Abstract
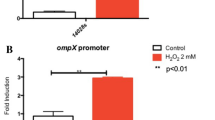
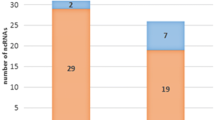
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) is the cause of typhoid fever, a food-borne disease that is prevalent worldwide, most particularly in developing countries. RNA polymerase sigma factors RpoE (σE) and RpoS (σS) govern transcription initiation of two sets of genes in Escherichia and Salmonella. It was previously suggested that some genes might be coregulated by RpoE and RpoS in Salmonella under conditions of environmental stress, but experimental evidence has been lacking. We therefore constructed rpoS deletion (ΔrpoS) and double rpoE/rpoS deletion (ΔrpoE/ΔrpoS) mutants of S. Typhi and compared their growth properties with an rpoE mutant (ΔrpoE) and wild-type strains under conditions of hyperosmotic stress. We report that the ΔrpoE, ΔrpoS, and ΔrpoE/ΔrpoS strains grew more slowly under hyperosmotic stress conditions than the wild-type strain, and the ΔrpoE/ΔrpoS strain grew most slowly. The global transcriptional profiles of ΔrpoE, ΔrpoS, ΔrpoE/ΔrpoS after 30 min of hyperosmotic stress were investigated using a Salmonella genomic DNA microarray. The results of microarray indicated that the expression levels of 38 genes were markedly reduced during hyperosmotic stress in the double mutant ΔrpoE/ΔrpoS strain, but expression levels were not significantly affected by single ΔrpoE or ΔrpoS mutations. This was confirmed for several key genes by qRT-PCR. This study therefore indicated crosstalk between sigma factors RpoE and RpoS in S. Typhi under hyperosmotic conditions and provides new insights into the regulatory networks of S. Typhi.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba BM, Gross CA (2004) Regulation of the Escherichia coli sigma-dependent envelope stress response. Mol Microbiol 52:613–619
Alba BM, Leeds JA, Onufryk C et al (2002) DegS and YaeL participate sequentially in the cleavage of RseA to activate the sigma(E)-dependent extracytoplasmic stress response. Genes Dev 16:2156–2168
Balaji B, O’Connor K, Lucas JR et al (2005) Timing of induction of osmotically controlled genes in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium, determined with quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8273–8283
Bouvier J, Gordia S, Kampmann G et al (1998) Interplay between global regulators of Escherichia coli: effect of RpoS, Lrp and H-NS on transcription of the gene osmC. Mol Microbiol 28:971–980
Coynault C, Robbe-Saule V, Norel F (1996) Virulence and vaccine potential of Salmonella typhimurium mutants deficient in the expression of the RpoS (sigma S) regulon. Mol Microbiol 22:149–160
Daniel MS, Karsten H, Michael SL, Charles JD (2009) Compensatory evolution of gene regulation in response to stress by Escherichia coli lacking RpoS. PLoS Genet 5:e1000671
Davalos-Garcia M, Conter A, Toesca I et al (2001) Regulation of osmC gene expression by the two-component system rcsB-rcsC in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183:5870–5876
Du H, Sheng X, Zhang H et al (2011) RpoE may promote flagellar gene expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi under hyperosmotic stress. Curr Microbiol 62:492–500
Everest P, Wain J, Roberts M et al (2001) The molecular mechanisms of severe typhoid fever. Trends Microbiol 9:316–320
Gordia S, Gutierrez C (1996) Growth-phase-dependent expression of the osmotically inducible gene osmC of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Microbiol 19:729–736
Grigorova IL, Chaba R, Zhong HJ et al (2004) Fine-tuning of the Escherichia coli sigmaE envelope stress response relies on multiple mechanisms to inhibit signal-independent proteolysis of the transmembrane anti-sigma factor, RseA. Genes Dev 18:2686–2697
Gutierrez C, Devedjian JC (1991) Osmotic induction of gene osmC expression in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol 220:959–973
Han Y, Zhou D, Pang X et al (2005) Comparative transcriptome analysis of Yersinia pestis in response to hyperosmotic and high-salinity stress. Res Microbiol 156:403–415
Hengge-Aronis R (1996) Back to log phase: sigma S as a global regulator in the osmotic control of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 21:887–893
Hengge-Aronis R, Klein W, Lange R et al (1991) Trehalose synthesis genes are controlled by the putative sigma factor encoded by rpoS and are involved in stationary-phase thermotolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173:7918–7924
Hengge-Aronis R, Lange R, Henneberg N, Fischer D (1993) Osmotic regulation of rpoS-dependent genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 175:259–265
House D, Bishop A, Parry C et al (2001) Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and disease. Curr Opin Infect Dis 14:573–578
Huang X, le Phung V, Dejsirilert S et al (2004) Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the z66 antigen of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 234:239–246
Huang X, Xu H, Sun X et al (2007) Genome-wide scan of the gene expression kinetics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi during hyperosmotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 8:116–135
Jones BD, Falkow S (1996) Salmonellosis: host immune responses and bacterial virulence determinants. Annu Rev Immunol 14:533–561
Jung JU, Gutierrez C, Martin F et al (1990) Transcription of osmB, a gene encoding an Escherichia coli lipoprotein, is regulated by dual signals: osmotic stress and stationary phase. J Biol Chem 265:10574–10581
Kaasen I, Falkenberg P, Styrvold OB, Strom AR (1992) Molecular cloning and physical mapping of the otsBA genes, which encode the osmoregulatory trehalose pathway of Escherichia coli: evidence that transcription is activated by katF (AppR). J Bacteriol 174:889–898
Lin ECC (1976) Glycerol dissimilation and its regulation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 30:535–578
McCann MP, Kidwell JP, Matin A (1991) The putative sigma factor KatF has a central role in development of starvation-mediated general resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173:4188–4194
Miticka H, Rowley G, Rezuchova B et al (2003) Transcriptional analysis of the rpoE gene encoding extracytoplasmic stress response sigma factor sigmaE in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:307–314
Nickerson CA, Curtiss R (1997) Role of sigma factor RpoS in initial stages of Salmonella typhimurium infection. Infect Immun 65:1814–1823
Rhodius VA, Suh WC, Nonaka G et al (2006) Conserved and variable functions of the sigmaE stress response in related genomes. PLoS Biol 4:e2
Rowley G, Spector M, Kormanec J, Roberts M (2006) Pushing the envelope: extracytoplasmic stress responses in bacterial pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:383–394
Ruberg S, Tian ZX, Krol E et al (2003) Construction and validation of a Sinorhizobium meliloti whole genome DNA microarray: genome-wide profiling of osmoadaptive gene expression. J Biotechnol 106:255–268
Schweizer H, Argast M, Boos W (1982) Characteristics of a binding protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate in Escherichia coli that is part of the pho regulon. J Bacteriol 150:1154–1163
Sheng X, Huang X, Mao L et al (2009) Preparation of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi genomic DNA microarrays for gene expression profiling analysis. Prog Biochem Biophys 36:306–312
Spector MP, Garcia del Portillo F, Bearson SM et al (1999) The rpoS-dependent starvation-stress response locus stiA encodes a nitrate reductase (narZYWV) required for carbon-starvation-inducible thermotolerance and acid tolerance in Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiology 145:3035–3045
Stephanie JC, Wenjing J, Jeffrey AC (2006) Role of the Escherichia coli nitrate transport protein, NarU, in survival during severe nutrient starvation and slow growth. Microbiology 152:2091–2100
Testerman TL, Vazquez-Torres A, Xu Y et al (2002) The alternative sigma factor sigmaE controls antioxidant defences required for Salmonella virulence and stationary-phase survival. Mol Microbiol 43:771–782
Xu S, Zhang H, Sheng X et al (2008) Transcriptional expression of fljB:z66, a flagellin gene located on a novel linear plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi under environmental stresses. New Microbiol 31:241–247
Yang K, Wang M, Metcalf WW (2009) Uptake of glycerol-2-phosphate via the ugp-encoded transporter in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 191:4667–4670
Yim HH, Brems RL, Villarejo M (1994) Molecular characterization of the promoter of osmY, an rpoS-dependent gene. J Bacteriol 176:100–107
Acknowledgments
We thank T. Ezaki (Gifu University) for bacterial strains and continuous support. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30870095), National Special Scientific Program (2008ZX10004-009), Professional Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Jiangsu University (No. 10JDG044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, H., Wang, M., Luo, Z. et al. Coregulation of Gene Expression by Sigma Factors RpoE and RpoS in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi During Hyperosmotic Stress. Curr Microbiol 62, 1483–1489 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9890-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9890-8