Abstract
Purpose
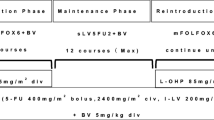
To compare the pharmacokinetics (PK) of bevacizumab (BV) at steady-state under two different dosing regimens, 7.5 mg/kg q3w and 5.0 mg/kg q2w, concomitantly with a combination of capecitabine and oxaliplatin (XELOX) and FOLFOX-4 (oxaliplatin in combination with infusional 5-FU/LV), respectively, in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC).
Methods
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either XELOX + BV or FOLFOX-4 + BV. Blood samples for steady-state PK of BV were collected on day 1 of cycle 5 (at the earliest) for XELOX + BV treatment and day 1 of cycle 7 (at the earliest) for FOLFOX-4 + BV treatment.
Results
A total of 64 patients were enrolled, of which 37 were eligible for PK analyses. The primary PK parameter of BV, AUCss(per week), was statistically similar between the two dosing regimens with the 90% confidence interval in the commonly used no-effect boundaries of 0.8 and 1.25. The V ss and CL did not differ between the two regimens; t ½ during the PK cycle was also similar for both arms at approximately 16 days. These results demonstrated no clinically relevant change in BV PK when co-administered with either XELOX or FOLFOX-4. BV in combination with XELOX and FOLFOX-4 was generally well tolerated with no unexpected safety signals and no deaths. Nine patients in the XELOX + BV arm and 15 patients in the FOLFOX-4 + BV arm experienced at least one SAE (most commonly gastrointestinal disorders) which led to dose modification in 7 and 2 patients, respectively, and to premature withdrawal in 9 and 5 patients, respectively. All 64 patients experienced at least one non-serious AE. Laboratory tests and vital signs were unremarkable.
Conclusions
No clinically relevant differences in overall steady-state exposure of BV occurred when BV was given 7.5 mg/kg q3w in combination with XELOX or 5.0 mg/kg q2w with FOLFOX-4 in patients with mCRC, and the pharmacokinetics of BV were very similar between the two regimens. No unexpected adverse events or deaths were identified.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249
Thirion P, Michiels S, Pignon JP, Buyse M, Braud AC, Carlson RW, O’Connell M, Sargent P, Piedbois P, Meta-Analysis Group in Cancer (2004) Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: an updated meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 22(18):3766–3775. Erratum in: J Clin Oncol. 2005 Feb 20; 23(6):1337–1338
Lokich JJ, Ahlgren JD, Gullo JJ, Philips JA, Fryer JG (1989) A prospective randomized comparison of continuous infusion fluorouracil with a conventional bolus schedule in metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a Mid-Atlantic Oncology Program Study. J Clin Oncol 7(4):425–432
Hansen RM (1991) 5-Fluorouracil by protracted venous infusion: a review of recent clinical studies. Cancer Invest 9(6):637–642
Koukourakis GV, Kouloulias V, Koukourakis MJ, Zacharias GA, Zabatis H, Kouvaris J (2008) Efficacy of the oral fluorouracil pro-drug capecitabine in cancer treatment: a review. Molecules 13(8):1897–1922
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M et al (2000) Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:2938–2947
Diaz-Rubio E, Evans TRJ, Tabernero J et al (2002) Capecitabine (Xeloda®) in combination with oxaliplatin: a phase I, dose-escalation study in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumor. Ann Oncol 13:558–565
Arkenau HT, Arnold D, Cassidy J, Diaz-Rubio E, Douillard JY, Hochster H, Martoni A, Grothey A, Hinke A, Schmiegel W, Schmoll HJ, Porschen R (2008) Efficacy of oxaliplatin plus capecitabine or infusional fluorouracil/leucovorin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a pooled analysis of randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 26(36):5910–5917 Epub 2008 Nov 17
Cassidy J, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS, Rivera F, Couture F, Sirzén F, Saltz L (2008) Randomized phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(12):2006–2012
Díaz-Rubio E, Tabernero J, Gómez-España A, Massutí B, Sastre J, Chaves M, Abad A, Carrato A, Queralt B, Reina JJ, Maurel J, González-Flores E, Aparicio J, Rivera F, Losa F, Aranda E, Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors Trial (2007) Phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with continuous-infusion fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: final report of the Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors Trial. J Clin Oncol 25(27):4224–4230. Epub 2007 Jun 4
Hurwitz H (2004) Integrating the anti-VEGF-A humanized monoclonal antibody bevacizumab with chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 4:S62–S68
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavar F (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350(23):2335–2342
Lu JF, Bruno R, Eppler S, Novotny W, Lum B, Gaudreault J (2008) Clinical pharmacokinetics of bevacizumab in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62(5):779–786
Conflict of interest
Dr. Major has Novartis and Amgen consultancy/advisory role. None for others.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, J., Chen, E., Major, P. et al. A multicenter, randomized, open-label study to assess the steady-state pharmacokinetics of bevacizumab given with either XELOX or FOLFOX-4 in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68, 1199–1206 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-011-1606-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-011-1606-z