effects of dual inoculation with phosphate solubilising microorganisms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on chickpea. Aust J Exp Agric 47:1016–1022. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA06046
Matias SR, Pagano MC, Muzzi FC, Oliveira CA, Carneiro AA, Horta SN, Scotti MR (2009) Effect of rhizobia, mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in the rhizosphere of native plants used to recover an iron ore area in Brazil. Eur J Soil Biol 45:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2009.02.003
Bernaola L, Stout MJ (2021) The effect of mycorrhizal seed treatments on rice growth, yield, and tolerance to insect herbivores. J Pest Sci 94:375–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-020-01279-7
Begum N, Qin C, Ahanger MA, Raza S, Khan MI, Ashraf M, Ahmed N, Zhang L (2019) Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant growth regulation: implications in abiotic stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci, Sec Plant Abiotic Stress 10(1068):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01068
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the help of Dr. Y.S. Shivay, Professor, Division of Agronomy, ICAR-IARI for soil analysis.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS: conceptualization, JR, PS: methodology, JS, LN, RP: formal analysis and investigation, JS, JR, and PS: writing—original draft preparation, NRM: writing-data analysis, figures designing and editing, RP: writing—review and editing, LN: supervision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to Participate
All authors give the consent to participate in Current Microbiology.
Consent for Publication
All authors give the consent to use the information to publish in Current Microbiology.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Research Involving Human Participants/and or Animals
No human or animal involvement in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rawat, J., Saxena, J., Sanwal, P. et al. Improving the Growth and Productivity of Macrotyloma uniflorum Medicinal Plant by the Co-inoculation of P, Zn and K-Solubilizing Fungi Under Field Conditions. Curr Microbiol 80, 277 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03385-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03385-y