Abstract
Introduction
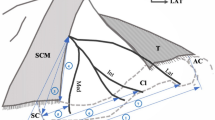
The aim of this study was to determine the location and distribution pattern of neurovascular structures superior and inferior to the clavicle by detailed dissection.
Methods
Fifteen adult non-embalmed cadavers with a mean age of 71.5 years were studied. For measurements, the most prominent point of the sternal end of the clavicle (SEC) on anterior view and the most prominent point of the acromial end of the clavicle (AEC) were identified and divided five equal sections before dissection. A line connecting the SEC and AEC was used as a reference line. The surrounding neurovascular structures were investigated.
Results
The supraclavicular nerve was mainly distributed in the second and the third sections (distribution frequency: 41.30% and 30.43%, respectively) from AEC. Branches of the thoracoacromial artery were mainly distributed in the second, third, and fourth sections (distribution frequency: 21.15%, 26.92%, and 28.85%, respectively). Branches of the subclavian vein were mainly distributed in the third and fourth sections (distribution frequency: 23.26 and 30.23%, respectively). Distribution frequency of subclavian vein, subclavian artery, and brachial plexus ranged from 31.3 to 57.5%.
Discussion
When the clavicle was divided into five sections, there was relatively little distribution of neurovascular damage in the first section or the fifth section. This study reveals the average location of subclavian vein with artery and brachial plexus. Results of this study could be used as reference during surgery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdellaoui H, Atarraf K, Chater L, Afifi MA (2017) Congenital pseudarthrosis of the clavicle treated by Masquelet technique. BMJ Case Rep
Anastasopoulos N, Paraskevas G, Apostolidis S, Natsis K (2015) Three superficial veins coursing over the clavicles: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat 37:1129–1131
Der Tavitian J, Davison J, Dias J (2002) Clavicular fracture non-union surgical outcome and complications. Injury 33:135–143
Di Gennaro GL, Cravino M, Martinelli A, Berardi E, Rao A, Stilli S, Trisolino G (2017) Congenital pseudarthrosis of the clavicle: a report on 27 cases. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 26:e65–e70
Havet E, Duparc F, Tobenas-Dujardin A, Muller J, Delas B, Fréger P (2008) Vascular anatomical basis of clavicular non-union. Surg Radiol Anat 30:23–28
Havet E, Duparc F, Tobenas-Dujardin A, Muller J, Fréger P (2007) Morphometric study of the shoulder and subclavicular innervation by the intermediate and lateral branches of supraclavicular nerves. Surg Radiol Anat 29:605–610
Hussey MM, Chen Y, Fajardo RA, Dutta AK (2013) Analysis of neurovascular safety between superior and anterior plating techniques of clavicle fractures. J Orthop Trauma 27:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31828c1e37
Lazarides S, Zafiropoulos G (2006) Conservative treatment of fractures at the middle third of the clavicle: the relevance of shortening and clinical outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 15:191–194
Naimark M, Dufka FL, Han R, Sing DC, Toogood P, Ma CB, Zhang AL, Feeley BT (2016) Plate fixation of midshaft clavicular fractures: patient-reported outcomes and hardware-related complications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25:739–746
Natsis K, Totlis T, Chorti A, Karanassos M, Didagelos M, Lazaridis N (2016) Tunnels and grooves for supraclavicular nerves within the clavicle: review of the literature and clinical impact. Surg Radiol Anat 38:687–691
Navarro RA, Gelber JD, Harrast JJ, Seiler JG, Jackson KR, Garcia IA (2016) Frequency and complications after operative fixation of clavicular fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25:e125–e129
O’Neill BJ, Hirpara KM, O’Briain D, McGarr C, Kaar TK (2011) Clavicle fractures: a comparison of five classification systems and their relationship to treatment outcomes. Int Orthop 35:909–914
Qiu X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Guo X, Chen Y (2016) Anatomical study of the clavicles in a Chinese population. Biomed Res Int
Robinson L, Persico F, Lorenz E, Seligson D (2014) Clavicular caution: an anatomic study of neurovascular structures. Injury 45:1867–1869
Sinha A, Edwin J, Sreeharsha B, Bhalaik V, Brownson P (2011) A radiological study to define safe zones for drilling during plating of clavicle fractures. J Bone Jt Surg Br 93:1247–1252. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.93B9.25739
Stillwell A, Ioannou C, Daniele L, Tan S (2017) Osteosynthesis for clavicle fractures: how close are we to penetration of neurovascular structures? Injury 48:460–463
Studer K, Baker MP, Krieg AH (2017) Operative treatment of congenital pseudarthrosis of the clavicle: a single-centre experience. J Pediatr Orthop B 26:245–249
Van der Meijden OA, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ (2012) Treatment of clavicle fractures: current concepts review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21:423–429
Viciano J, Urbani V, D’Anastasio R (2017) Congenital anatomical variant of the clavicle. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 300:1401–1408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AJ: data collection, data management, performing dissection, and writing manuscript. CMS: data collection and performing dissection. J-HL: project development, data analysis, performing dissection, and manuscript writing and editing. S-HH: project development and data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, A., Seo, C.M., Lee, JH. et al. The distributed pattern of the neurovascular structures around clavicle to minimize structural injury in clinical field: anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat 40, 1261–1265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2091-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2091-4