Abstract
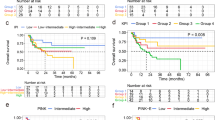
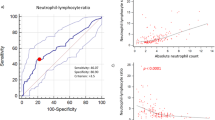
Coagulative dysfunction is frequently observed among patients with extranodal nasal-type natural killer/T cell lymphoma (NKTCL) in our clinical practice. However, the true prognostic value of coagulation factors in patients with NKTCL has not been evaluated systemically. Data for patients with stage I/II NKTCL who were treated in the Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, from January 2008 to January 2019 were collected retrospectively. The patients enrolled in this study were initially diagnosed as having early-stage disease. The patients’ baseline characteristics and pretreatment laboratory tests for coagulation function, including fibrinogen (FIB) and d-dimer (d-D), were reviewed and analyzed. The influence of coagulative factors on the responses and prognosis of patients with early-stage NKTCL was evaluated. Among 394 patients assessed, 154 were included in this study. Abnormal coagulation function was found in nearly half of the patients (48.1%). Univariate analysis showed that reduced complete remission (CR) was associated with elevated d-D (P = 0.001) and elevated FIB levels (P = 0.006). The d-D level was demonstrated as associated with unfavorable progression-free survival (PFS) (P = 0.003) and overall survival (OS) (P = 0.002). Multivariate analysis indicated that an elevated d-D level was an independent factor for poor clinical response (P = 0.019), PFS (P = 0.046), and OS (P = 0.024). Elevated pretreatment levels of coagulation factors, especially d-D and plasma FIB, are unfavorable predictors for clinical response, OS, and PFS in early-stage NKTCL.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Zhang YJ, Zhu Y et al (2015) Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in previously untreated patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a multicenter study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93S:E448–E449
Yang Y, Zhu Y, Cao JZ, Zhang YJ, Xu LM, Yuan ZY, Wu JX, Wang W, Wu T, Lu B, Zhu SY, Qian LT, Zhang FQ, Hou XR, Li YX (2015) Risk-adapted therapy for early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma: analysis from a multicenter study. BLOOD 126:1424–1432
SHIPP MA, HARRINGTON DP, ANDERSON JR et al (1993) A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkins-lymphoma. N Engl J Med 329:987–994
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH, Lee DH, Huh J, Oh SY, Kwon HC, Kim HJ, Lee SI, Kim JH, Park J, Oh SJ, Kim K, Jung C, Park K, Kim WS (2006) Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 24:612–618
Ye Z, Cao Q, Niu G, Liang Y, Liu Y, Jiang L, Yu X, Han A (2013) p63 and p53 expression in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type. J Clin Pathol 66:676–680
Kim SJ, Kim BS, Choi CW, Choi J, Kim I, Lee YH, Kim JS (2007) Ki-67 expression is predictive of prognosis in patients with stage I/II extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol 18:1382–1387
Bi XW, Wang L, Zhang WW, Yan SM, Sun P, Xia Y, Li ZM, Jiang WQ (2016) The pretreatment albumin to globulin ratio predicts survival in patients with natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. PeerJ 4:e1742
Jaffe ES (2009) The 2008 WHO classification of lymphomas: implications for clinical practice and translational research. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 523–31. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.523
Au WY, Weisenburger DD, Intragumtornchai T, Nakamura S, Kim WS, Sng I, Vose J, Armitage JO, Liang R, for the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project (2009) Clinical differences between nasal and extranasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a study of 136 cases from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 113:3931–3937
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H, Park Y, Chang KM, Maeda Y, Ishida F, Shin DY, Kim JS, Jeong SH, Yang DH, Jo JC, Lee GW, Choi CW, Lee WS, Chen TY, Kim K, Jung SH, Murayama T, Oki Y, Advani R, d’Amore F, Schmitz N, Suh C, Suzuki R, Kwong YL, Lin TY, Kim WS (2016) A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 17:389–400
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, Lister TA, Alliance, Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group, European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Consortium, Italian Lymphoma Foundation, European Organisation for Research, Treatment of Cancer/Dutch Hemato-Oncology Group, Grupo Español de Médula Ósea, German High-Grade Lymphoma Study Group, German Hodgkin’s Study Group, Japanese Lymphorra Study Group, Lymphoma Study Association, NCIC Clinical Trials Group, Nordic Lymphoma Study Group, Southwest Oncology Group, United Kingdom National Cancer Research Institute (2014) Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol 32:3059–3068
Fan S, Zhao G, An G (2019) High pretreatment plasma D-dimer levels are associated with shorter overall survival in patients with small cell lung cancer. J Int Med Res 47:215–224
Liu FT, Gao H, Wu CW, Zhu ZM (2017) The association of plasma fibrinogen with clinicopathological features and prognosis in esophageal cancer patients. Oncotarget 8:93029–93038
Liu P, Zhu Y, Liu L (2015) Elevated pretreatment plasma D-dimer levels and platelet counts predict poor prognosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 8:1335–1340
Sun ZQ, Han XN, Wang HJ, Tang Y, Zhao ZL, Qu YL, Xu RW, Liu YY, Yu XB (2014) Prognostic significance of preoperative fibrinogen in patients with colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 20:8583–8591
Dirix LY, Salgado R, Weytjens R, Colpaert C, Benoy I, Huget P, van Dam P, Prové A, Lemmens J, Vermeulen P (2002) Plasma fibrin D-dimer levels correlate with tumour volume, progression rate and survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 86:389–395
Sanfilippo K, Wang T, Gage B et al (2016) Incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Thromb Res 143:86–90
Borg IH, Bendtsen MD, Bogsted M et al (2016) Incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 57:2771–2776
Colombo R, Gallipoli P, Castelli R (2014) Thrombosis and hemostatic abnormalities in hematological malignancies. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 14:441–450
Kang HJ, Bae K, Kim JH, Cho CK, Yoo HS (2018) Correlation between natural killer cell activity and systemic inflammatory markers for heterogeneous cancer patients treated with wheel balance cancer therapy. Integr Cancer Ther 17:322–331
Kattula S, Byrnes JR, Wolberg AS (2017) Fibrinogen and fibrin in hemostasis and thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37:e13–e21
Martino MM, Briquez PS, Ranga A, Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA (2013) Heparin-binding domain of fibrin(ogen) binds growth factors and promotes tissue repair when incorporated within a synthetic matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:4563–4568
Zheng S, Shen J, Jiao Y, Liu Y, Zhang C, Wei M, Hao S, Zeng X (2009) Platelets and fibrinogen facilitate each other in protecting tumor cells from natural killer cytotoxicity. Cancer Sci 100:859–865
Bi XW, Wang L, Zhang WW et al (2016) High pretreatment D-dimer levels correlate with adverse clinical features and predict poor survival in patients with natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. PLoS One 11:e152842
Diao D, Cheng Y, Song Y, Zhang H, Zhou Z, Dang C (2017) D-dimer is an essential accompaniment of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 17:56
Funding
This work was supported by the special fund of Beijing Hope Run Project (grant number, LC2014L11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, Y., Qi, F., Chen, B. et al. Abnormal pretreatment coagulation factor levels correlate with poor prognosis in patients with early-stage extranodal nasal-type natural/killer T cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 99, 1303–1309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04035-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04035-0