Abstract
Purpose
Navitoclax (ABT-263), a novel, oral Bcl-2 inhibitor, enhances the antitumor effects of chemotherapy in vitro by lowering the apoptotic threshold. This phase I study (NCT01009073) evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary antitumor activity of navitoclax combined with erlotinib in patients with advanced solid tumors.
Patients and methods
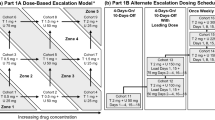
An open-label dose escalation study included an arm evaluating navitoclax combined with erlotinib, which included a dose escalation cohort and a planned safety expansion cohort. Patients with documented cancers for whom erlotinib therapy was appropriate received erlotinib 150 mg orally once daily plus navitoclax 150 mg orally once daily, with navitoclax dose escalation via a continuous reassessment method model.
Results
Eleven patients were enrolled, including six patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Dose-limiting toxicities, most commonly diarrhea, were observed in 4 patients. Navitoclax dosing remained at 150 mg/day because the maximum tolerated dose was exceeded at this starting dose. The planned dose escalation did not occur; no recommended phase II dose (RPTD) was identified, and there was no safety expansion cohort. The most common treatment-related adverse events were diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed no apparent interactions between co-administered navitoclax and erlotinib. No objective responses were observed; the disease control rate was 27 % (95 % CI, 6–61 %).
Conclusion
At the erlotinib and navitoclax doses administered, RPTD was not reached, but the safety profile of the combination was consistent with data from monotherapy studies. There were no apparent pharmacokinetic interactions between erlotinib and navitoclax. Three patients had stable disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Del Gaizo Moore V, Letai A (2008) Rational design of therapeutics targeting the BCL-2 family: are some cancer cells primed for death but waiting for a final push? Adv Exp Med Biol 615:159–175
Kitada S, Pedersen IM, Schimmer AD, Reed JC (2002) Dysregulation of apoptosis genes in hematopoietic malignancies. Oncogene 21:3459–3474
Azmi AS, Mohammad RM (2009) Non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors against Bcl-2 for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol 218:13–21
Simonian PL, Grillot DA, Nunez G (1997) Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL can differentially block chemotherapy-induced cell death. Blood 90:1208–1216
Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson MG, Chen J, Jin S, Johnson EF, Marsh KC, Mitten MJ, Nimmer P, Roberts L, Tahir SK, Xiao Y, Yang X, Zhang H, Fesik S, Rosenberg SH, Elmore SW (2008) ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res 68:3421–3428
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman PM, Day CL, Adams JM, Huang DC (2005) Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 17:393–403
Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC, Jeffers JR, Zambetti GP, Hsieh JJ, Cheng EH (2006) Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol 8:1348–1358
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA, Letai A (2006) Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 9:351–365
Willis SN, Fletcher JI, Kaufmann T, van Delft MF, Chen L, Czabotar PE, Ierino H, Lee EF, Fairlie WD, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Kluck RM, Adams JM, Huang DC (2007) Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science 315:856–859
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Garon EB, Ribeiro de Oliveira M, Bonomi PD, Camidge DR, Chu Q, Giaccone G, Khaira D, Ramalingam SS, Ranson MR, Dive C, McKeegan EM, Chyla BJ, Dowell BL, Chakravartty A, Nolan CE, Rudersdorf N, Busman TA, Mabry MH, Krivoshik AP, Humerickhouse RA, Shapiro GI, Gandhi L (2012) Phase II study of single-agent navitoclax (ABT-263) and biomarker correlates in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18:3163–3169
Gandhi L, Camidge DR, Ribeiro de Oliveira M, Bonomi P, Gandara D, Khaira D, Hann CL, McKeegan EM, Litvinovich E, Hemken PM, Dive C, Enschede SH, Nolan C, Chiu YL, Busman T, Xiong H, Krivoshik AP, Humerickhouse R, Shapiro GI, Rudin CM (2011) Phase I study of Navitoclax (ABT-263), a novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in patients with small-cell lung cancer and other solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 29:909–916
Vlahovic G, Karantza V, Wang D, Cosgrove D, Rudersdorf N, Yang J, Xiong H, Busman T, Mabry M (2014) A phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of ABT-263 in combination with carboplatin/paclitaxel in the treatment of patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 32:976–984
Wilson WH, O’Connor OA, Czuczman MS, LaCasce AS, Gerecitano JF, Leonard JP, Tulpule A, Dunleavy K, Xiong H, Chiu YL, Cui Y, Busman T, Elmore SW, Rosenberg SH, Krivoshik AP, Enschede SH, Humerickhouse RA (2010) Navitoclax, a targeted high-affinity inhibitor of BCL-2, in lymphoid malignancies: a phase 1 dose-escalation study of safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and antitumour activity. Lancet Oncol 11:1149–1159
Cleary JM, Lima CM, Hurwitz HI, Montero AJ, Franklin C, Yang J, Graham A, Busman T, Mabry M, Holen K, Shapiro GI, Uronis H (2014) A phase I clinical trial of navitoclax, a targeted high-affinity Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in combination with gemcitabine in patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 32:937–945
Chen J, Jin S, Abraham V, Huang X, Liu B, Mitten MJ, Nimmer P, Lin X, Smith M, Shen Y, Shoemaker AR, Tahir SK, Zhang H, Ackler SL, Rosenberg SH, Maecker H, Sampath D, Leverson JD, Tse C, Elmore SW (2011) The Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L)/Bcl-w inhibitor, navitoclax, enhances the activity of chemotherapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2340–2349
Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, Cicenas S, Szczesna A, Juhasz E, Esteban E, Molinier O, Brugger W, Melezinek I, Klingelschmitt G, Klughammer B, Giaccone G, Investigators S (2010) Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 11:521–529
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, van Kooten M, Dediu M, Findlay B, Tu D, Johnston D, Bezjak A, Clark G, Santabarbara P, Seymour L, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353:123–132
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, Campos D, Lim R, Ding K, Clark G, Voskoglou-Nomikos T, Ptasynski M, Parulekar W, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2007) Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 25:1960–1966
Tarceva (erlotinib) (2012) Full prescribing information. Astellas and Genentech, Northbrook
Prados MD, Lamborn KR, Chang S, Burton E, Butowski N, Malec M, Kapadia A, Rabbitt J, Page MS, Fedoroff A, Xie D, Kelley SK (2006) Phase 1 study of erlotinib HCl alone and combined with temozolomide in patients with stable or recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol 8:67–78
Zannetti A, Iommelli F, Speranza A, Salvatore M, Del Vecchio S (2012) 3′-deoxy-3′-18F-fluorothymidine PET/CT to guide therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists and Bcl-xL inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med 53:443–450
Yeo W-L, Riely GJ, Yeap BY, Lau MW, Warner JL, Bodio K, Huberman MS, Kris MG, Tenen DG, Pao W, Kobayashi S, Costa DB (2010) Erlotinib at a dose of 25 mg daily for non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations. J Thorac Oncol 5:1048–1053
Roberts AW, Seymour JF, Brown JR, Wierda WG, Kipps TJ, Khaw SL, Carney DA, He SZ, Huang DC, Xiong H, Cui Y, Busman TA, McKeegan EM, Krivoshik AP, Enschede SH, Humerickhouse R (2012) Substantial susceptibility of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to BCL2 inhibition: results of a phase I study of navitoclax in patients with relapsed or refractory disease. J Clin Oncol 30:488–496
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the patients and their caregivers for their participation in this study. We also acknowledge medical writing assistance from Amy Zanikos, PhD, and Tiffany Brake, PhD, which was supported by AbbVie Inc. This study was funded by AbbVie Inc and Genentech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Anthony W. Tolcher has advisory/consulting agreements with AbbVie, Akebia, AP Pharma, ArQule, Inc., Asana, Astex, Avid Biologics, Bayer HealthCare, Bind Therapeutics, BioMed Valley Discoveries, Blend Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb Japan, Celator, Clovis, Curis, De Novo Sciences, Dicerna, Eisai, Endo, Genentech, Heron, Janssen, Lilly MedImmune, Mersana, Merus, Nanobiotix S.A., Nektar, Neumedicines, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Pierre Fabre, Proimagen, Sanofi-Aventis, Symphogen, Vaccinex, Valent Technologies, and Zyngenia. Patricia LoRusso has no conflicts to disclose. Lee S. Rosen receives research funding from Abbott/AbbVie Inc. Jennifer Arzt, Todd A. Busman, Guinan Lian, Niki S. Rudersdorf, Carol Ann Vanderwal, Whitney Kirschbrown, and Kyle D. Holen are employees of and may own stock in AbbVie Inc.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolcher, A.W., LoRusso, P., Arzt, J. et al. Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of navitoclax (ABT-263) in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76, 1025–1032 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2883-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2883-8