Abstract
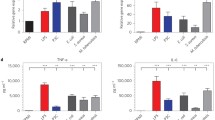
Quorum sensing (QS) is a type of cell-to-cell communication. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa QS molecule N-3-(oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone (3-o-C12-HSL) has the potential to modulate the immune system of its host. However, the mechanism of that activity is yet to be fully characterized. To be able to understand this activity, we determined whether 3-o-C12-HSL has a direct effect on the immune function and the expression of toll-like receptors (TLRs) in monocytes. Monocytes were cultured with 3-o-C12-HSL at different concentrations (0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 μmol/L) for 12 h; upon exposure to 3-o-C12-HSL, IL-12 production in monocytes was inhibited, monocyte proliferation was blocked, TLR2- and 4-mRNA expressions were reduced, and TLR5-mRNA expression was increased in a dose-dependent manner. Strikingly, 3-o-C12-HSL was able to significantly induce mRNA changes in the monocytes even at the lowest concentration (10 μmol/L, P < 0.05). Interestingly, though TLR2- and 4-protein levels were reduced, TLR5 protein expression was not changed. These findings provide a new perspective toward understanding the persistence of chronic inflammation in P. aeruginosa infections. They also suggest that TLR2, 4, and 5 may not share the same signaling pathways during monocyte activation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arikawa E, Sun Y, Wang J, Zhou Q, Ning B, Dial SL, Guo L, Yang J (2008) Cross-platform comparison of SYBR green real-time PCR with TaqMan PCR, microarrays and other gene expression measurement technologies evaluated in the microarray qualitycontrol (MAQC) study. BMC Genomics 9:328
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Du X, Ulevitch RJ (2003) How we detect microbes and respond to them: the toll-like receptors and their transducers. J Leukoc Biol 74:479–485
Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M (2007) The role of quorum sensing in the pathogenicity of the cunningaggressor Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:409–414
Chhabra SR, Harty C, Hooi DS, Daykin M, Williams P, Telford G, Pritchard DI, Bycroft BW (2003) Synthetic analogues of the bacterial signal (quorum sensing) molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone as immune modulators. J Med Chem 46:97–104 19
Colonna M (2007) TLR pathways and IFN-regulatory factors: to each its own. Eur J Immunol 37:306–309
Devaraj S, Dasu MR, Rockwood J, Winter W, Griffen SC, Jialal I (2008) Increased toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 expression in monocytes from patients with type 1 diabetes: further evidence of a proinflammatory state. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:578–583
Feng CQ, Ma WL, Song YB, Guo QY, Wu QH, Zheng WL (2002) Detection of cell apoptosis by MTT assay. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 22(3):262–263
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Routsi C, Plachouras D, Markaki V, Raftogiannis M, Zervakis D, Koussoulas V, Orfanos S, Kotanidou A, Armaganidis A, Roussos C, Giamarellou H (2006) Early apoptosis of blood monocytes as a mechanism of protection of the septic host. Crit Care 10:R76
Gómez MI, Lee A, Reddy B, Muir A, Soong G, Pitt A, Cheung A, Prince A (2004) Staphylococcus aureus protein A induces airway epithelial inflammatory responses by activating TNFR1. Nat Med 10:842–848
Hauber HP, Tulic MK, Tsicopoulos A, Wallaert B, Olivenstein R, Daigneault P, Hamid Q (2005) Toll-like receptors 4 and 2 expression in the bronchial mucosa of patients with cystic fibrosis. Can Respir J 12:13–18
Hooi DS, Bycroft BW, Chhabra SR, Williams P, Pritchard DI (2004) Differential immune modulatory activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signalmolecules. Infect Immun 72:6463–6470
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Karl IE (2003) Role of apoptotic cell death in sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis 35:585–593
Jahr TG, Ryan L, Sundan A, Lichenstein HS, Skjåk-Braek G, Espevik T (1997) Induction of tumor necrosis factor production from monocytes stimulated with mannuronic acid polymers and involvement of lipo-polysaccharide-binding protein, CD14, and bactericidal/permeability in creasing factor. Infect Immun 65:89–94
Jeyaseelan S, Young SK, Yamamoto M, Arndt PG, Akira S, Kolls JK, Worthen GS (2006) Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP) is a critical mediator of antibacterial defense in the lung against klebsiella pneumoniae but not Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Immunol 177:538–547
Kerber-Momot T, Leemhuis D, Lührmann A, Munder A, Tümmler B, Pabst R, Tschernig T (2010) Beneficial effects of TLR-2/6 ligation in pulmonary bacterial infection and immunization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Inflammation 33:58–64
Koch C, Hoiby N (1993) Pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet 341:1065–1069
Koller B, Kappler M, Latzin P, Gaggar A, Schreiner M, Takyar S, Kormann M, Kabesch M, Roos D, Griese M, Hartl D (2008) TLR expression on neutrophils at the pulmonary site of infection: TLR1/TLR2-mediated up-regulation of TLR5 expression in cystic fibrosis lung disease. J Immunol 181:2753–2763
Qi L, Yu J, Lin L, Ran T, Deng B, Li Y, Yang X (2009) Expression of toll-like receptors in human peripheral blood monocyte stimulated with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signal molecule. Chin J Microecol 21:308–310
Lyczak JB, Cannon C, Pier GB (2000) Establishment of Pseudomona aeruginosa infection: lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect 2:1051–1060
Mossmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
O’Neill LA (2006) How toll-like receptors signal: what we know and what we don’t know. Curr Opin Immunol 18:3–9
Pearson JP, Gray KM, Passador L, Tucker KD, Eberhard A, Iglewski BH, Greenberg EP (1994) Structure of the autoinducer required for expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:197–201
Pearson JP, Passador L, Iglewski BH, Greenberg EP (1995) A second N-acylhomoserine lactone signal produce by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:1490–1494
Pier GB (1998) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a key problem in cystic fibrosis. ASM News 6:339–347
Ramphal R, Balloy V, Huerre M, Si-Tahar M, Chignard M (2005) TLRs 2 and 4 are not involved in hypersusceptibility to acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections. J Immunol 175:3927–3934
Rifkin IR, Leadbetter EA, Busconi L, Viglianti G, Marshak-Rothstein A (2005) Toll-like receptors, endogenous ligands, and systemic autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev 204:27–42
Skerrett SJ, Liggitt HD, Hajjar AM, Wilson CB (2004) Cutting edge: myeloid differentiation factor 88 is essential for pulmonary host defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa but not Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 172:3377–3381
Skerrett SJ, Wilson CB, Liggitt HD, Hajjar AM (2007) Redundant toll-like receptor signaling in the pulmonary host response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Physiol 292:312–322
Smith RS, Harris SG, Phipps R, Iglewski B (2002) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)homoserine lactone contributes to virulence and induces inflammation in vivo. J Bacteriol 184:1132–1139
Smith RS, Kelly R, Iglewski BH, Phipps RP (2002) The Pseudo-monas autoinducer N-(3-oxododecanoyl)homoserine lactone induces cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 production in human limplications for inflammation. J Immunol 169:2636–2642
Tateda K, Ishii Y, Horikawa M, Matsumoto T, Miyairi S, Pechere JC, Standiford TJ, Ishiguro M, Yamaguchi K (2003) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer N-3-oxododecanoyl homoserine lactone accelerates apoptosis in macrophages and neutrophils. Infect Immun 71:5785–5793
Telford G, Wheeler D, Williams P, Tomkins PT, Appleby P, Sewell H, Stewart GS, Bycroft BW, Pritchard DI (1998) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signal molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone has immunomodulatory activity. Infect Immun 66:36–42
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to Zhengqiu Liu and Yasha Li for their invaluable assistance with this study. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30772363; 30901279).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Q., Lin, Y., Yang, X. et al. Regulation on Expression of Toll-like Receptors on Monocytes After Stimulation with the 3-o-C12-HSL Molecule from Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Curr Microbiol 65, 384–389 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0162-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0162-z