Abstract
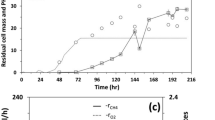
The ammonia oxidizers Nitrosomonas europaea and Nitrosomonas eutropha are able to grow chemoorganotrophically under anoxic conditions with pyruvate, lactate, acetate, serine, succinate, α-ketoglutarate, or fructose as substrate and nitrite as terminal electron acceptor. The growth yield of both bacteria is about 3.5 mg protein (mmol pyruvate)−1 and the maximum growth rates of N. europaea and N. eutropha are 0.094 d−1 and 0.175 d−1, respectively. In the presence of pyruvate and CO2 about 80% of the incorporated carbon derives from pyruvate and about 20% from CO2. Pyruvate is used as energy and only carbon source in the absence of CO2 (chemoorganoheterotrophic growth). CO2 stimulates the chemoorganotrophic growth of both ammonia oxidizers and the expression of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase is down-regulated at increasing CO2 concentration. Ammonium, although required as nitrogen source, is inhibitory for the chemoorganotrophic metabolism of N. europaea and N. eutropha. In the presence of ammonium pyruvate consumption and the expression of the genes aceE, ppc, gltA, odhA, and ppsA (energy conservation) as well as nirK, norB, and nsc (denitrification) are reduced.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abeliovich A (1987) Nitrifying bacteria in wastewater reservoirs. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:754–760
Abeliovich A, Vonshak A (1992) Anaerobic metabolism of Nitrosomonas europaea. Arch Microbiol 158:267–270
Arp DJ, Chain PS, Klotz MG (2007) The impact of genome analyses on our understanding of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:503–528
Beaumont HJ, Hommes NG, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Arp DJ, Arciero DM, Hooper AB, Westerhoff HV, van Spanning RJ (2002) Nitrite reductase of Nitrosomonas europaea is not essential for production of gaseous nitrogen oxides and confers tolerance to nitrite. J Bacteriol 184:2557–2560
Beaumont HJ, van Schooten B, Lens SI, Westerhoff HV, van Spanning RJ (2004) Nitrosomonas europaea expresses a nitric oxide reductase during nitrification. J Bacteriol 186:4417–4421
Beyer S, Gilch S, Meyer O, Schmidt I (2009) Transcription of genes coding for metabolic key functions in Nitrosomonas europaea during aerobic and anaerobic growth. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 16:187–197. doi:10.1159/000142531
Bock E, Schmidt I, Stüven R, Zart D (1995) Nitrogen loss caused by denitrifying Nitrosomonas cells using ammonium or hydrogen as electron donors and nitrite as electron acceptor. Arch Microbiol 163:16–20
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein, utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chain P, Lamerdin J, Larimer F, Regala W, Lao V, Land M, Hauser L, Hooper A, Klotz M, Norton J, Sayavedra-Soto L, Arciero D, Hommes N, Whittaker M, Arp D (2003) Complete genome sequence of the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium and obligate chemolithoautotroph Nitrosomonas europaea. J Bacteriol 185:2759–2773
Clark C, Schmidt EL (1966) Effect of mixed culture on Nitrosomonas europaea simulated by uptake and utilization of pyruvate. J Bacteriol 91:367–373
Clark C, Schmidt EL (1967) Growth response of Nitrosomonas europaea to amino acids. J Bacteriol 93:1302–1309
Hommes NG, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Arp DJ (2003) Chemolithoorganotrophic growth of Nitrosomonas europaea on fructose. J Bacteriol 185:6809–6814
Hooper AB (1969) Biochemical basis of obligate autotrophy in Nitrosomonas europaea. J Bacteriol 97:776–779
Hooper AB, Vannelli T, Bergmann DJ, Arciero DM (1997) Enzymology of the oxidation of ammonia to nitrite by bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 71:59–67
Hyman MR, Arp DJ (1992) 14C2H2 and 14CO2-labeling studies of the de novo synthesis of polypeptides by Nitrosomonas europaea during recovery from acetylene and light inactivation of ammonia monooxygenase. J Biol Chem 267:1534–1545
Hyman MR, Arp DJ (1995) Effects of ammonia on the de novo synthesis of polypeptides in cells of Nitrosomonas europaea denied ammonia as an energy source. J Bacteriol 177:4974–4979
Kester RA, de Boer W, Laanbroek HJ (1997) Production of NO and N2O by pure cultures of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria during changes in aeration. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3872–3877
Kreutz FH (1962) Enzymatische Gycerinbestimmung. Klin Wochenschr 40:362–363
Krümmel A, Harms H (1982) Effect of organic matter on growth and cell yield of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 133:50–54
Marti R, Varela E, Segura RM, Alegre J, Surin JM, Pascual C (1997) Determination of D-lactate by enzymatic methods in biological fluids: study of interferences. Clin Chem 43:1010–1015
Martiny H, Koops H-P (1982) Incorporation of organic compounds into cell protein by lithotrophic, ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 48:327–336
Poth M (1986) Dinitrogen production from nitrite by a Nitrosomonas isolate. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:957–959
Poth M, Focht DD (1985) 15N kinetic analysis of N2O production by Nitrosomonas europaea: an examination of nitrifier denitrification. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1134–1141
Rees M, Nason A (1966) Incorporation of atmospheric oxygen into nitrite formed during ammonia oxidation by Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochim Biophys Acta 113:398–401
Richter H, Vlad D, Unden G (2001) Significance of pantothenate for glucose fermentation by Oenococcus oeni and for suppression of the erythritol and acetate production. Arch Microbiol 175:26–31
Sambrook J, Fritsch EJ, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sato C, Schnoor JL, McDonald DB, Huey J (1985) Test medium for the growth of Nitrosomonas europaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1101–1107
Sayavedra-Soto LA, Hommes NG, Russell SA, Arp DJ (1996) Induction of ammonia monooxygenase and hydroxylamine oxidoreductase mRNAs by ammonium in Nitrosomonas europaea. Mol Microbiol 20:541–548
Schmidt I, Bock E (1997) Anaerobic ammonia oxidation with nitrogen dioxide by Nitrosomonas eutropha. Arch Microbiol 167:106–111
Schmidt I, Bock E (1998) Anaerobic ammonia oxidation by cell-free extracts of Nitrosomonas eutropha. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:271–278
Schmidt I, Zart D, Bock E (2001) Effects of gaseous NO2 on cells of Nitrosomonas eutropha previously incapable of using ammonia as an energy source. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 79:39–47
Schmidt I, Hermelink C, van de Pas-Schoonen K, Strous M, op den Camp HJ, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (2002) Anaerobic ammonia oxidation in the presence of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by two different lithotrophs. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5351–5357
Schmidt I, Sliekers O, Schmid M, Cirpus I, Strous M, Bock E, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (2002) Aerobic and anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria—competitors or natural partners? FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:175–181
Schmidt I, van Spanning RJM, Jetten MSM (2004) Denitrification and ammonia oxidation by Nitrosomonas europaea wild-type, and NirK and NorB-deficient mutants. Microbiology 150:4107–4114
Stein LY, Arp DJ, Berube PM, Chain PS, Hauser L, Jetten MS, Klotz MG, Larimer FW, Norton JM, Op den Camp HJ, Shin M, Wei X (2007) Whole-genome analysis of the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium, Nitrosomonas eutropha C91: implications for niche adaptation. Environ Microbiol 9:2993–3007
Van de Graaf AA, de Bruijn P, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1996) Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing micro-organisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology 142:2187–2196
Völker U, Engelmann S, Maul B, Riethdorf S, Völker A, Schmid R, Mach H, Hecker M (1994) Analysis of the induction of general stress proteins of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 140:741–752
Wallace W, Knowles SE, Nicholas DJD (1970) Intermediary metabolism of carbon compounds by nitrifying bacteria. Arch Microbiol 70:26–42
Wei X, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Arp DJ (2004) The transcription of the cbb operon in Nitrosomonas europaea. Microbiology 150:1869–1879
Whitman WB, Bowen TL, Boone DR (1992) The methanogenic bacteria. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer K-H (eds) The procaryotes: a handbook on the biology of bacteria: ecophysiology, isolation, identification, applications. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 719–767
Whittaker M, Bergmann D, Arciero D, Hooper AB (2000) Electron transfer during the oxidation of ammonia by the chemolithotrophic bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochim Biophys Acta 1459:346–355
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, I. Chemoorganoheterotrophic Growth of Nitrosomonas europaea and Nitrosomonas eutropha . Curr Microbiol 59, 130–138 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9409-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9409-8