Abstract
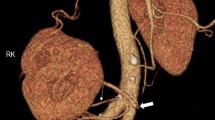
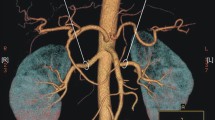
From a study of renal vascularization, we present 54 cases of double renal arteries supplying one kidney and originating from the aorta. Of the 54 cases, 42 were unilateral, showing a left predominance (25 cases), three of them with triple renal arteries on the opposite side. In six cases we encountered bilateral double renal arteries. Most often, the supplementary renal artery originated from the lateral side of the aorta (58%). Examination of the renal approach showed that in 28 cases the supplementary renal artery entered the kidney through the hilum (proper supplementary renal artery), in 16 cases it was inferior polar, in five cases it was superior polar and in five cases the supplementary renal artery terminated in two branches, equal in caliber, one polar and the other hilar, thus showing a combined character, identical with the manner of termination of the main renal artery. In most of the samples the supplementary renal artery ended with a bifurcation inside the kidney, either into the renal sinus (proper supplementary renal artery) or inside the renal parenchyma (polar supplementary renal artery). The course of the double renal arteries showed multiple variations: retro-ureteral passage of the supplementary renal artery (6 cases), right supplementary renal artery passing anterior to the inferior vena cava (5 cases), crossed course of the double renal arteries (5 cases). Double renal arteries may coexist with other uro-vascular variations, such as: double renal veins on the same side (4 cases) or on the opposite side (3 cases), double ureter on the same side (2 cases) or on the opposite side (1 case), persistence of the fetal renal lobulation on the adult kidney (3 cases) and genital artery originating from the supplementary renal artery (3 cases).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderhuber F, Weiglein A (1992) Zur Nomenklatur der Nierengefässe. Ann Anat 174:229–234
Bayazit M, Göl MK, Zorlutuna Y, Tasdemir O, Bayasit K (1992) Bilateral triple renal arteries in a patient with iliac artery occlusion: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat 14:81–83
Bordei P, Antohe DS (2002) Étude anatomique des artères rénales triples. Morphologie 86:37–41
Callas F, Martin R, Convert A (1963) Contribution à l’étude de la vascularisation du rein. C R Assoc Anat 117:408–421
Chevrel JP (1994) Anatomie clinique. Le Tronc. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 495
Chugh KS, Malik N, Ghosh AK, Sakhuja V, Minz M (1993) Pattern of renal arteries in normal subjects: a study of 170 renal donor angiograms. Indian J Nephrol 3:9―11
Coen LD, Raftery AT (1992) Anatomical variations of the renal arteries and renal transplantation. Clin Anat 5:425–432
Edsman G (1954) Accessory vessels of the kidneys and their diagnosis in hydronephrosis. Acta Radiol 42:26–30
Geyer JR, Poutasse EF (1962) Incidence of multiple renal arteries on aortography. Report of a series of 400 patients, 381 of whom had arterial hypertension. JAMA 182:118–125
Goscicka D, Szipinda M, Kochan J (1996) Accessory renal arteries in human fetuses. Anat Anz 178:559–563
Graves FT (1956) The aberrant renal artery. J Anat 90:553–558
Guntz M (1967) Radioanatomie de l’artère rénale. Déductions chirurgicales. C R Assoc Anat 148:623–631
Langman J, Sadler TW (1996) Embryologie médicale. Pradel, Paris, p 301
Lippert H, Pabst R (1985) Arterial variations in man. Bergman, Munich, pp 26–27
Merklin RJ, Michels NA (1958) The variant renal and suprarenal blood supply with data on the inferior phrenic, ureteral and gonadal arteries. J Int Coll 29:41–47
Moore K (1985) Clinically oriented anatomy. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p 266
Papin E (1928) Chirurgie du rein, vol 1. Gaston Doin, Paris, pp 263–273
Paturet G (1958) Traité d’anatomie humaine, vol III, part 1: Appareil circulatoire. Masson, Paris, pp 511–526
Pick JW, Anson BJ (1940) The renal vascular pedicle. An anatomical study of 430 body-halves. J Urol 44:411–434
Poisel S, Spangler HP (1969) Über aberranke und akzessorische Nierrenarterien bei Nieren typischer Lage. Anat Anz 124:244–259
Sampaio FJB, Passos MARF (1992) Renal arteries: anatomic study for surgical and radiological practice. Surg Radiol Anat 14:113–117
Satyapal KS, Haffajee AA, Singh B, Ramsaroop L, Robbs JV, Kalideen JM (2001) Additional renal arteries: incidence and morphometry. Surg Radiol Anat 23:33–3
Sykes D (1963) The arterial supply of the human kidney with special reference to accessory renal arteries. Br J Surg 50:368–374
Testut L (1921) Traité d’anatomie humaine, vol 2: Angéiologie—Système nerveux central. Doin, Paris, pp 213–215
Vilhova I, Kryvko YY, Maciejewski R (2002) The frequency of different plural renal arteries rare variants. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska (Med) 57:68–73
Williams PL, Bannister LH, Berry MB, Collins P, Dyson M, Dussek JE, Ferguson MWJ (1995) Gray’s anatomy, 38th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Baltimore London, pp 218, 248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bordei, P., Şapte, E. & Iliescu, D. Double renal arteries originating from the aorta. Surg Radiol Anat 26, 474–479 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-004-0272-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-004-0272-9