Abstract
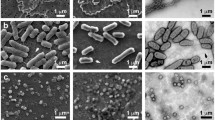
Freeze-substitution technique was applied to thin-sectioning electron microscopy of Mycoplasma mobile, M. pneumoniae, and M. gallisepticum, all of which can glide in the direction of the tapered cell end. M. mobile presented a flask-like cell morphology. An additional layer was found around the tapered end. The cell images of M. pneumoniae showed a protruding membrane extension, the attachment organelle, composed of a low density space inside the cells and featuring a filamentous dense core anchored to the terminal end. The detailed structures were more obvious than those observed by the conventional chemical fixation. The cells of M. gallisepticum presented irregular dense granules, in contrast to regular particles, which can be observed in the images of chemically fixed thin sections, in the rear portion of the cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 September 2001 / Accepted: 25 September 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, T., Miyata, M. Electron Microscopic Studies of Three Gliding Mycoplasmas, Mycoplasma mobile, M. pneumoniae, and M. gallisepticum, by Using the Freeze-Substitution Technique. Curr Microbiol 44, 431–434 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-001-0014-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-001-0014-8