Abstract
Background
Preclinical results showing therapeutic effect and low toxicity of metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide (Cy) + celecoxib (Cel) for mammary tumors encouraged its translation to the clinic for treating advanced breast cancer patients (ABCP).
Patients and methods
A single-arm, mono-institutional, non-randomized, phase II, two-step clinical trial (approved by Bioethics Committee and Argentine Regulatory Authority) was designed. Patients received Cy (50 mg po.d) + Cel (200 mg p.o.bid). Patient eligibility criteria included: ABCP who progressed to anthracyclines, taxanes and capecitabine, ≤4 chemotherapy schemes, with good performance status. Several pro- and anti-angiogenic molecules and cells were determined as biomarkers. Informed consent was signed by all patients. Primary endpoint was clinical benefit (CB).
Results
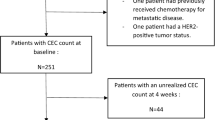
Twenty patients were enrolled. Main clinical outcomes were prolonged disease stabilization and partial remission in 10/20 and 1/20 patients, respectively. CB was 55 %, and time to progression (TTP) was 21.1 weeks. Median TTP in patients who achieved CB was 35.6 weeks, and mean overall survival was 44.20 weeks. There were no grade 3/4 toxicities associated with treatment. Circulating endothelial cells (CECs) increased at the time of progression in patients who showed CB (P = 0.014). Baseline CECs and circulating endothelial progenitor cells showed marginal associations with TTP. Serum VEGF decreased (P = 0.050), sVEGFR-2 increased (P = 0.005) and VEGF/sVEGFR-2 ratio decreased during treatment (P = 0.041); baseline VEGF and VEGF/sVEGFR-2 were associated with TTP (P = 0.035 and P = 0.030, respectively), while sVEGFR-2 did not.
Conclusions
Treatment was effective, showing low toxicity profile and excellent tolerability. The combination had anti-angiogenic effect. Increased levels of CEC could be useful for detecting progression. Baseline VEGF and VEGF/sVEGFR-2 values could be useful as early predictors of response.
Trial registration
ANMAT#4596/09.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palumbo R, Sottotetti F, Riccardi A, Teragni C, Pozzi E, Quaquarini E, Tagliaferri B, Bernardo A (2013) Which patients with metastatic breast cancer benefit from subsequent lines of treatment? An update for clinicians. Ther Adv Med Oncol 5(6):334–350. doi:10.1177/1758834013508197
Nelson R (2013) Targeted therapies offer promise, but are they affordable? Medscape. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/810147#vp_2. Accessed March 13 2015
Hanahan D, Bergers G, Bergsland E (2000) Less is more, regularly: metronomic dosing of cytotoxic drugs can target tumor angiogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest 105(8):1045–1047. doi:10.1172/JCI9872
Colleoni M, Rocca A, Sandri MT, Zorzino L, Masci G, Nole F, Peruzzotti G, Robertson C, Orlando L, Cinieri S, de Braud F, Viale G, Goldhirsch A (2002) Low-dose oral methotrexate and cyclophosphamide in metastatic breast cancer: antitumor activity and correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor levels. Ann Oncol 13(1):73–80
Perroud HA, Rico MJ, Alasino CM, Queralt F, Mainetti LE, Pezzotto SM, Rozados VR, Scharovsky OG (2013) Safety and therapeutic effect of metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and celecoxib in advanced breast cancer patients. Future Oncol 9(3):451–462. doi:10.2217/fon.12.196
Lansiaux A, Salingue S, Dewitte A, Clisant S, Penel N (2012) Circulating thrombospondin 1 level as a surrogate marker in patients receiving cyclophosphamide-based metronomic chemotherapy. Invest New Drugs 30(1):403–404. doi:10.1007/s10637-010-9443-1
Perroud HA, Rico MJ, Alasino CM, Pezzotto SM, Rozados VR, Scharovsky OG (2013) Association between baseline VEGF/sVEGFR-2 and VEGF/TSP-1 ratios and response to metronomic chemotherapy using cyclophosphamide and celecoxib in patients with advanced breast cancer. Indian J Cancer 50(2):115–121. doi:10.4103/0019-509X.117031
Mancuso P, Colleoni M, Calleri A, Orlando L, Maisonneuve P, Pruneri G, Agliano A, Goldhirsch A, Shaked Y, Kerbel RS, Bertolini F (2006) Circulating endothelial-cell kinetics and viability predict survival in breast cancer patients receiving metronomic chemotherapy. Blood 108(2):452–459. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-11-4570
Rozados VR, Mainetti LE, Rico MJ, Zacarias Fluck MF, Matar P, Scharovsky OG (2010) The immune response and the therapeutic effect of metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide. Oncol Res 18(11–12):601–605
Ghiringhelli F, Menard C, Puig PE, Ladoire S, Roux S, Martin F, Solary E, Le Cesne A, Zitvogel L, Chauffert B (2007) Metronomic cyclophosphamide regimen selectively depletes CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells and restores T and NK effector functions in end stage cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56(5):641–648. doi:10.1007/s00262-006-0225-8
Martin-Padura I, Marighetti P, Agliano A, Colombo F, Larzabal L, Redrado M, Bleau AM, Prior C, Bertolini F, Calvo A (2012) Residual dormant cancer stem-cell foci are responsible for tumor relapse after antiangiogenic metronomic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts. Lab Invest 92(7):952–966. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2012.65
Vives M, Ginesta MM, Gracova K, Graupera M, Casanovas O, Capella G, Serrano T, Laquente B, Vinals F (2013) Metronomic chemotherapy following the maximum tolerated dose is an effective anti-tumour therapy affecting angiogenesis, tumour dissemination and cancer stem cells. Int J Cancer 133(10):2464–2472. doi:10.1002/ijc.28259
Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J (2000) Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res 60(7):1878–1886
Dai ZJ, Ma XB, Kang HF, Gao J, Min WL, Guan HT, Diao Y, Lu WF, Wang XJ (2012) Antitumor activity of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell Int 12(1):53. doi:10.1186/1475-2867-12-53
Young SD, Lafrenie RM, Clemons MJ (2012) Phase ii trial of a metronomic schedule of docetaxel and capecitabine with concurrent celecoxib in patients with prior anthracycline exposure for metastatic breast cancer. Curr Oncol 19(2):e75–e83. doi:10.3747/co.19.879
Simon R (1989) Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 10(1):1–10
Bouche G, Andre N, Banavali S, Berthold F, Berruti A, Bocci G, Brandi G, Cavallaro U, Cinieri S, Colleoni M, Curigliano G, Di Desidero T, Eniu A, Fazio N, Kerbel R, Hutchinson L, Ledzewicz U, Munzone E, Pasquier E, Graciela Scharovsky O, Shaked Y, Sterba J, Villalba M, Bertolini F (2014) Lessons from the fourth metronomic and anti-angiogenic therapy meeting, 24–25 June 2014, Milan. Ecancermedicalscience 8:463. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2014.463
Mainetti LE, Rozados VR, Rossa A, Bonfil RD, Scharovsky OG (2011) Antitumoral and antimetastatic effects of metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide combined with celecoxib on murine mammary adenocarcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(1):151–163. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0869-9
Mainetti LE, Rico MJ, Fernandez-Zenobi MV, Perroud HA, Roggero EA, Rozados VR, Scharovsky OG (2013) Therapeutic efficacy of metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin on murine mammary adenocarcinomas. Ann Oncol 24(9):2310–2316. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt164
Colleoni M, Orlando L, Sanna G, Rocca A, Maisonneuve P, Peruzzotti G, Ghisini R, Sandri MT, Zorzino L, Nole F, Viale G, Goldhirsch A (2006) Metronomic low-dose oral cyclophosphamide and methotrexate plus or minus thalidomide in metastatic breast cancer: antitumor activity and biological effects. Ann Oncol 17(2):232–238. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdj066
Dellapasqua S, Bertolini F, Bagnardi V, Campagnoli E, Scarano E, Torrisi R, Shaked Y, Mancuso P, Goldhirsch A, Rocca A, Pietri E, Colleoni M (2008) Metronomic cyclophosphamide and capecitabine combined with bevacizumab in advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(30):4899–4905. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.17.4789
Orlando L, Cardillo A, Ghisini R, Rocca A, Balduzzi A, Torrisi R, Peruzzotti G, Goldhirsch A, Pietri E, Colleoni M (2006) Trastuzumab in combination with metronomic cyclophosphamide and methotrexate in patients with HER-2 positive metastatic breast cancer. BMC Cancer 6:225. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-6-225
Gampenrieder SP, Bartsch R, Matzneller P, Pluschnig U, Dubsky P, Gnant MX, Zielinski CC, Steger GG (2010) Capecitabine and vinorelbine as an all-oral chemotherapy in HER2-negative locally advanced and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Care (Basel) 5(3):158–162. doi:10.1159/000314214
Rau KM, Li SH, Chen SM, Tang Y, Huang CH, Wu SC, Chen YY (2011) Weekly paclitaxel combining with gemcitabine is an effective and safe treatment for advanced breast cancer patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41(4):455–461. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyq232
Bottini A, Generali D, Brizzi MP, Fox SB, Bersiga A, Bonardi S, Allevi G, Aguggini S, Bodini G, Milani M, Dionisio R, Bernardi C, Montruccoli A, Bruzzi P, Harris AL, Dogliotti L, Berruti A (2006) Randomized phase II trial of letrozole and letrozole plus low-dose metronomic oral cyclophosphamide as primary systemic treatment in elderly breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 24(22):3623–3628. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.5773
Montagna E, Cancello G, Bagnardi V, Pastrello D, Dellapasqua S, Perri G, Viale G, Veronesi P, Luini A, Intra M, Calleri A, Rampinelli C, Goldhirsch A, Bertolini F, Colleoni M (2012) Metronomic chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab and erlotinib in patients with metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer: clinical and biological activity. Clin Breast Cancer 12(3):207–214. doi:10.1016/j.clbc.2012.03.008
Gebbia V, Boussen H, Valerio MR (2012) Oral metronomic cyclophosphamide with and without methotrexate as palliative treatment for patients with metastatic breast carcinoma. Anticancer Res 32(2):529–536
Taguchi T, Nakayama T, Masuda N, Yoshidome K, Akagi K, Nishida Y, Yoshikawa Y, Ogino N, Abe C, Sakamoto J, Noguchi S (2010) Study of low-dose capecitabine monotherapy for metastatic breast cancer. Chemotherapy 56(2):166–170. doi:10.1159/000313531
Fedele P, Marino A, Orlando L, Schiavone P, Nacci A, Sponziello F, Rizzo P, Calvani N, Mazzoni E, Cinefra M, Cinieri S (2012) Efficacy and safety of low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with capecitabine in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 48(1):24–29. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.040
Kraan J, Sleijfer S, Foekens JA, Gratama JW (2012) Clinical value of circulating endothelial cell detection in oncology. Drug Discov Today 17(13–14):710–717. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2012.01.011
Cramarossa G, Lee EK, Sivanathan L, Georgsdottir S, Lien K, Santos KD, Chan K, Emmenegger U (2014) A systematic literature analysis of correlative studies in low-dose metronomic chemotherapy trials. Biomark Med 8(6):893–911. doi:10.2217/bmm.14.14
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP, Novotny W (2004) Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(5):391–400. doi:10.1038/nrd1381
Kerbel RS, Kamen BA (2004) The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4(6):423–436. doi:10.1038/nrc1369
Guo S, Colbert LS, Fuller M, Zhang Y, Gonzalez-Perez RR (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1806(1):108–121. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.04.004
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Bogdanovic E, Alami J, Van Slyke P, Francia G, Xu P, Mutsaers AJ, Dumont DJ, Kerbel RS (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated decrease in plasma soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 levels as a surrogate biomarker for tumor growth. Cancer Res 68(2):521–529. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3217
El-Arab LR, Swellam M, El Mahdy MM (2012) Metronomic chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer: impact on VEGF. J Egypt Natl Cancer Inst 24(1):15–22. doi:10.1016/j.jnci.2011.12.002
Allegrini G, Di Desidero T, Barletta MT, Fioravanti A, Orlandi P, Canu B, Chericoni S, Loupakis F, Di Paolo A, Masi G, Fontana A, Lucchesi S, Arrighi G, Giusiani M, Ciarlo A, Brandi G, Danesi R, Kerbel RS, Falcone A, Bocci G (2012) Clinical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluations of metronomic UFT and cyclophosphamide plus celecoxib in patients with advanced refractory gastrointestinal cancers. Angiogenesis 15(2):275–286. doi:10.1007/s10456-012-9260-6
Bhatt RS, Merchan J, Parker R, Wu HK, Zhang L, Seery V, Heymach JV, Atkins MB, McDermott D, Sukhatme VP (2010) A phase 2 pilot trial of low-dose, continuous infusion, or “metronomic” paclitaxel and oral celecoxib in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer 116(7):1751–1756. doi:10.1002/cncr.24902
Fontana A, Galli L, Fioravanti A, Orlandi P, Galli C, Landi L, Bursi S, Allegrini G, Fontana E, Di Marsico R, Antonuzzo A, D’Arcangelo M, Danesi R, Del Tacca M, Falcone A, Bocci G (2009) Clinical and pharmacodynamic evaluation of metronomic cyclophosphamide, celecoxib, and dexamethasone in advanced hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(15):4954–4962. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3317
Khan OA, Blann AD, Payne MJ, Middleton MR, Protheroe AS, Talbot DC, Taylor M, Kirichek O, Han C, Patil M, Harris AL (2011) Continuous low-dose cyclophosphamide and methotrexate combined with celecoxib for patients with advanced cancer. Br J Cancer 104(12):1822–1827. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.154
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank NCI “National Cancer Institute of Argentina” and the National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) for their support in this study, as well as Cibic S.A. and especially to Dr. Ricardo Giordano, for their help in flow cytometry studies.
Funding
This work was supported by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT) [Grant Number: PICT 2006/1908 to OGS, VRR, SMP and CMA]. The National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health grants for doctoral fellows to HAP. HAP is a fellow of Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The authors declare that the protocol herein described complies with the current laws of Argentina. The protocol was authorized by the School of Medicine Bioethics Committee and by A.N.M.A.T. (Argentine Regulatory Agency).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perroud, H.A., Alasino, C.M., Rico, M.J. et al. Metastatic breast cancer patients treated with low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and celecoxib: clinical outcomes and biomarkers of response. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 77, 365–374 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2947-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2947-9