Abstract
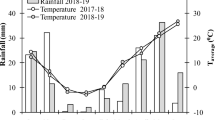
Fresh water shortages are severally restricting sustainable agriculture development in coastal saline-alkali land in Hebei Province, China. Saline water used for irrigation can increase crop yields as well as the risk of soil salinization. To identify safe and simple ways of using saline water in this region, a continuous two growth period of winter wheat field study was conducted from 2016 to 2018 to evaluate the effect of saline water irrigation on soil salt and winter wheat yield under a subsurface drainage system. This study comprised three treatments (non-irrigation, freshwater irrigation, and 6 g/L saline water irrigation), with winter wheat irrigated at the jointing-heading stage. The results indicated that the yield of winter wheat under the irrigation treatment was more than 1.5 times than that of rainfed winter wheat, and there was no significant difference between the yield under freshwater and saline water irrigation. The soil salt content decreased yearly after saline irrigation treatments. Based on subsurface drainage system, two consecutive years of saline water irrigation would not cause salt accumulation in the soil, and has increased winter wheat yield. This makes safe utilization of saline water resources realized. Saline water irrigation is equivalent to an increase of 600 m3 of irrigation water resources per hectare. The results provided scientific basis for the safe utilization of saline water resources, grain yield guarantee, and soil sustainable development in coastal area of Hebei Province.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbas A, Khan S, Hussain N, Hanjra MA, Akbar S (2013) Characterizing soil salinity in irrigated agriculture using a remote sensing approach. Phys Chem Earth 55–57:43–52
Chen YH, Yuan CF, Chen S (2009) Precipitation demand in wheat growth key period. Mete Environ Sci 32:95–98 (In Chinese)
Chen Y, Zhang ZY, Feng GX, Wan CY (2014) Desalination of subsurface pipe drainage in saline-alkali land of coastal areas. Jour Irrig Drain 33(3):38–41 (In Chinese)
Cheng MH, Wang HD, Fan JL, Wang XK, Sun X, Yang L, Zhang SH, Xiang YZ, Zhang FC (2021) Crop yield and water productivity under salty water irrigation: a global meta-analysis. Agr Water Manage 256:107105
Ding BB, Zhang XL, Zhao ZT, Hou YH (2021) Change in winter wheat yield and its water use efficiency as affected by limited irrigation in North China Plain: a Meta-analysis. Jour Irrig Drain 40(12):7–17 (In Chinese)
Feng GX, Zhang ZY, Wan CY, Lu PR, Bakour A (2017) Effects of saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of summer maize (Zea mays L) in subsurface drainage system. Agr Water Manage 193:205–213
Feng D, Sun CT, Li XB, Sun XA, Wang SQ, Li KX, Ning SR (2022) Reclamation of heavy coastal silt saline soil and optimal tomato production through a drip irrigation system with saline water. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05799-2
Gao HQ, Fei YH, Luo GZ, Liu LJ (2010) Effect analysis of saline groundwater utilization in Hebei Plain. South-to-North Water Trans Water Sci Tech 8(2):53–56 (In China)
Gao H, Liu JT, Eneji AE, Han LP, Tan LM (2016) Using modified remote sensing imagery to interpret changes in cultivated land under saline-alkali conditions. Sustain 8:619
Guan XY, Wang SL, Gao ZY, Lv Y, Fu XJ (2012) Spatio- temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district. Acta Ecol Sin 32(4):1202–1210 (in Chinese)
He XL, Liu HG, Ye JW, Yang G, Li MS, Gong P, Aernaguli A (2016) Comparative investigation on soil salinity leaching under subsurface drainage and ditch drainage in Xinjiang arid region. Inter J Agr Bio Eng 9:109–118
Jin Z, Guo L, Wang YQ, Yu YL, Lin H, Chen YP, Chu GC, Zhang J, Zhang NP (2019) Valley reshaping and damming induce water table rise and soil salinization on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma 339:115–125
Kumar P, Sarangi A, Singh DK, Parihar SS, Sahoo RN (2015) Simulation of salt dynamics in the root zone and yield of wheat crop under irrigated saline regimes using SW AP model. Irrig Drain 148:72–83
Li XB (2018) Salt leaching and Iris germanica L. growth in two coastal saline soils under drip irrigation with saline water. Sci Hortic 237:164–168
Li XB (2019) Vegetation establishment in coastal salt-affected wasteland using drip-irrigation with saline water. Land Degrad Dev 30(12):1423–1436
Li CQ, Li BG, Hong KQ (2009a) Trend of crop water requirement in recent 35 years in Hebei Province. Chinese J Eco-Agr 17(2):359–363 (In Chinese)
Li YY, Liu BH, Liu QX, Zhang WY, Zhang SM, Xie LL, Li X, Ma JM, Li AG, Su YQ (2009b) Effect of climatic conditions on winter wheat Hebei low plain. Journal of Triticeae Crops 29(2):330–334 (In Chinese)
Li YS, Fei YH, Qian Y, Jian M, Han ZT, Wang P, Zhang ZJ (2013) Discussion on evolution characteristics and formation mechanism of deep groundwater depression cone in Cangzhou region. J Ari Land Res Environ 27(1):181–184 (In Chinese)
Li ZZ, Qu ZY, Yang W, Wang LP, Gao XY, Chen M (2021) The Influence of subsurface drain on solute movement in soils severely affected by salinity and alkalinity in Ordos region. Jour Irrig Drain 40(7):122–129 (In Chinese)
Liu HT, Tan LM, Yu SH, Li Xu, Liu JT (2012) Response of water and salt movement to subsurface pipe drainage system in saline-alkali coastal areas of Hebei Province. Chinese J Appl Ecol 20(12):1693–1699 (In Chinese)
Liu XW, Shao LW, Sun HY, Chen SY (2018) Zhang X Y Responses of yield and water use efficiency to irrigation amount decided by pan evaporation for winter wheat. Agr Water Manage 129:173–180
Liu CC, Sun HY, Guo K, Dong XL, Cheng DJ (2022) Infiltration characteristics of saline water with different salinity in coastal saline-alkali land with typical vegetation. Soil 54(01):177–183 (In Chinese)
Ma FJ, Tan LM, Liu HT, Yu SH, Liu HJ, Yu Y, Liu JT (2011) Evaluation of the rainfall effectiveness for reclaim of saline soil by subsurface pipe drainage system in coastal saline regions of Hebei Province. Chinese J Appl Ecol 19(2):409–414 (In Chinese)
Nicolás E, Alarcón JJ, Mounzer O, Pedrero F, Nortes PA, Alcobendas R, Romero-Trigueros C, Bayona JM, Maes-tre-Valero JF (2016) Long-term physiological and agronomic responses of mandarin trees to irrigation with saline reclaimed water. Agr Water Manage 166:1–8
Pang HC, Li YY, Yang JS, Liang YS (2010) Effect of brackish water irrigation and straw mulching on soil salinity and crop yields under monsoonal climatic conditions. Agr Water Manage 97:1971–1977
Qian YZ, Zhu Y, Ye M, Huang JS, Wu JW (2021) Experiment and numerical simulation for designing layout parameters of subsurface drainage pipes in arid agricultural areas. Agri Water Manag 243:106455
Ren DY, Wei BY, Xu X, Engel B, Li GY, Huang QZ, Xiong YW, Huang GH (2019) Analyzing spatiotemporal characteristics of soil salinity in arid irrigated agro-ecosystems using integrated approaches. Geoderma 356:113935
Sun HY, Shen Y, Yu Q, Flerchinger GN, Zhang YQ, Liu CM, Zhang XY (2010) Effect of precipitation change on water balance and WUE of the winter wheat-summer maize rotation in the North China Plain. Agr Water Manage 97:1139–1145
Tesfaye S, Birhane E, Leijnse T, Vander ZSE (2017) Climatic controls of ecohydrological responses in the highlands of northern Ethiopia. Sci Total Environ 609:77–91
Verma AK, Gupta SK, Isaaca RK (2017) Use of saline water for irrigation in monsoon climate and deep water table regions, simulation modeling with SWAP. Agr Water Manage 115:186–193
Wang XP, Yang JS, Liu GM, Yao RJ, Yu SP (2015) Impact of irrigation volume and water salinity on winter wheat productivity and soil salinity distribution. Agr Water Manage 149:44–54
Wang QM, Huo ZL, Zhang LD, Wang JH, Zhao Y (2016) Impact of saline water irrigation on water use efficiency and soil salt accumulation for spring maize in arid regions of China. Agr Water Manage 163:125–138
Wang HX, Xu ZH, Pang GB, Zhang LZ, Wang XR (2017) Effects of brackish water irrigation on water-salt distribution and winter wheat growth. J Soil Water Conser 31(3):291–297 (In Chinese)
Yu SH, Han LP, Gao H, Liu JT (2016a) Ecological effects of soil salinity regulation through saline water irrigation and sub-surface drainage in high water table level area. Chinese J Appl Ecol 27(4):1061–1068 (In Chinese)
Yu SH, Liu JT, Eneji AE, Han LP, Tan LM, Liu HT (2016b) Dynamic of soil water and salinity under subsurface drainage of a coastal area with high groundwater table in spring and rainy season. Irrig Drain 65:360–370
Yuan CF, Feng SY, Hua ZL, Huo ZL, Ji QY (2019) Effects of deficit irrigation with saline water on soil water-salt distribution and water use efficiency of maize for seed production in arid Northwest China. Agr Water Manage 212:424–432
Zhang XY, Liu XJ, Chen SY, Sun HY, Shao LW, Niu JF (2016) Efficient utilization of various water sources in farmlands in the low plain nearby Bohai Sea. Chinese J Eco-Agr 24(8):995–1004 (In Chinese)
Zheng LS (2009) Water resources and development based on the capacity of the water. China Water Resources and Hydropower Publishing House, Beijing, pp 10–13 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from the Key Research and Development Program of Hebei Province in China (Grant No. 20373304D and 22374202D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HG and TF wrote the main manuscript text. HG prepared figures. TF prepared Tables. ST provided data. JL provide project funding and supervised paper quality. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Fu, T., Tang, S. et al. Effects of saline water irrigation on winter wheat and its safe utilization under a subsurface drainage system in coastal saline-alkali land of Hebei Province, China. Irrig Sci 41, 251–260 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-023-00849-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-023-00849-8