Abstract
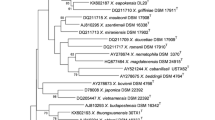
Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii is closely associated with the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora and has, to date, not been isolated from other nematode species. This study is the first report of P. luminescens subsp. laumondii from two South African isolates of entomopathogenic nematodes, Heterorhabditis safricana SF281 and H. bacteriophora SF351. Both symbiotic bacterial strains are phenotypically closely related to P. luminescens subsp. laumondii previously isolated and described from H. bacteriophora. The genetic relatedness between P. luminescens subsp. laumondii strains SF281B and SF351B was confirmed by comparing 16S rDNA, recA, gyrB and gltX sequences with sequences of P. luminescens subsp. laumondii, including the type strain (TT01T) and strain E21.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE, Janssen PH, Peel MM, Alfredson DA, Beard CE (2004) Taxonomy of Australian clinical isolates of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica subsp. australis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1301–1310
An R, Grewal PS (2010) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. stackebrandtii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol 61:291–297
An R, Grewal PS (2011) Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kleinii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol 62:539–543
Boemare NE (2002) Biology, taxonomy and systematics of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CAB International, London, pp 35–50
Buchanan JT, Simpson AJ, Aziz RK, Liu GY, Kristian SA, Kotb M, Feramisco J, Nizet V (2006) DNase expression allows the pathogen group A Streptococcus to escape killing in neutrophil extracellular traps. Curr Biol 1:396–400
Crouse J, Amorese D (1987) Ethanol precipitation: ammonium acetate as an alternative to sodium acetate. Focus 9:3–5
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie JM (2008) Phylogeny. fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W465–W469
Duchaud E, Rusniok C, Frangeul L, Buchrieser C, Givaudan A, Taourit S, Bocs S, Boursaux-Eude C, Chandler M, Charles JF, Dassa E, Derose R, Derzelle S, Freyssinet G, Gaudriault S, Médigue C, Lanois A, Powell K, Siguier P, Vincent R, Wingate V, Zouine M, Glaser P, Boemare N, Danchin A, Kunst F (2003) The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nat Biotechnol 21:1307–1313
Ferreira T, Van Reenen CA, Endo A, Tailliez P, Pagès S, Spröer C, Malan AP, Dicks LMT (2014) Photorhabdus zealandica sp. nov., a symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis zealandica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1540–1545
Ferreira T, Van Reenen CA, Pagès S, Tailliez P, Malan AP, Dicks LMT (2013) Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. noenieputensis subsp. nov., a symbiotic bacterium associated with a novel Heterorhabditis species related to Heterorhabditis indica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1853–1858
Ferreira T, Van Reenen CA, Tailliez P, Pagès S, Malan AP, Dicks LMT (2016) First report of the symbiotic bacterium, Xenorhabdus indica, associated with the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema yirgalemense. J Helminthol 90:108–112
Ffrench-Constant R, Waterfield N, Daborn P, Joyce S, Bennett H, Au C, Dowling A, Boundy S, Reynolds S, Clarke D (2003) Photorhabdus: towards a functional genomic analysis of a symbiont and pathogen. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:433–456
Fischer-Le Saux M, Viallardt V, Brunelt B, Normand P, Boemare NE (1999) Polyphasic classification of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of new taxa: P. luminescens subsp. luminescens subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. laumondii subsp. nov., P. temperata sp. nov., P. temperata subsp. temperata subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1645–1656
Forst S, Clarke D (2002) Bacteria-Nematode Symbiosis. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CAB International, London, pp 57–77
Forst S, Nealson K (1996) Molecular biology of the symbiotic-pathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. Microbiol Rev 60:21–43
Gaudriault S, Duchaud E, Lanois A, Canoy AS, Bourot S, DeRose R, Kunst F, Boemare N, Givaudan A (2006) Whole-genome comparison between Photorhabdus strains to identify genomic regions involved in the specificity of nematode interaction. J Bacteriol 188:809–814
Gerdes E, Upadhyay D, Mandjiny S, Bullard-Dillard R, Storms M, Menefee M, Holmes LD (2015) Photorhabdus luminescens: virulent properties and agricultural applications. Am J Agric For 3:171–177
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321
Hazir S, Stackebrandt E, Lang E, Schumann P, Ehlers RU, Keskin N (2004) Two new subspecies of Photorhabdus luminescens, isolated from Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae): Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kayaii subsp. nov. and Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. thracensis subsp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:36–42
Jeffries CD, Holtman DF, Guse DG (1957) Rapid method of determining the activity of microorganisms on nucleic acid. J Bacteriol 73:590–591
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Koppenhöffer HS (2007) Bacterial symbionts of Steinernema and Heterorhabditis. In: Nguyen DJ, Hunt KB (eds) Nematology monographs & perspectives. New Brunswick, Brill, pp 735–808
Lango-Scholey L, Brachmann AO, Bode HB, Clarke DJ (2013) The expression of stlA in Photorhabdus luminescens is controlled by nutrient limitation. PLoS One 8:e82152
Malan AP, Nguyen KB, Addison MF (2006) Entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) from the southwestern parts of South Africa. Afr Plant Prot 12:65–69
Malan AP, Nguyen KB, De Waal J, Tiedt L (2008) Heterorhabditis safricana n. sp. (Rhabditidae: Heterorhabditidae), a new entomopathogenic nematodes from South Africa. Nematology 10:281–396
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sawyer S (1989) Statistical tests for detecting gene conversion. Mol Biol Evol 6:526–538
Sierra G (1957) A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 23:1–22
Stock P (2015) Diversity, biology and evolutionary relationships. In: Campos-Herrera R (ed) Sustainability in plant and crop protection: ecology and applied technologies for sustainable plant and crop protection. Springer, Basel, pp 3–27
Tailliez P, Laroui C, Ginibre N, Paule A, Pagès S, Boemare N (2010) Phylogeny of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus based on universally conserved protein-coding sequences and implications for the taxonomy of these two genera. Proposal of new taxa: X. vietnamensis sp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. caribbeanensis subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. hainanensis subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. khanii subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. tasmaniensis subsp. nov., and the reclassification of P. luminescens subsp. thracensis as P. temperata subsp. thracensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1921–1937
Toth T, Lakatos T (2008) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. cinerea subsp. nov., isolated from Heterorhabditis nematodes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2579–2581
Vojtek L, Dobes P, Buyukguzel E, Atosuo J, Hyrsl P (2014) Bioluminescent assay for evaluating antimicrobial activity in insect haemolymph. Eur J Entomol 111:335–340
Acknowledgments
The Central Analytical Facility (CAF) of Stellenbosch University for DNA sequencing. The research was supported with funding from the National Research Foundation (NRF), South Africa (Grant number NRF-THRIP TP14062571871) and the South African Apple and Pear Producers’ Association (SAAPPA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
284_2016_1116_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Bioluminescence produced by Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii SF281B after 48 h of growth at 30°C on MacConkey agar (Biolab) (TIFF 336 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geldenhuys, J., Malan, A.P. & Dicks, L.M.T. First Report of the Isolation of the Symbiotic Bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii Associated with Heterorhabditis safricana from South Africa. Curr Microbiol 73, 790–795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1116-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1116-7