Abstract
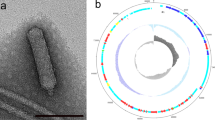
To search for candidate control agents against Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida infections in aquaculture, one bacteriophage (phage), designated as PAS-1, was isolated from the sediment samples of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) culture farm in Korea. The PAS-1 was morphologically classified as Myoviridae and possessed approximately 48 kb of double-strand genomic DNA. The phage showed broad host ranges to other subspecies of A. salmonicida as well as A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida including antibiotic-resistant strains. Its latent period and burst size were estimated to be approximately 40 min and 116.7 PFU/cell, respectively. Furthermore, genomic and structural proteomic analysis of PAS-1 revealed that the phage was closely related to other Myoviridae phages infecting enterobacteria or Aeromonas species. The bacteriolytic activity of phage PAS-1 was evaluated using three subspecies of A. salmonicida strain at different doses of multiplicity of infection, and the results proved to be efficient for the reduction of bacterial growth. Based on these results, PAS-1 could be considered as a novel Aeromonas phage and might have potentiality to reduce the impacts of A. salmonicida infections in aquaculture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann HW (2007) 5500 Phages examined in the electron microscope. Arch Virol 152:227–243
Ackermann HW, Dauguet C, Paterson WD, Popoff M, Rouf MA, Vieu JF (1985) Aeromonas bacteriophages: reexamination and classification. Ann Inst Pasteur Virol 136:175–199
Adams M (1959) Bacteriophages. Interscience Publishers, New York
Beilstein F, Dreiseikelmann B (2008) Temperate bacteriophage φO18P from an Aeromonas media isolate: characterization and complete genome sequence. Virology 373:25–29
Comeau AM, Bertrand C, Letarov A, Tétart F, Krisch HM (2007) Modular architecture of the T4 phage superfamily: a conserved core genome and a plastic periphery. Virology 362:384–396
Fauquet C, Mayo M, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball A (2005) Virus taxonomy. VIIIth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, pp 35–85
Han JE, Kim JH, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Jun JW, Chai JY, Han SY, Park SC (2011) First description of the qnrS-like (qnrS5) gene and analysis of quinolone resistance-determining regions in motile Aeromonas spp. from diseased fish and water. Res Microbiol. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2011.09.001
Imbeault S, Parent S, Lagacé M, Uhland CF, Blais JF (2006) Using bacteriophages to prevent furunculosis caused by Aeromonas salmonicida in farmed brook trout. J Aquat Anim Health 18:203–214
Jamalludeen N, Kropinski AM, Johnson RP, Lingohr E, Harel J, Gyles CL (2007) Complete genomic sequence of bacteriophage φEcoM-GJ1: a novel phage that has myovirus morphology and a podovirus-like RNA polymerase. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:516–525
Karunasagar I, Shivu MM, Girisha SK, Krohne G, Karunasagar I (2007) Biocontrol of pathogens in shrimp hatcheries using bacteriophages. Aquaculture 268:288–292
Kim JH, Gomez DK, Nakai T, Park SC (2010) Isolation and identification of bacteriophages infecting ayu Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis specific Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Vet Microbiol 140:109–115
Kim JH, Hwang SY, Son JS, Han JE, Jun JW, Shin SP, Choresca CH, Choi YJ, Park YH, Park SC (2011) Molecular characterization of tetracycline- and quinolone-resistant Aeromonas salmonicida isolated in Korea. J Vet Sci 12:41–48
Konopa G, Taylor K (1979) Coliphage λ ghosts obtained by osmotic shock or LiCl treatment are devoid of J- and H-gene products. J Gen Virol 43:729–733
Lavigne R, Darius P, Summer E, Seto D, Mahadevan P, Nilsson A, Ackermann H, Kropinski A (2009) Classification of Myoviridae bacteriophages using protein sequence similarity. BMC Microbiol 9:224
Lukashin AV, Borodovsky M (1998) GeneMark.hmm: new solutions for gene finding. Nucleic Acids Res 26:1107–1115
Munro J, Oakey J, Bromage E, Owens L (2003) Experimental bacteriophage-mediated virulence in strains of Vibrio harveyi. Dis Aquat Org 54:187–194
Nakai T, Park SC (2002) Bacteriophage therapy of infectious diseases in aquaculture. Res Microbiol 153:13–18
Nolan J, Petrov V, Bertrand C, Krisch H, Karam J (2006) Genetic diversity among five T4-like bacteriophages. Virol J 3:30
Petrov V, Nolan J, Bertrand C, Levy D, Desplats C, Krisch H, Karam J (2006) Plasticity of the gene functions for DNA replication in the T4-like phages. J Mol Biol 361:46–68
Petrov VM, Ratnayaka S, Karam JD (2010) Genetic insertions and diversification of the PolB-Type DNA polymerase (gp43) of T4-related phages. J Mol Biol 395:457–474
Popoff M (1971) Étude sur les Aeromonas salmonicida—II. Caractérisation des bactériophages actifs sur les Aeromonas salmonicida et lysotypie. Ann Rech Vét 2:33–45
Son JS, Jun SY, Kim EB, Park JE, Paik HR, Yoon SJ, Kang SK, Choi YJ (2010) Complete genome sequence of a newly isolated lytic bacteriophage, EFAP-1 of Enterococcus faecalis, and antibacterial activity of its endolysin EFAL-1. J Appl Microbiol 108:1769–1779
Tétart F, Repoila F, Monod C, Krisch HM (1996) Bacteriophage T4 host range is expanded by duplications of a small domain of the tail fiber adhesin. J Mol Biol 258:726–731
Uchiyama J, Rashel M, Maeda Y, Takemura I, Sugihara S, Akechi K, Muraoka A, Wakiguchi H, Matsuzaki S (2008) Isolation and characterization of a novel Enterococcus faecalis bacteriophage φEF24C as a therapeutic candidate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 278:200–206
Verner-Jeffreys DW, Algoet M, Pond MJ, Virdee HK, Bagwell NJ, Roberts EG (2007) Furunculosis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) is not readily controllable by bacteriophage therapy. Aquaculture 270:475–484
Vinod MG, Shivu MM, Umesha KR, Rajeeva BC, Krohne G, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2006) Isolation of Vibrio harveyi bacteriophage with a potential for biocontrol of luminous vibriosis in hatchery environments. Aquaculture 255:117–124
Wiklund T, Dalsgaard I (1998) Occurrence and significance of atypical Aeromonas salmonicida in non-salmonid and salmonid fish species: a review. Dis Aquat Org 32:49–69
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Basic Science Research Program (2010-0016748) and Priority Research Centers Program (2009-0093822) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and by Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2008-331-E00385).
Conflict of Interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. H. Kim and J. S. Son have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Son, J.S., Choi, Y.J. et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Lytic Myoviridae Bacteriophage PAS-1 with Broad Infectivity in Aeromonas salmonicida . Curr Microbiol 64, 418–426 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0091-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0091-x