Abstract
A total of 168 Campylobacter strains (154 C. jejuni and 14 C. coli) isolated from human clinical samples and chicken meat were typed using Penner serotyping, randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) with four restriction enzymes (Sac II, Sal I, Sma I, Kpn I).
The 168 strains were found to represent 13 different Penner-types and 72 different RAPD-types. However, the discriminatory potential of PFGE was dependent on the restriction enzymes used. The 168 strains were divided into 74 (Sac II), 73 (Sal I), 72 (Sma I) and 69 (Kpn I) types. The DNA of some strains was not digested by Sal I, Sma I and Kpn I. Although three RAPD-types were further subdivided by PFGE, RAPD showed good discriminatory power and a high level of agreement with PFGE patterns in terms of strain differentiation.
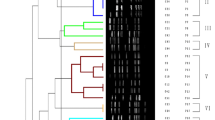
To compare the similarities of PFGE patterns (Sac II) among the strains, a dendrogram was constructed based on the unweighted pair group method with averages (UPGMA). In most cases, DNA types of C. coli were different from those of C. jejuni. The similarities between human and meat isolates were less than 0.42 except for one outbreak in which the isolates from both patients and chicken meat showed the same DNA types.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ono, ., Kurazono, ., Niwa, . et al. Comparison of Three Methods for Epidemiological Typing of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. Curr Microbiol 47, 364–371 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-4037-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-4037-6