Abstract
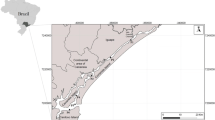
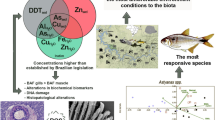
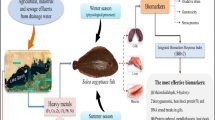
To evaluate the physiological state of the wild fish inhabiting the Biobío River in South-Central Chile, susceptible to the chemical contamination from different sources, biochemical and physiological biomarkers were applied to wild fish Percilia irwini and Trichomycterus areolatus in situ. Fish caught in the Biobío river in low, medium, and high anthropic impacts areas, with different pollution degrees along the river. Ethoxyresorufin O–O deethylase (EROD) activity was evaluated in fish liver. Length, weight, Gonad weight and Liver weight, Physiological Index, and gill and liver histopathology were conducted. Physicochemical parameters (pH, Temperature, Conductivity, and TDS) were measured at each sampling site. The results indicated a deteriorating condition in the biological parameters of both species in a high anthropic zone. Fishes show an increase in physiological indices and EROD liver activity, agreeing with previous studies supporting evidence of reproductive change development as we move downstream the river. Also, an increase in histopathological lesions towards the lower third stretch of the Biobío River. The Integrated Index of Physiological Biomarkers (IPBR) indicated that sites located in the high impact area (P. irwini: BC: 4.09; RC: 3.38; PC: 3.50; SJ: 2.34 and T. areolatus BC: 6.06, PC: 5.37; SJ: 5.42) have the most detrimental environmental quality, compared to reference area. The integrated biomarker analysis demonstrates that the alterations observed are related to the high anthropic activity levels downstream from the sites with the least intervention, demonstrating that the IPBR used is a complementary tool for studies of the Environmental Effects Monitoring approach.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aedo JR, Belk MC, Habit E (2009) Geographic variation in age, growth and size structure of Percilia irwini from south-central Chile. J Fish Biol 74:278–284
Alonso A, Figueroa R, Castro-Díez P (2017) Pollution assessment of the Biobío river (Chile): prioritization of substances of concern under an ecotoxicological approach. Environ Manag 59(5):856–869
Barra R, Quiroz R, Saez K, Araneda A, Urrutia R, Popp P (2009) Sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments of the Biobio River in south central Chile. Environ Chem Lett 7:133–139
Beliaeff B, Burgeot T (2002) Integrated biomarker response: a useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(6):1316–1322
Bernet D, Schmidt-Posthaus H, Wahli T, Burkhardt-Holm P (2004) Evaluation of two monitoring approaches to assess effects of waste water disposal on histological alterations in fish. Hydrobiologia 524:53–66
Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T (1999) Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Dis 22:25–34
Capela R, Raimundo J, Santos MM, Caetano M, Micaelo C, Vale C, Guimarães L, Reis-Henriques MA (2016) The use of biomarkers as integrative tools for transitional water bodies monitoring in the Water Framework Directive context—a holistic approach in Minho river transitional waters. Sci Total Environ 539:85–96
Cerejeira MJ, Viana P, Batista S, Pereira T, Silva E, Valério MJ, Silva A, Ferreira M, Silva-Fernandes AM (2003) Pesticides in Portuguese surface and ground waters. Water Res 37:1055–1063
Chiang G, Munkittrick K, Orrego R, Barra R (2010) Monitoring of the environmental effects of pulp mill discharges in chilean rivers: Lessons learned and challenges. Water Qual Res J Can 45:111–122
Chiang G, Munkittrick K, McMaster M, Barra R, Servos M (2014) Regional cumulative effects monitoring framework: gaps and challenges for the Biobío river basin in South Central Chile. Gayana 78:109–119
Chiang G, Munkittrick K, Urrutia R, Concha C, Rivas M, Diaz-Jaramillo M, Barra R (2012) Liver ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase and brain acetylcholinesterase in two freshwater fish species of South America; the effects of seasonal variability on study design for biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 86:147–155
Colin N, Porte C, Fernandes D, Barata C, Padrós F, Carrassón M, Monroy M, Cano Rocabayera O, de Sostoa A, Piña B, Maceda-Veiga A (2016) Ecological relevance of biomarkers in monitoring studies of macro-invertebrates and fish in Mediterranean rivers. Sci Total Environ 540:307–323
Couillard CM, Lebeuf M, Ikonomou MG, Poirier GG, Cretney WJ (2005) Low hepatic ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity correlates with high organochlorine concentrations in Atlantic tomcod from the Canadian east coast. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2459–2469
Death RG, Winterbourn MJ (1995) Diversity pattern in stream benthic invertebrate communities: the influence of habitat stability. Ecology 76:1446–1460
Delfino C, Gomes P, Lunardelli B, Fernandes de Oliveira L, da Costa L, Risso W, Primel E, Meletti P, Fillmann G, Claudia Bueno dos RM (2016) Multiple biomarker responses in Prochilodus lineatus subjected to short-term in situ exposure to streams from agricultural areas in Southern Brazil. Sci Total Environ 542:44–56
Figueroa R, Bonada N, Guevara M, Pedreros P, Correa-Araneda F, Diaz ME, Ruiz VH (2013) Freshwater biodiversity and conservation in mediterranean climate streams of Chile. Hydrobiologia 719:269–289
Habit E, Belk MC (2007) Threatened fishes of the world: Percilia irwini (Eigenmann 1927) (Perciliidae). Environ Biol Fishes 78:213–214
Habit E, Dyer B, Vila (2006a) Estado de conocimiento de los peces dulceacuícolas de Chile. Gayana Zoolía 70(1):100–113
Habit E, Belk MC, Tuckfield RC, Parra O (2006b) Response of the fish community to human-induced changes in the Biobío River in Chile. Freshw Biol 51:1–11
Habit E, García A, Díaz G, Arriagada P, Link P, Parra O, Martin T (2019) River science and management issues in Chile: hydropower development and native fish communities. River Res Appl 35:489–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.3374
Inzunza B, Orrego R, Peñalosa M, Gavilán JF, Barra R (2006) Analysis of CYP4501A1, PAHs metabolites in bile, and genotoxic damage in Oncorhynchus mykiss exposed to Biobio River sediments, Central Chile. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65:242–251
Jönsson, ME, Orrego, R, Woodin, BR, Goldstone, JV, Stegeman, JJ (2007) Basal and 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl-induced expression of cytochrome P450 1A, 1B and 1C genes in zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 221:29–41
Karrasch B, Parra O, Cid H, Mehrens M, Pacheco P, Urrutia R, Valdovinos C, Zaror C (2006) Effects of pulp and paper mill effluents on the microplankton and microbial self-purification capabilities Of The Biobío River, Chile. Sci Total Environ 359:194–208
Konstantinou IK, Hela DG, Albanis TA (2006) The status of pesticide pollution in surface waters (rivers and lakes) of Greece. Part I. Review on occurrence and levels. Environ Pollut 141:555–570
Lewis DFV (2004) 57 varieties: the human cytochromes P450. Pharmacogenomics 5:305–318
Lubert RA, Nims RW, Mayer RT, Cameron JW, Schechtman LM (1985) Measurement of cytochrome P450–dependent dealkylation of alkoxyphenoxazones in hepatic S9s and hepatocyte homogenates: Effects of dicumarol. Mutat Res 142:127–131
Murussi C, Costa M, Menezes C, Leitemperger J, Guerra L, Lópes T, Severo E, Zanella R, Vania LL (2015) Integrated assessment of biomarker response in Carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Silver Catfish (Rhamdia quelen) Exposed to Clomazone. Arch Environ Contamination Toxicol 68:646–654
Oliveira M, Pacheco M, Santos MA (2011) Fish thyroidal and stress responses in contamination monitoring- an integrated biomarker approach. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1265–1270
Orrego R, Moraga-Cid G, Gonzalez M, Ricardo Barra (2005b) Reproductive, physiological, and biochemical responses in juvenile female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to sediment from pulp and paper mill industrial discharge areas. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(8):92–100
Orrego R, Moraga-Cid G, González M, Barra R, Valenzuela A, Burgos A, Gavilán JF (2005a) Reproductive, physiological and biochemical responses in juvenile female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to sediment from pulp and paper mill industrial discharge areas. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(8):1935–1943
Orrego R, Guchardi J, Hernandez V, Krause R, Roti L, Armour J, Ganeshakumar M, Holdway D (2009) Pulp and paper mill effluent treatments have differential endocrine-disrupting effects on rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:181–188
Orrego R, Milestone CB, Hewitt M, Guchardi J, Heid-Furley T, Slade A, Maclatchy DL, Holdway D (2017) Evaluating the potential of effluent extracts from pulp and paper mills in Canada, Brazil and New Zealand to affect fish reproduction: estrogenic effects in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 36:1547–1555
Orrego R, Hewitt LM, McMaster M, Chiang G, Quiroz M, Munkittrick K, Gavilán JF, Barra R (2019) Assessing wild fish exposure to ligands for sex steroid receptors from pulp and paper mill effluents in the Biobio River Basin, Central Chile. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:256–263
Orrego R, Adams S, Barra R, Chiang G, Gavilán JF (2008) Patterns of fish community composition along a river affected by agricultural and urban disturbance in south-central Chile. Hydrobiologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9613-8
Orrego R, Burgos A, Moraga-Cid G, Inzunza B, Gonzalez M, Valenzuela A, Barra R, Gavilan JF (2006) Effects of pulp and paper mill discharges on caged rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): biomarker responses along a pollution gradient in the Biobio River, Chile. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2280–2287
Orrego R, Guchardi J, Krause R, Holdway D (2010) Estrogenic and antiestrogenic effects of wood extractives present in pulp and paper mill effluents on rainbow trout. Aquat Toxicol 99:160–167
Parra O, Figueroa R, Valdovinos C, Habit E, Diaz M (2013) Programa de Monitoreo de la Calidad del Agua del Sistema Río Biobío 1994 – 2012: Aplicación del Anteproyecto de Norma de la Calidad Ambiental (NSCA) del río Biobío. Editorial Universidad de Concepción, Chile, p 165
Rozas O, Vidal V, Baeza C, Jardim W, Rossner A, Héctor M (2016) Organic micropollutants (OMPs) in natural waters: Oxidation by UV/H2O2 treatment and toxicity assessment. Water Res 98:109–118
Ruiz VH, Berra TM (1994) Fishes of the high Biobio river of south-central Chile with notes on diet and spec-ulation on the origin of the ichthyofauna. Ichthyol Explor Freshw 5:5–18
Sanchez W, Burgeot T, Jean-Marc P (2013) A novel “Integrated Biomarker Response” calculation based on reference deviation concept. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2721–2725
Seabra C, Abessa D, Choueri R, Almagro-Pastor V, Cesar A, Maranhod L, Martín-Díaz M, Torres R, Gusso- Choueri P, Almeida J, Cortez F, Mozetof A, Silbiger H, Sousa E, Del Valls T, Bainy ACD (2014) Ecological relevance of sentinels’ biomarker responses: a multi-level approach. Mar Environ Res 96:118–126
RStudio Team (2020) RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, Inc., Boston, MA. http://www.rstudio.com/
Van Der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Acknowledgements
This work was possible through the financial support of CONICYT scholarship No. 21140314 and was partially funded by CRHIAM, Universidad de Concepción (ANID/FONDAP/CRHIAM 15130015). The researchers thank W. San Martin, R. Sanchez for their support during field sampling; A. Acuña supports histological analysis. The author thanks DSFTA of Università di Siena, Italy, for support in data analysis.
Author contributions
MQ wrote the main manuscript text, analysis of the data and, prepared figures. JFG and RB. contributed to the conception and design of the study. SC, CF, and RO contributed to the assistance of data analysis and writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All the methods used in the present study followed relevant guidelines and regulations. Also, the competent authority (Ethics Committee of the Universidad de Concepción, Chile) approved the experiment and protocols of the present study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quiroz-Jara, M., Casini, S., Fossi, M.C. et al. Integrated Physiological Biomarkers Responses in Wild Fish Exposed to the Anthropogenic Gradient in the Biobío River, South-Central Chile. Environmental Management 67, 1145–1157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-021-01465-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-021-01465-y