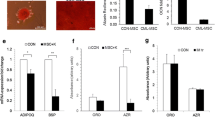
Abstract
The effect of bone marrow microenvironment on the cell cycle of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and the underlying mechanism has not been elucidated. In this study, we found that in normal condition, bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) had no significant effect on the cell cycle and apoptosis of ALL; in the condition when the cell cycle of ALL was blocked by genotoxic agents, BM-MSCs could increase the S-phase cell ratio and decrease the G2/M phase ratio of ALL. Besides, BM-MSCs could protect ALL cells from drug-induced apoptosis. Then, we proved that BM-MSCs affect the cell cycle arrest effect of genotoxic agents on ALL cells via p21 down-regulation. Moreover, our results indicated that activation of Wnt/β-catenin and Erk pathways might be involved in the BM-MSC-induced down-regulation of p21 in ALL cells. Targeting microenvironment-related signaling pathway may therefore be a potential novel approach for ALL therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Pui CH, Robison LL, Look AT (2008) Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 371(9617):1030–1043
Fielding AK, Richards SM, Chopra R et al (2007) Outcome of 609 adults after relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); an MRC UKALL12/ECOG 2993 study. Blood 109(3):944–950
Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL, Wang S, Jablonski E, Sipkins DA (2008) Leukemic cells create bone marrow niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Science 322(5909):1861–1865
Tesfai Y, Ford J, Carter KW et al (2012) Interactions between acute lymphoblastic leukemia and bone marrow stromal cells influence response to therapy. Leuk Res 36(3):299–306
Parameswaran R, Yu M, Lyu MA et al (2012) Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with an rGel/BLyS fusion toxin. Leukemia 26(8):1786–1796
Gaundar SS, Bradstock KF, Bendall LJ (2009) p38MAPK inhibitors attenuate cytokine production by bone marrow stromal cells and reduce stroma-mediated proliferation of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cell Cycle 8(18):2975–2983
Scupoli MT, Donadelli M, Cioffi F et al (2008) Bone marrow stromal cells and the upregulation of interleukin-8 production in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis and the NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 pathways. Haematologica 93(4):524–532
Juarez J, Dela Pena A, Baraz R et al (2007) CXCR4 antagonists mobilize childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells into the peripheral blood and inhibit engraftment. Leukemia 21(6):1249–1257
Juarez J, Baraz R, Gaundar S, Bradstock K, Bendall L (2007) Interaction of interleukin-7 and interleukin-3 with the CXCL12-induced proliferation of B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 92(4):450–459
O'Leary H, Akers SM, Piktel D et al (2010) VE-cadherin regulates Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia sensitivity to apoptosis. Cancer Microenviron 3(1):67–81
Wang L, O'Leary H, Fortney J, Gibson LF (2007) Ph+/VE-cadherin + identifies a stem cell like population of acute lymphoblastic leukemia sustained by bone marrow niche cells. Blood 110(9):3334–3344
Zhang X, Liu Y, Si YJ et al (2012) Effect of Cx43 gene-modified leukemic bone marrow stromal cells on the regulation of Jurkat cell line in vitro. Leuk Res 36(2):198–204
Nwabo Kamdje AH, Mosna F, Bifari F et al (2011) Notch-3 and Notch-4 signaling rescue from apoptosis human B-ALL cells in contact with human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood 118(2):380–389
Yang Y, Mallampati S, Sun B et al (2013) Wnt pathway contributes to the protection by bone marrow stromal cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells and is a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Lett 333:9–17
Silva A, Laranjeira AB, Martins LR et al (2011) IL-7 contributes to the progression of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Cancer Res 71(14):4780–4789
de Vasconcellos JF, Laranjeira AB, Zanchin NI et al (2011) Increased CCL2 and IL-8 in the bone marrow microenvironment in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 56(4):568–577
Batista A, Barata JT, Raderschall E et al (2011) Targeting of active mTOR inhibits primary leukemia T cells and synergizes with cytotoxic drugs and signaling inhibitors. Exp Hematol 39(4):457–472 e453
Dosen-Dahl G, Munthe E, Nygren MK, Stubberud H, Hystad ME, Rian E (2008) Bone marrow stroma cells regulate TIEG1 expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells: role of TGFbeta/BMP-6 and TIEG1 in chemotherapy escape. Int J Cancer 123(12):2759–2766
Markovic A, MacKenzie KL, Lock RB (2012) Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells via the FLT-3 signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 11(1):183–193
Fragoso R, Pereira T, Wu Y, Zhu Z, Cabecadas J, Dias S (2006) VEGFR-1 (FLT-1) activation modulates acute lymphoblastic leukemia localization and survival within the bone marrow, determining the onset of extramedullary disease. Blood 107(4):1608–1616
Fung KL, Liang RH, Chan GC (2010) Vincristine but not imatinib could suppress mesenchymal niche's support to lymphoid leukemic cells. Leuk Lymphoma 51(3):515–522
Iwamoto S, Mihara K, Downing JR, Pui CH, Campana D (2007) Mesenchymal cells regulate the response of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to asparaginase. J Clin Invest 117(4):1049–1057
Frolova O, Samudio I, Benito JM et al (2012) Regulation of HIF-1alpha signaling and chemoresistance in acute lymphocytic leukemia under hypoxic conditions of the bone marrow microenvironment. Cancer Biol Ther 13(10):858–870
Dong-Feng Z, Ting L, Cheng C et al (2012) Silencing HIF-1alpha reduces the adhesion and secretion functions of acute leukemia hBMSCs. Braz J Med Biol Res 45(10):906–912
Benito J, Shi Y, Szymanska B et al (2011) Pronounced hypoxia in models of murine and human leukemia: high efficacy of hypoxia-activated prodrug PR-104. PLoS One 6(8):e23108
Hande KR (1998) Etoposide: four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Eur J Cancer 34(10):1514–1521
Zhu Y, Sun Z, Han Q et al (2009) Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit cancer cell proliferation by secreting DKK-1. Leukemia 23(5):925–933
Warfel NA, El-Deiry WS (2013) p21WAF1 and tumourigenesis: 20 years after. Curr Opin Oncol 25(1):52–58
Shiu TY, Huang SM, Shih YL, Chu HC, Chang WK, Hsieh TY (2013) Hepatitis C virus core protein down-regulates p21(Waf1/Cip1) and inhibits curcumin-induced apoptosis through microRNA-345 targeting in human hepatoma cells. PLoS One 8(4):e61089
Ahmad N, Feyes DK, Agarwal R, Mukhtar H (1998) Photodynamic therapy results in induction of WAF1/CIP1/P21 leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(12):6977–6982
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE et al (1993) WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75(4):817–825
Mitchell KO, El-Deiry WS (1999) Overexpression of c-Myc inhibits p21WAF1/CIP1 expression and induces S-phase entry in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-sensitive human cancer cells. Cell Growth Differ 10(4):223–230
Bornstein G, Bloom J, Sitry-Shevah D, Nakayama K, Pagano M, Hershko A (2003) Role of the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase in the degradation of p21Cip1 in S phase. J Biol Chem 278(28):25752–25757
Cornils H, Kohler RS, Hergovich A, Hemmings BA (2011) Human NDR kinases control G(1)/S cell cycle transition by directly regulating p21 stability. Mol Cell Biol 31(7):1382–1395
Drexler HG, Quentmeier H, Dirks WG, Uphoff CC, MacLeod RA (2002) DNA profiling and cytogenetic analysis of cell line WSU-CLL reveal cross-contamination with cell line REH (pre B-ALL). Leukemia 16(9):1868–1870
Zhao YM, Li JY, Lan JP et al (2008) Cell cycle dependent telomere regulation by telomerase in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369(4):1114–1119
Tanaka T, Nakatani T, Kamitani T (2012) Inhibition of NEDD8-conjugation pathway by novel molecules: potential approaches to anticancer therapy. Mol Oncol 6(3):267–275
Chen H, Landen CN, Li Y, Alvarez RD, Tollefsbol TO (2013) Enhancement of cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through potentiating G2/M arrest and p21 upregulation by combinatorial epigallocatechin gallate and sulforaphane. J Oncol 2013:872957
Vijayaraghavalu S, Dermawan JK, Cheriyath V, Labhasetwar V (2013) Highly synergistic effect of sequential treatment with epigenetic and anticancer drugs to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer cells is mediated via activation of p21 gene expression leading to G2/M cycle arrest. Mol Pharm 10(1):337–352
Wu KN, Zhao YM, He Y et al (2014) Rapamycin interacts synergistically with idarubicin to induce T-leukemia cell apoptosis in vitro and in a mesenchymal stem cell simulated drug-resistant microenvironment via Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin and extracellular signal-related kinase signaling pathways. Leuk Lymphoma 55(3):668–676
Li Y, Gao Q, Yin G, Ding X, Hao J (2012) WNT/beta-catenin-signaling pathway stimulates the proliferation of cultured adult human Sertoli cells via upregulation of C-myc expression. Reprod Sci 19(11):1232–1240
Pintus G, Tadolini B, Posadino AM et al (2002) Inhibition of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway by the novel antimetastatic agent NAMI-A down regulates c-myc gene expression and endothelial cell proliferation. Eur J Biochem 269(23):5861–5870
Lanza F, Campioni D, Moretti S et al (2007) Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigen by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells from patients affected by acute lymphoproliferative disorders. Leukemia 21(2):378–381
Campioni D, Lanza F, Moretti S, Ferrari L, Cuneo A et al (2008) Loss of Thy-1 (CD90) antigen expression on mesenchymal stromal cells from hematologic malignancies is induced by in vitro angiogenic stimuli and is associated with peculiar functional and phenotypic characteristics. Cytotherapy 10(1):69–82
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program, grant No. N20120221) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. Y2110152).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Hu, K., Hu, Y. et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells affect the cell cycle arrest effect of genotoxic agents on acute lymphocytic leukemia cells via p21 down-regulation. Ann Hematol 93, 1499–1508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2069-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2069-1