Abstract
Aims
To determine the sizes and shapes of ablation zones in 4-antenna microwave ablation in ex vivo bovine liver model under different conditions of power delivery patterns, antenna spacings, and ablation durations, for further using of multi-antenna MWA strategies in the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods
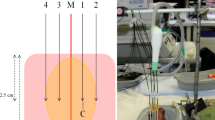
We tested protocols of eight ablations each on ex vivo bovine livers, involving simultaneous or sequential activation of four microwave antennas, spaced either 3 cm, 4 cm, or 5 cm apart, for either 10 or 15 min, at 60-W power. We determined the diameters, shapes, and temperatures of the ablation zones.
Results
Compared to sequential power delivery, simultaneous power delivery resulted in significantly larger ablation zone diameters (P < .001). The temperatures in ablation zones were significantly higher for simultaneous than for sequential power delivery. The largest ablation diameter (7.45 ± 0.06 cm) resulted from simultaneous delivery for 15 min using 4-cm antenna spacing.
Conclusions
Simultaneous 4-antenna microwave ablation results in larger ablation zones than sequential ablation, and 4-cm antenna spacing with a 15-minute ablation duration creates the largest ablation zone. This information may provide multi-antenna MWA strategies for large HCC in the further clinical practice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim YS, Lim HK, Rhim H, Lee MW. Ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;28(5):897–908.
Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(4):835–53.
Xu Y, Shen Q, Wang N, Liu P, Wu P, Peng Z, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation of 5-6 cm unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: local efficacy and long-term outcomes. Int J Hyperthermia. 2016;9:1–8.
Dou JPLP, Yu J. Microwave ablation for liver tumors. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41(4):650–8.
Harari CM, Magagna M, Bedoya M, Lee FT Jr, Lubner MG, Hinshaw JL, et al. Microwave ablation: comparison of simultaneous and sequential activation of multiple antennas in liver model systems. Radiology. 2016;278(1):95–103.
Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K, Zou MW, Solbiati L, Liu JB, et al. Large liver tumors: protocol for radiofrequency ablation and its clinical application in 110 patients—mathematic model, overlapping mode, and electrode placement process. Radiology. 2004;232(1):260–71.
Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Hahn PF, Cosman E, Conrad JE, Fogle R, et al. Large-volume tissue ablation with radio frequency by using a clustered, internally cooled electrode technique: laboratory and clinical experience in liver metastases. Radiology. 1998;209(2):371–9.
Haemmerich D, Lee FT Jr, Schutt DJ, Sampson LA, Webster JG, Fine JP, et al. Large-volume radiofrequency ablation of ex vivo bovine liver with multiple cooled cluster electrodes. Radiology. 2005;234(2):563–8.
Choi TW, Lee JM, Lee DH, Lee JH, Yu SJ, Kim YJ, et al. Percutaneous dual-switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a separable clustered electrode: a preliminary study. Korean J Radiol. 2017;18(5):799–808.
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Hwang EJ, Hwang IP, Baek J, Han JK, et al. Monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a dual-switching system and a separable clustered electrode: evaluation of the in vivo efficiency. Korean J Radiol. 2014;15(2):235–44.
Brace CL, Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Frey TM, van der Weide DW, Lee FT Jr. Microwave ablation with multiple simultaneously powered small-gauge triaxial antennas: results from an in vivo swine liver model. Radiology. 2007;244(1):151–6.
Oshima F, Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H, Makita M, Takeda K. Simultaneous microwave ablation using multiple antennas in explanted bovine livers: relationship between ablative zone and antenna. Radiat Med. 2008;26(7):408–14.
Wright AS, Lee FT Jr, Mahvi DM. Hepatic microwave ablation with multiple antennae results in synergistically larger zones of coagulation necrosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10(3):275–83.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Iannitti DA, Lu DS, Yu NC, Aswad BI, et al. Intraoperative triple antenna hepatic microwave ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187(4):W333–40.
Yu NC, Lu DS, Raman SS, Dupuy DE, Simon CJ, Lassman C, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: microwave ablation with multiple straight and loop antenna clusters—pilot comparison with pathologic findings. Radiology. 2006;239(1):269–75.
Farina L, Weiss N, Nissenbaum Y, Cavagnaro M, Lopresto V, Pinto R, et al. Characterisation of tissue shrinkage during microwave thermal ablation. Int J Hyperthermia. 2014;30(7):419–28.
Ren H, An C, Liang P, Yu J, Cheng Z, Han Z, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation assisted by a three-dimensional visualization treatment platform combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for a single large hepatocellular carcinoma 5 cm or larger: a preliminary clinical application. Int J Hyperthermia. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1530459.
Kang TW, Lim HK, Cha DI. Percutaneous ablation for perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: refining the current status based on emerging evidence and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(47):5331–7.
Dou JP, Yu J, Yang XH, Cheng ZG, Han ZY, Liu FY, et al. Outcomes of microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to large vessels: a propensity score analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(17):28758–68.
Jiang C, Liu B, Chen S, Peng Z, Xie X, Kuang M. Safety margin after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: precise assessment with a three-dimensional reconstruction technique using CT imaging. Int J Hyperthermia. 2018;34(8):1135–41.
Adeyanju OO, Al-Angari HM, Sahakian AV. The optimization of needle electrode number and placement for irreversible electroporation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiol Oncol. 2012;46(2):126–35.
Sakakibara M, Ohkawa K, Imanaka K, Miyazaki M, Nawa T, Kimura H, et al. Quick and stable parallel puncture of hepatic tumors using a double-barreled needle direction system for ultrasound-guided bipolar radiofrequency ablation. Hepatol Res. 2016;46(11):1152–7.
Mulier S, Jiang Y, Wang C, Jamart J, Marchal G, Michel L, et al. Bipolar radiofrequency ablation with four electrodes: ex vivo liver experiments and finite element method analysis. Influence of inter-electrode distance on coagulation size and geometry. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012;28(7):686–97.
Brace CL, Sampson LA, Hinshaw JL, Sandhu N, Lee FT Jr. Radiofrequency ablation: simultaneous application of multiple electrodes via switching creates larger, more confluent ablations than sequential application in a large animal model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(1):118–24.
Amabile C, Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Solbiati M, Cassarino S, et al. Microwave ablation of primary and secondary liver tumours: ex vivo, in vivo, and clinical characterisation. Int J Hyperthermia. 2017;33(1):34–42.
Amabile C, Farina L, Lopresto V, Pinto R, Cassarino S, Tosoratti N, et al. Tissue shrinkage in microwave ablation of liver: an ex vivo predictive model. Int J Hyperthermia. 2017;33(1):101–9.
Farina L, Nissenbaum Y, Cavagnaro M. Tissue shrinkage in microwave thermal ablation: comparison of three commercial devices. Int J Hyperthermia. 2017;16:1–10.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ms. Xin Zheng for providing support and encouragement to Dr. Tianqi Zhang on his scientific research work.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81771955), Guangzhou Science and Technology Program, key projects of collaborative innovation of health medicine (No. 201704020228), and Guangzhou Science and Technology Program, key projects of collaborative innovation of production, learning and research (No. 201704020134), Sun Yat-sen University Clinical Trial 5010 Project (No. 2016002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tian-Qi Zhang and Sen-Miao Huang participated equally in experiments and analyzed the data; Zhi-Mei Huang and Han-Xia Deng finished the statistical analysis; Tian-Qi Zhang finished the manuscript drafting; Yang-Kui Gu and Xiong-Ying Jiang gave the critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; Jin-Hua Huang designed and coordinated the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Tq., Huang, Sm., Gu, Yk. et al. Sequential and Simultaneous 4-Antenna Microwave Ablation in an Ex Vivo Bovine Liver Model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42, 1466–1474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02241-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02241-6