Abstract
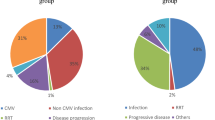
To gain insight into the natural history of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection following unrelated cord blood transplantation (UCBT) in seropositive patients, we analyzed the data of 349 seropositive patients who received UCBT in Korea between 2000 and 2011. CMV reactivation occurred in 49 % (171/349) of the CMV-seropositive transplant recipients at a median of 31 days post UCBT. One hundred sixty-four out of 171 patients (96 %) received preemptive therapy. The median duration of CMV reactivation was 29 days. In multivariate analysis, weight >22 kg, use of total body irradiation, use of pre-transplant antithymocyte globulin, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis with mycophenolate mofetil, and presence of grade II–IV acute GVHD were independent predictors of CMV reactivation. CMV reactivation did not impact transplantation-related mortality (TRM), leukemia relapse, or survival. CMV disease was diagnosed in 62 patients (17.8 %) at a median 55 days after UCBT. Longer duration of CMV reactivation was the only risk factor for progression to CMV disease (p = 0.01). CMV disease resulted in higher TRM (56.0 vs. 31.4 %, p < 0.01) and lower survival (36.1 vs. 55.1 %, p = 0.02).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albano MS, Taylor P, Pass RF, Scaradavou A, Ciubotariu R, Carrier C, Dobrila L, Rubinstein P, Stevens CE (2006) Umbilical cord blood transplantation and cytomegalovirus: posttransplantation infection and donor screening. Blood 108:4275–4282
Beck JC, Wagner JE, DeFor TE, Brunstein CG, Schleiss MR, Young JA, Weisdorf DH, Cooley S, Miller JS, Verneris MR (2010) Impact of cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation after umbilical cord blood transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 16:215–222
D'Arena G, Musto P, Cascavilla N, Di Giorgio G, Fusilli S, Zendoli F, Carotenuto M (1998) Flow cytometric characterization of human umbilical cord blood lymphocytes: immunophenotypic features. Haematologica 83:197–203
Komanduri KV, St John LS, de Lima M, McMannis J, Rosinski S, McNiece I, Bryan SG, Kaur I, Martin S, Wieder ED, Worth L, Cooper LJ, Petropoulos D, Molldrem JJ, Champlin RE, Shpall EJ (2007) Delayed immune reconstitution after cord blood transplantation is characterized by impaired thymopoiesis and late memory T-cell skewing. Blood 110:4543–4551
Boeckh M, Nichols WG, Papanicolaou G, Rubin R, Wingard JR, Zaia J (2003) Cytomegalovirus in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: current status, known challenges, and future strategies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 9:543–558
Broers AE, van Der Holt R, van Esser JW, Gratama JW, Henzen-Logmans S, Kuenen-Boumeester V, Lowenberg B, Cornelissen JJ (2000) Increased transplant-related morbidity and mortality in CMV-seropositive patients despite highly effective prevention of CMV disease after allogeneic T-cell-depleted stem cell transplantation. Blood 95:2240–2245
Ljungman P, Hakki M, Boeckh M (2010) Cytomegalovirus in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Infect Dis Clin N Am 24:319–337
Walker CM, van Burik JA, De For TE, Weisdorf DJ (2007) Cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic transplantation: comparison of cord blood with peripheral blood and marrow graft sources. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 13:1106–1115
George B, Kerridge I, Gilroy N, Huang G, Hertzberg M, Gottlieb D, Bradstock K (2010) Fludarabine-based reduced intensity conditioning transplants have a higher incidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation compared with myeloablative transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant 45:849–855
Yoo KH, Lee SH, Sung KW, Koo HH, Chung NG, Cho B, Kim HK, Kang HJ, Shin HY, Ahn HS, Baek HJ, Han DK, Kook H, Hwang TJ, Kim SY, Lee YH, Hah JO, Im HJ, Seo JJ, Park SK, Jung HJ, Park JE, Lim YJ, Park SS, Lim YT, Yoo ES, Ryu KH, Park HJ, Park BK (2011) Current status of pediatric umbilical cord blood transplantation in Korea: a multicenter retrospective analysis of 236 cases. Am J Hematol 86:12–17
Ljungman P, Griffiths P, Paya C (2002) Definitions of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 34:1094–1097
Frangoul H, Wang L, Harrell FE Jr, Ho R, Domm J (2009) Preengraftment syndrome after unrelated cord blood transplant is a strong predictor of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant : J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant 15:1485–1488
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, Apperley J, Slavin S, Pasquini M, Sandmaier BM, Barrett J, Blaise D, Lowski R, Horowitz M (2009) Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15:1628–1633
Patel KJ, Rice RD, Hawke R, Abboud M, Heller G, Scaradavou A, Young JW, Barker JN (2010) Pre-engraftment syndrome after double-unit cord blood transplantation: a distinct syndrome not associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 16:435–440
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, Thomas ED (1995) 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 15:825–828
Vigorito AC, Campregher PV, Storer BE, Carpenter PA, Moravec CK, Kiem HP, Fero ML, Warren EH, Lee SJ, Appelbaum FR, Martin PJ, Flowers ME (2009) Evaluation of NIH consensus criteria for classification of late acute and chronic GVHD. Blood 114:702–708
Tomonari A, Takahashi S, Ooi J, Tsukada N, Konuma T, Kato S, Kasahara S, Iseki T, Yamaguchi T, Tojo A, Asano S (2008) Impact of cytomegalovirus serostatus on outcome of unrelated cord blood transplantation for adults: a single-institute experience in Japan. Eur J Haematol 80:251–257
Mikulska M, Raiola AM, Bruzzi P, Varaldo R, Annunziata S, Lamparelli T, Frassoni F, Tedone E, Galano B, Bacigalupo A, Viscoli C (2012) CMV infection after transplant from cord blood compared to other alternative donors: the importance of donor-negative CMV serostatus. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 18:92–99
Buyck HC, Prentice HG, Griffiths PD, Emery VC (2010) The risk of early and late CMV DNAemia associated with Campath use in stem cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 45:1212–1219
Pinana JL, Martino R, Barba P, Margall N, Roig MC, Valcarcel D, Sierra J, Rabella N (2010) Cytomegalovirus infection and disease after reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation: single-centre experience. Bone Marrow Transplant 45:534–542
Barron MA, Gao D, Springer KL, Patterson JA, Brunvand MW, McSweeney PA, Zeng C, Baron AE, Weinberg A (2009) Relationship of reconstituted adaptive and innate cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific immune responses with CMV viremia in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 49:1777–1783
Yi ES, Kim YJ (2012) Cytomegalovirus infection according to cell source after hematopoietic cell transplantation in pediatric patients. Yonsei Med J 53:393–400
Montesinos P, Sanz J, Cantero S, Lorenzo I, Martin G, Saavedra S, Palau J, Romero M, Montava A, Senent L, Martinez J, Jarque I, Salavert M, Cordoba J, Gomez L, Weiss S, Moscardo F, de la Rubia J, Larrea L, Sanz MA, Sanz GF (2009) Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in patients receiving prophylaxis with oral valganciclovir or intravenous ganciclovir after umbilical cord blood transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15:730–740
Al-Hajjar S, Al Seraihi A, Al Muhsen S, Ayas M, Al Jumaah S, Al Jefri A, Shoukri M, El Solh H (2011) Cytomegalovirus infections in unrelated cord blood transplantation in pediatric patients: incidence, risk factors, and outcomes. Hematol/Oncol Stem Cell Ther 4:67–72
Ozdemir E, St John LS, Gillespie G, Rowland-Jones S, Champlin RE, Molldrem JJ, Komanduri KV (2002) Cytomegalovirus reactivation following allogeneic stem cell transplantation is associated with the presence of dysfunctional antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. Blood 100:3690–3697
Matsumura T, Narimatsu H, Kami M, Yuji K, Kusumi E, Hori A, Murashige N, Tanaka Y, Masuoka K, Wake A, Miyakoshi S, Kanda Y, Taniguchi S (2007) Cytomegalovirus infections following umbilical cord blood transplantation using reduced intensity conditioning regimens for adult patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 13:577–583
Kullberg-Lindh C, Mellgren K, Friman V, Fasth A, Ascher H, Nilsson S, Lindh M (2011) Opportunistic virus DNA levels after pediatric stem cell transplantation: serostatus matching, anti-thymocyte globulin, and total body irradiation are additive risk factors. Transpl Infect Dis 13:122–130
Hambach L, Stadler M, Dammann E, Ganser A, Hertenstein B (2002) Increased risk of complicated CMV infection with the use of mycophenolate mofetil in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 29:903–906
Lipsky JJ (1996) Mycophenolate mofetil. Lancet 348:1357–1359
Heemann U, Azuma H, Hamar P, Schmid C, Tilney N, Philipp T (1996) Mycophenolate mofetil inhibits lymphocyte binding and the upregulation of adhesion molecules in acute rejection of rat kidney allografts. Transpl Immunol 4:64–67
Milano F, Pergam SA, Xie H, Leisenring WM, Gutman JA, Riffkin I, Chow V, Boeckh MJ, Delaney C (2011) Intensive strategy to prevent CMV disease in seropositive umbilical cord blood transplant recipients. Blood 118:5689–5696
Bacigalupo A, Boyd A, Slipper J, Curtis J, Clissold S (2012) Foscarnet in the management of cytomegalovirus infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 10:1249–1264
Shereck EB, Cooney E, van de Ven C, Della-Lotta P, Cairo MS (2007) A pilot phase II study of alternate day ganciclovir and foscarnet in preventing cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections in at-risk pediatric and adolescent allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49:306–312
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of Kyowa Hakko Kirin Korea Co., Ltd., 2011.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Authors’ contributions
M. Park designed the study, performed the analysis, and wrote the paper; Y.H. Lee designed the study, performed the research, and reviewed the manuscript; S.H. Lee, K.H. Yoo, K.W. Sung, H.H. Koo, H.J. Kang, K.D. Park, H.Y. Shin, H.S. Ahn, N.G. Chung, B. Cho, H.K. Kim, K.N. Koh, H.J. Im, J.J. Seo, H.J. Baek, H. Kook, T.J. Hwang, J.M. Lee, J.O. Hah, Y.J. Lim, J.E. Park, C.J. Lyu, Y.T. Lim, S.Y. Chong, and D. Oh contributed to the analysis of data.
Participating centers
This study was conducted at the following institutions: College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju; Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul; Hanyang University Medical Center, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul; Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul; Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul; Asan Medical Center Children’s Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul; Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju; Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu; Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejon; Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon; CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam; Mokdong Hospital, Ehwa women’s University College of Medicine, Seoul; Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul; Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju; Pusan National University, School of Medicine, Pusan; National Cancer Center, Goyang; Konkuk University College of Medicine, Seoul; Gachon University Gil Hospital, Gachon University School of Medicine, Incheon; Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M., Lee, Y.H., Lee, S.H. et al. Cytomegalovirus infection in seropositive unrelated cord blood recipients: a study of 349 Korean patients. Ann Hematol 94, 481–489 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2222-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2222-x