Abstract
As it is known that food waste can be reduced by the larvae of Hermetia illucens (Black soldier fly, BSF), the scientific and commercial value of BSF larvae has increased recently. We hypothesised that the ability of catabolic degradation by BSF larvae might be due to intestinal microorganisms. Herein, we analysed the bacterial communities in the gut of BSF larvae by pyrosequencing of extracting intestinal metagenomic DNA from larvae that had been fed three different diets. The 16S rRNA sequencing results produced 9737, 9723 and 5985 PCR products from larval samples fed food waste, cooked rice and calf forage, respectively. A BLAST search using the EzTaxon program showed that the bacterial community in the gut of larvae fed three different diets was mainly composed of the four phyla with dissimilar proportions. Although the composition of the bacterial communities depended on the different nutrient sources, the identified bacterial strains in the gut of BSF larvae represented unique bacterial species that were unlike the intestinal microflora of other insects. Thus, our study analysed the structure of the bacterial communities in the gut of BSF larvae after three different feedings and assessed the application of particular bacteria for the efficient degradation of organic compounds.




Similar content being viewed by others
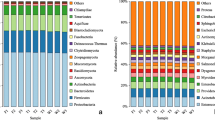
References
Andersson AF, Lindberg M, Jakobsson H, Bäckhed F, Nyrén P, Engstrand L (2008) Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 3:e2836
Bradley SW, Sheppard DC (1984) House fly oviposition inhibition by larvae of Hermetia illucens, the black soldier fly. J Chem Ecol 10:853–859
Brauman A, Dore J, Eggleton P, Bignell D, Breznak JA, Kane MD (2001) Molecular phylogenetic profiling of prokaryotic communities in guts of termites with different feeding habits. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:27–36
Breznak JA (1982) Intestinal microbiota of termites and other xylophagous insects. Annu Rev Microbiol 36:323–343
Breznak JA, Brune A (1994) Role of microorganisms in the digestion of lignocelluloses by termites. Annu Rev Entomol 39:453–487
Chun J, Goodfellow M (1995) A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardia with 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:240–245
Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261
Chun J, Kim KY, Lee JH, Choi Y (2010) The analysis of oral microbial communities of wild-type and toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice using a 454 GS FLX titanium pyrosequencing. BMC Microbiol 10:101
Claesson MJ, O’Sullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi JR, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Ross RP, O’Toole PW (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS ONE 4:e6669
Diener S, Zurbrügg C, Tockner K (2009) Conversion of organic material by black soldier fly larvae: establishing optimal feeding rates. Waste Manag Res 27:603–610
Donovan SE, Purdy KJ, Kane MD, Eggleton P (2004) Comparison of Euryarchaea strains in the guts and food-soil of the soil-feeding termite Cubitermes fungifaber across different soil types. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3884–3892
Durand L, Zbinden M, Cueff-Gauchard V, Duperron S, Roussel EG, Shillito B, Cambon-Bonavita MA (2010) Microbial diversity associated with the hydrothermal shrimp Rimicaris exoculata gut and occurrence of a resident microbial community. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 71:291–303
Erickson MC, Islam M, Sheppard C, Liao J, Doyle MP (2004) Reduction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis in chicken manure by larvae of the black soldier fly. J Food Prot 67:685–690
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hoffmann JA, Hetru C (1992) Insect defensins: inducible antibacterial peptides. Immunol Today 13:411–415
Hongoh Y (2009) Diversity and genomes of uncultured microbial symbionts in the termite gut. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:1145–1151
Hongoh Y, Ohkuma M, Kudo T (2003) Molecular analysis of bacterial microbiota in the gut of the termite Reticulitermes speratus (Isoptera; Rhinotermitidae). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44:231–242
Hongoh Y, Deevong P, Inoue T, Moriya S, Trakulnaleamsai S, Ohkuma M, Vongkaluang C, Noparatnaraporn N, Kudo T (2005) Intra- and interspecific comparisons of bacterial diversity and community structure support coevolution of gut microbiota and termite host. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6590–6599
Hongoh Y, Ekpornprasit L, Inoue T, Moriya S, Trakulnaleamsai S, Ohkuma M, Noparatnaraporn N, Kudo T (2006) Intracolony variation of bacterial gut microbiota among castes and ages in the fungus-growing termite Macrotermes gilvus. Mol Ecol 15:505–516
Huber JA, Mark Welch DB, Morrison HG, Huse SM, Neal PR, Butterfield DA, Sogin ML (2007) Microbial population structures in the deep marine biosphere. Science 318:97–100
Jung YJ, Jung D, Kim JY, Zo YG, Yim JH, Lee H, Ahn TS (2009) Distribution of bacterial decomposers in lake Khuvsgul, Mongolia. Korean J Microbiol 45:119–125 (Korean)
Kim JG, Choi YC, Choi JY, Kim WT, Jeong GS, Park KH, Hwang SJ (2008) Ecology of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Korea. Korean J Appl Entomol 47:337–343 (Korean)
Kim BS, Kim BK, Lee JH, Kim M, Lim YW, Chun J (2008) Rapid phylogenetic dissection of prokaryotic community structure in tidal flat using pyrosequencing. J Microbiol 46:357–363
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kudo T (2009) Termite-microbe symbiotic system and its efficient degradation of lignocellulose. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:2561–2567
Kudo T, Ohkuma M, Moriya S, Noda S, Ohtoko K (1998) Molecular phylogenetic identification of the intestinal anaerobic microbial community in the hindgut of the termite, Reticulitermes speratus, without cultivation. Extremophiles 2:155–161
Lee HK, Ahn MJ, Kwak SH, Song WH, Jeong BC (2003) Purification and characterization of cold active lipase from psychotropic Aeromonas sp. LPB 4. J Microbiol 41:22–27
Liu Q, Tomberlin JK, Brady JA, Sanford MR, Yu Z (2008) Black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae reduce Escherichia coli in dairy manure. Environment 37:1525–1530
Ohkuma M (2008) Symbioses of flagellates and prokaryotes in the gut of lower termites. Trends Microbiol 16:345–352
Ohkuma M, Kudo T (1996) Phylogenetic diversity of the intestinal bacterial community in the termite Reticulitermes speratus. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:461–468
Park DS, Oh HW, Jeong WJ, Kim H, Park HY, Bae KS (2007) A culture-based study of the bacterial communities within the guts of nine Longicorn beetle species and their exo-enzyme producing properties for degrading xylan and pectin. J Microbiol 45:394–401
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS et al (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464:59–65
Roesch LFW, Fulthorpe RR, Riva A, Casella G, Hadwin AKM, Kent AD, Daroub SH, Camargo FAO, Farmerie WG, Triplett EW (2007) Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. ISME J 1:283–290
Roh SW, Nam YD, Chang HW, Kim KH, Kim MS, Ryu JH, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Bae JW (2008) Phylogenetic characterization of two novel commensal bacteria involved with innate immune homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6171–6177
Roh SW, Kim KH, Nam YD, Chang HW, Park EJ, Bae JW (2010) Investigation of archaeal and bacterial diversity in fermented seafood using barcoded pyrosequencing. ISME J 4:1–16
Schmitt-Wagner D, Friedrich MW, Wagner B, Brune A (2003) Phylogenetic diversity, abundance, and axial distribution of bacteria in the intestinal tract of two soil-feeding termites. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6007–6017
Schmitt-Wagner D, Friedrich MW, Wagner B, Brune A (2003) Axial dynamics, stability, and interspecies similarity of bacterial community structure in the highly compartmentalized gut of soil-feeding termites (Cubitermes spp.). Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6018–6024
Shinzato N, Muramatsu M, Matsui T, Watanabe Y (2005) Molecular phylogenetic diversity of the bacterial community in the gut of the termite Coptotermes formosanus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:1145–1155
Shinzato N, Muramatsu M, Matsui T, Watanabe Y (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of the gut bacterial microflora of the fungus-growing termite Odontotermes formosanus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:906–915
Sogin ML, Morrison HG, Huber JA, Mark Welch D, Huse SM, Neal PR, Arrieta JM, Herndl GJ (2006) Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12115–12120
Suh SO, McHugh JV, Pollock DD, Blackwell M (2005) The beetle gut: a hyperdiverse source of novel yeasts. Mycol Res 109:261–265
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Teather RM, Wood PJ (1982) Use of Congo red polysaccharide interactions complex formation between Congo red and polysaccharide in detection and assay of polysaccharide hydrolases. Methods Enzymol 160:59–74
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Warnecke F, Luginbühl P, Ivanova N, Ghassemian M, Richardson TH et al (2007) Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 450:560–565
Yu H, Wang Z, Liu L, Xia Y, Cao Y, Yin Y (2008) Analysis of the intestinal microflora in Hepialus gonggaensis larvae using 16S rRNA sequences. Curr Microbiol 56:391–396
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Rural Development Administration, Korea (PJ006893). H. Jeon was supported by a graduate school scholarship from Kyung Hee University. Pyrosequencing data were analysed by the Chun Laboratory at Seoul National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, H., Park, S., Choi, J. et al. The Intestinal Bacterial Community in the Food Waste-Reducing Larvae of Hermetia illucens . Curr Microbiol 62, 1390–1399 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9874-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9874-8



